Einführung in gedruckte Schaltungen: Die Grundlagen verstehen
Printed Circuit Boards (PCB) are widely used in today’s electronic devices, such as smartphones, computers, and even household appliances. They are an essential component in the manufacturing of electronic products and have greatly evolved over the years. In this article, we will delve into the basics of PCB – how they work, their types, and their key components.
What is a Printed Circuit Board?
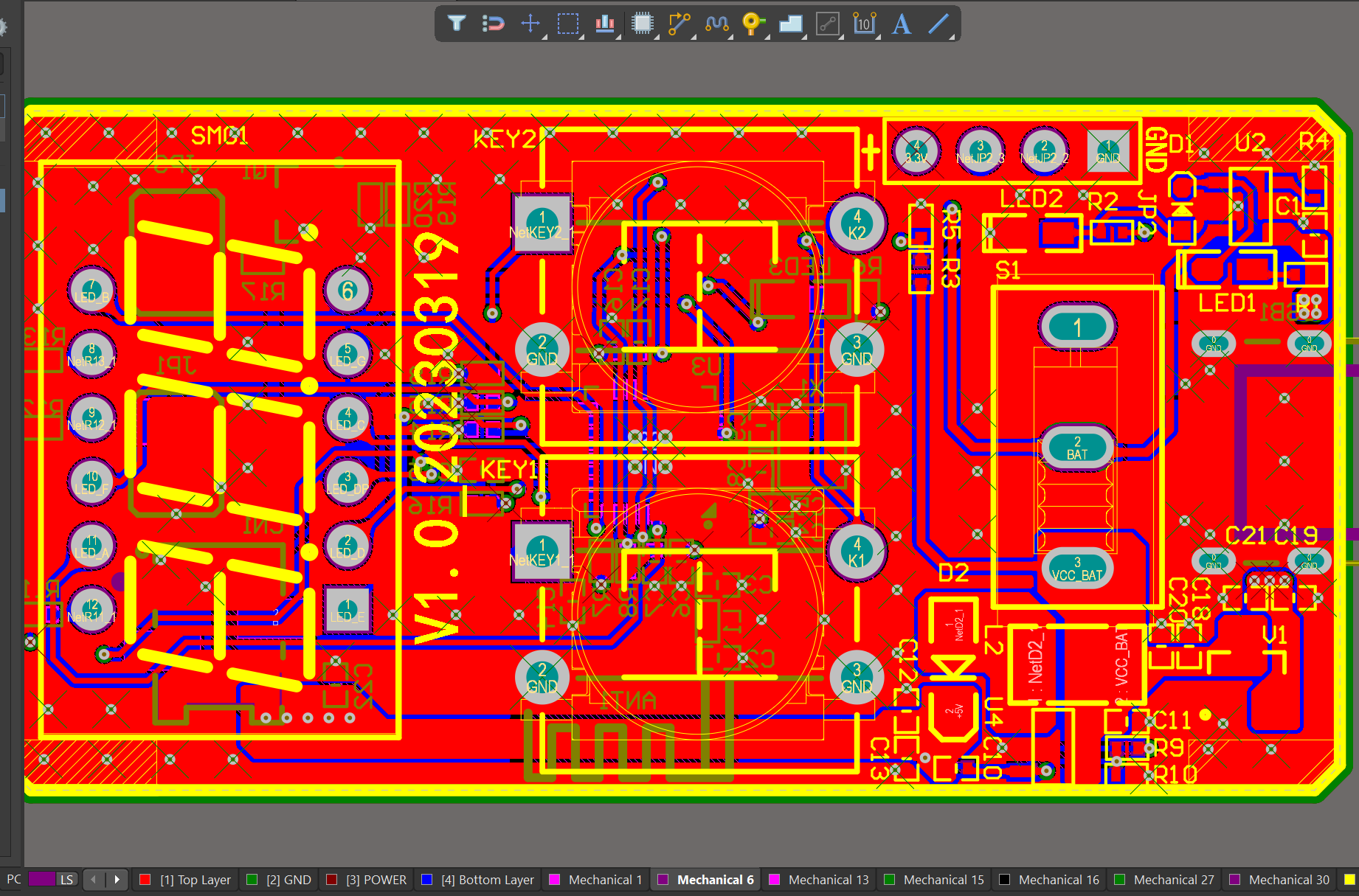
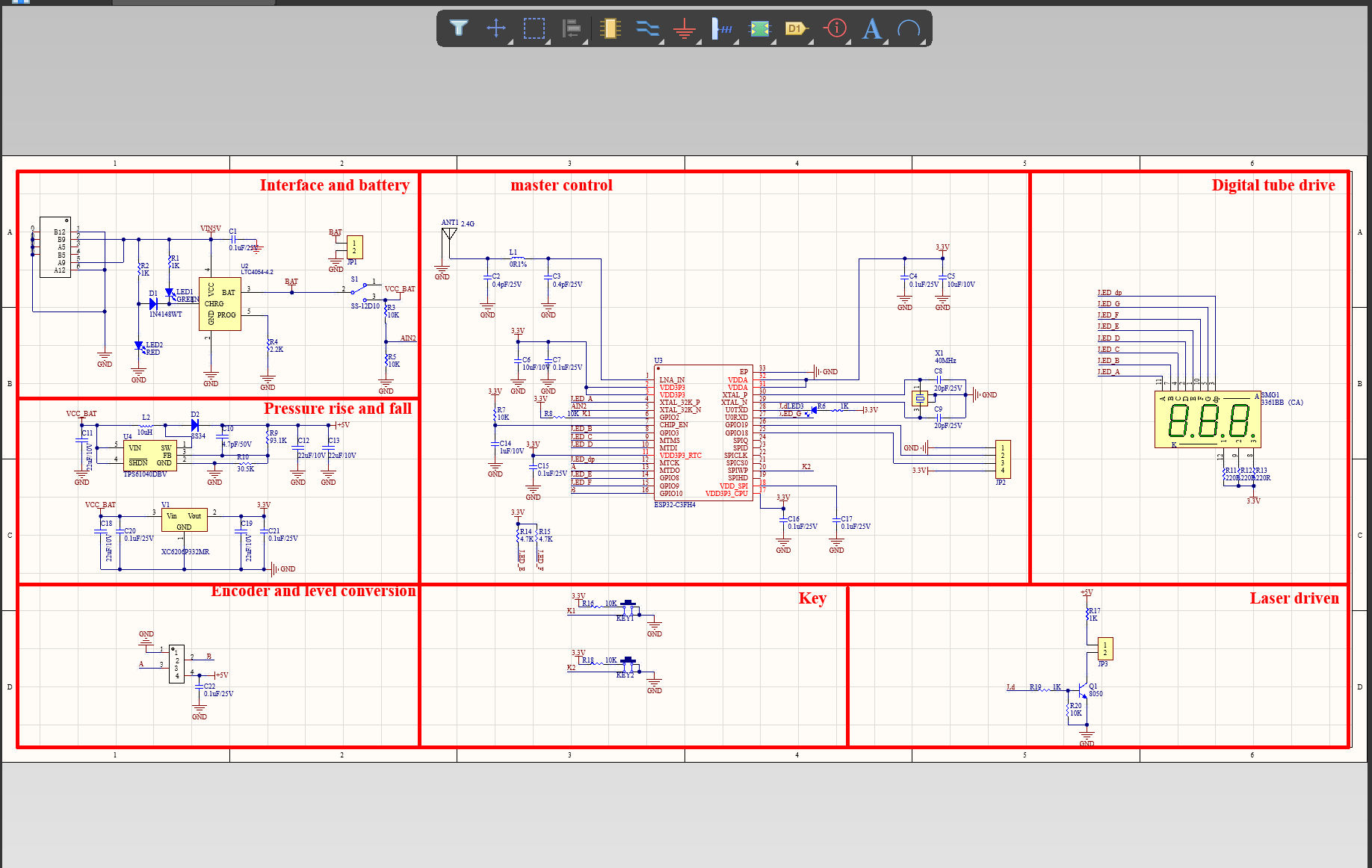
A Printed Circuit Board, also known as a PCB, is a thin board made of non-conductive material, usually fiberglass, that serves as the base for mounting and connecting electronic components. It is designed to provide a stable platform for the attachment of electrical components and serves as an interconnected pathway for the flow of electric signals between them. The board is printed with thin layers of conductive material, typically copper, which forms the circuitry and allows for the transmission of electricity.
Types of Printed Circuit Boards
There are various types of PCB each serving a different purpose. The most commonly used types are single-sided, double-sided, and multi-layer PCBs.
1. Single-Sided PCB: These are the most basic and commonly used type of PCB. They have a layer of conductive material, usually copper, on one side of the board, and the components are mounted on the other side. Single-sided PCB are mainly used in simple electronics with relatively few components.
2. Double-Sided PCB: As the name suggests, double-sided PCB have a layer of conductive material on both sides of the board. This allows for greater flexibility in design and enables the use of more complex circuits.
3. Multi-Layer PCB: These PCBs consist of several layers of conductive material separated by insulating layers, with the components mounted on the outer layers. Multi-layer PCB are used in complex electronics where space is limited and compact designs are required.
Key Components of a Printed Circuit Board
1. Substrate: The substrate is the base material of the PCB, usually made of fiberglass or composite epoxy material. It provides the necessary support for the conductive layers and components.
2. Conductive Layers: These are thin layers of conductive material, typically copper, that make up the circuitry of the PCB. They are usually etched onto the substrate and are responsible for carrying the electrical signals between components.
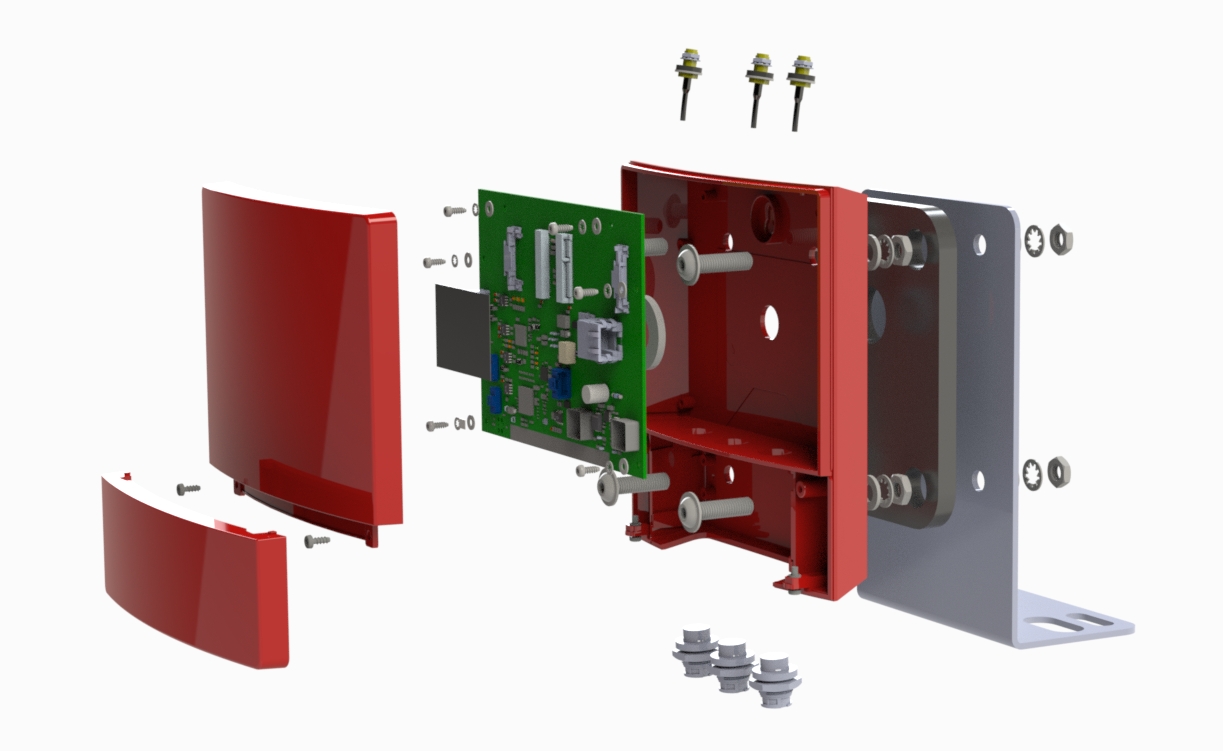
3. Components: Electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits (ICs) are mounted on the PCB. They are connected to the conductive layers through holes called vias or by traces on the surface of the board.
4. Solder Mask: The solder mask is a protective layer that covers the conductive layers, leaving only the connection points exposed. It protects the PCB from corrosion and protects against short circuits.
5. Silkscreen: This is the layer on top of the solder mask that is used to label and identify components and their placement on the board. It usually contains information such as component names, reference numbers, and polarity.
How do Printed Circuit Boards Work?
The functioning of a PCB is relatively simple. The components on the board are connected by a network of conductive paths, also known as traces, which allow the flow of electricity between them. These paths are created by etching the conductive layers, usually copper, to form a pattern that connects the components in the desired configuration.
The components are mounted on the board by soldering them to the conductive pads, which serve as connection points. The soldering process involves heating the pads and components, then melting the soldering material, usually a mixture of tin and lead, to create a strong and permanent bond.
Advantages of Using Printed Circuit Boards
The use of PCBs offers several advantages over other methods of connecting electronic components. These include:
1. Compact and Lightweight: PCBs are compact and lightweight, making them ideal for use in smaller electronic devices.
2. High Reliability: Due to their design and manufacturing process, PCBs have proven to be highly reliable and durable.
3. Cost-effective: The use of PCBs significantly reduces the cost of production and assembly of electronic devices, making them a cost-effective option.
4. Easy to Repair and Replace: In the event of a faulty component, the PCB can be easily repaired or replaced without the need for complex and time-consuming re-wiring.
Schlussfolgerung
Printed Circuit Boards are vital components in today’s electronic devices, allowing for compact and efficient designs. They come in various types, each serving different purposes, and are made up of key components such as the substrate, conductive layers, components, solder mask, and silkscreen. Their use offers numerous advantages, making them an essential element in the manufacturing of electronic products. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see further advancements in the design and use of PCBs.
The Evolution of Printed Circuit Boards: From Early Designs to Modern Technology
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are an essential component in most modern electronic devices. They serve as the foundation for electronic connections and are responsible for routing the electrical signals between the different components of a circuit. PCBs have undergone significant changes since their first inception, and their evolution has closely mirrored advancements in technology.
The Early Days
The origin of PCBs can be traced back to the late 19th century when they were used in a rudimentary form for telephone exchanges. These early PCBs were known as “printed wires” and were created by attaching thin metal wires to a wooden board. This early form of PCB was used to connect telephone switchboards and reduce the need for manual rewiring.
In the early 1900s, scientists started experimenting with the use of thin copper foils on flat bases to create electrical circuits. This led to the invention of “printed” wires on flat boards made by hand, which also reduced the size and complexity of electronic devices. These early PCBs were primarily used in military equipment and radios during World War II.
The Advent of Mass Production
The first commercially successful mass-produced PCB was developed in 1942 by Paul Eisler, an Austrian inventor. His innovative design used conductive ink on a Bakelite board, marking the beginning of modern PCB technology. His creation was initially used in the radio industry, but its use quickly spread to other electronic devices.
The introduction of transistors in the 1950s revolutionized the electronic industry. This development led to smaller and more efficient devices, and PCBs played a crucial role in their production. The early PCB designs used point-to-point connections, which limited the complexity and size of circuits. However, with the introduction of transistors, manufacturers were able to add more components to a PCB, leading to the creation of more advanced electronic devices.
The Rise of Integrated Circuits
In the late 1950s, scientists developed the first integrated circuit (IC), which was a significant breakthrough in the evolution of PCBs. ICs allowed for the miniaturization of electronic components, making devices smaller, faster, and more efficient. This technology paved the way for PCBs to become an integral part of electronic devices, from televisions and radios to computers and mobile phones.
As electronic devices became more complex and the demand for smaller and more efficient devices increased, PCBs continued to evolve. In the 1960s, the through-hole method of assembling components on a PCB was introduced, which allowed for the use of larger and more complex circuits. This method involved drilling holes into the board and inserting component wires through them before soldering them in place.
The Rise of Surface Mount Technology (SMT)
In the 1980s, surface mount technology (SMT) was introduced, bringing another significant change to the manufacturing of PCBs. SMT involves attaching components directly onto the surface of a PCB, eliminating the need for drilling holes. This method increased the complexity and density of electronic circuits, making devices even smaller and more powerful.
SMT also allowed for the use of automated assembly processes, reducing the cost and time required to produce PCBs. This resulted in the mass production of electronic devices, making them more accessible and affordable for the general population.
The Evolution Continues
The evolution of PCBs is ongoing, with new advancements and innovations being introduced regularly. Today, manufacturers are using advanced techniques, such as multi-layer PCBs and flexible PCBs, to further improve the performance and capabilities of electronic devices.
Multi-layer PCBs have multiple layers of circuitry, allowing for more complex circuits without increasing the size of the board. This technology is used in devices such as computers and smartphones, where space is limited, but functionality is crucial.
Flexible PCBs, as the name suggests, can be bent or twisted without damaging the circuitry. This technology has allowed for the creation of devices such as foldable smartphones and wearable technology, where rigid PCBs would not be suitable.
In addition to these advancements, there has also been a push towards more environmentally friendly PCB production. Lead-free and halogen-free materials are being used, and recycling methods are being developed to reduce the impact of electronic waste on the environment.