3070 pcb
MTI specializes in turn-key electronics manufacturing manufacturing service, providing comprehensive solutions from product documentation to high-quality product delivery worldwide.
With a wide range, good quality, reasonable prices and stylish designs, our products are extensively used in power supply.Our products are widely recognized and trusted by users and can meet continuously changing economic and social needs.We welcome new and old customers from all walks of life to contact us for future business relationships and mutual success!
| Product name | 3070 pcb |
| Keyword | 12 layer pcb,3080 pcb,1.6t pcb,eft pcb |
| Place of Origin | China |
| Board Thickness | 1~3.2mm |
| Applicable Industries | medical equipment, etc. |
| Service | OEM/ODM manufacturing |
| Certificate | ISO-9001:2015, ISO-14001:2015,ISO-13485:2012.UL/CSA |
| Solder Mask Color | White |
| Advantage | We keep good quality and competitive price to ensure our customers benefit |
| Sales country | All over the world for example:Slovenia,Hungary,Falkland Islands,Tunisia,Ireland,Lithuania,Azerbaijan,Saint Pierre and Miquelon |
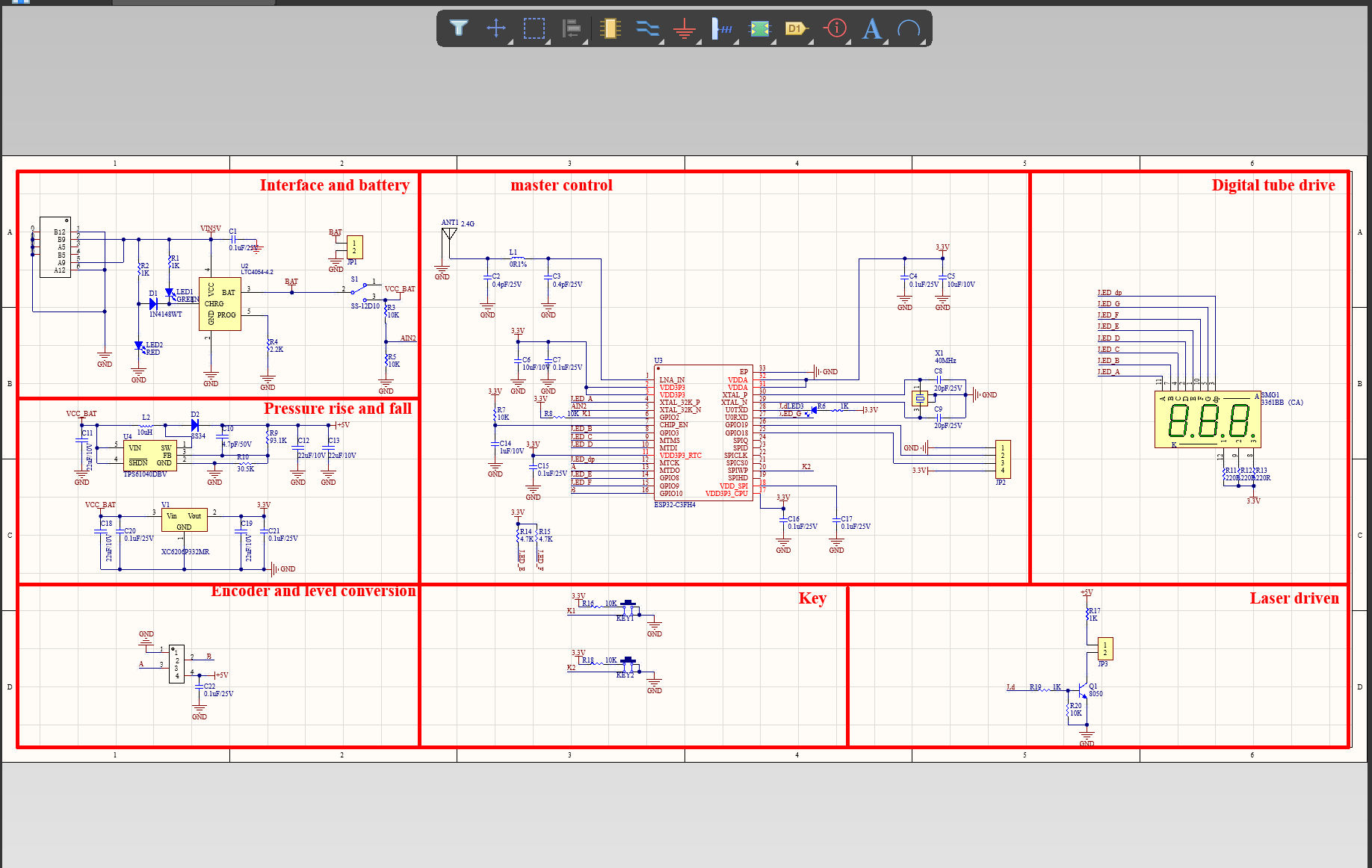
We have rich experience engineer to create a layout using a software platform like Altium Designer. This layout shows you the exact appearance and placement of the components on your board.
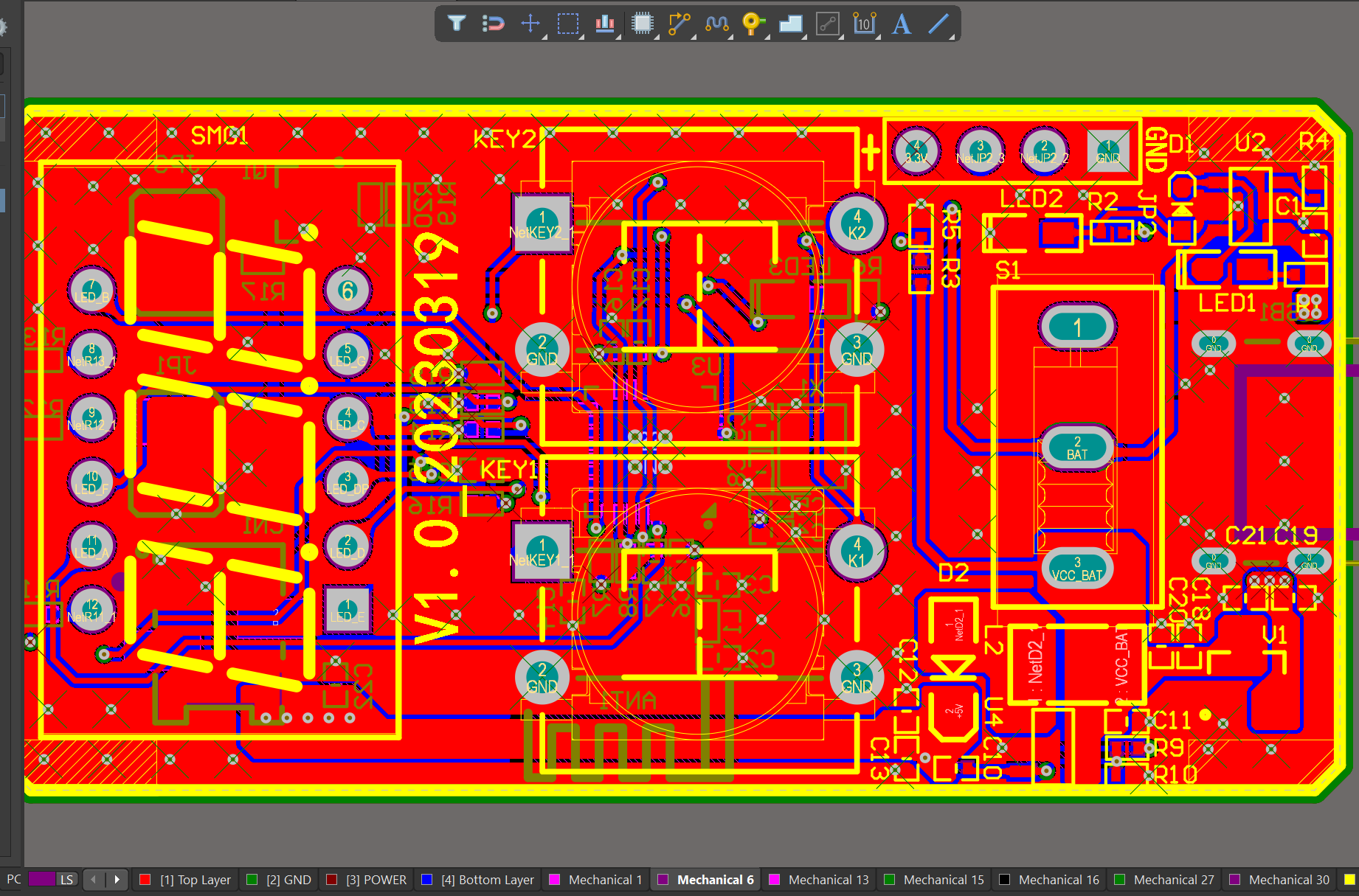
Your deliverables are always ahead of schedule and of the highest quality.
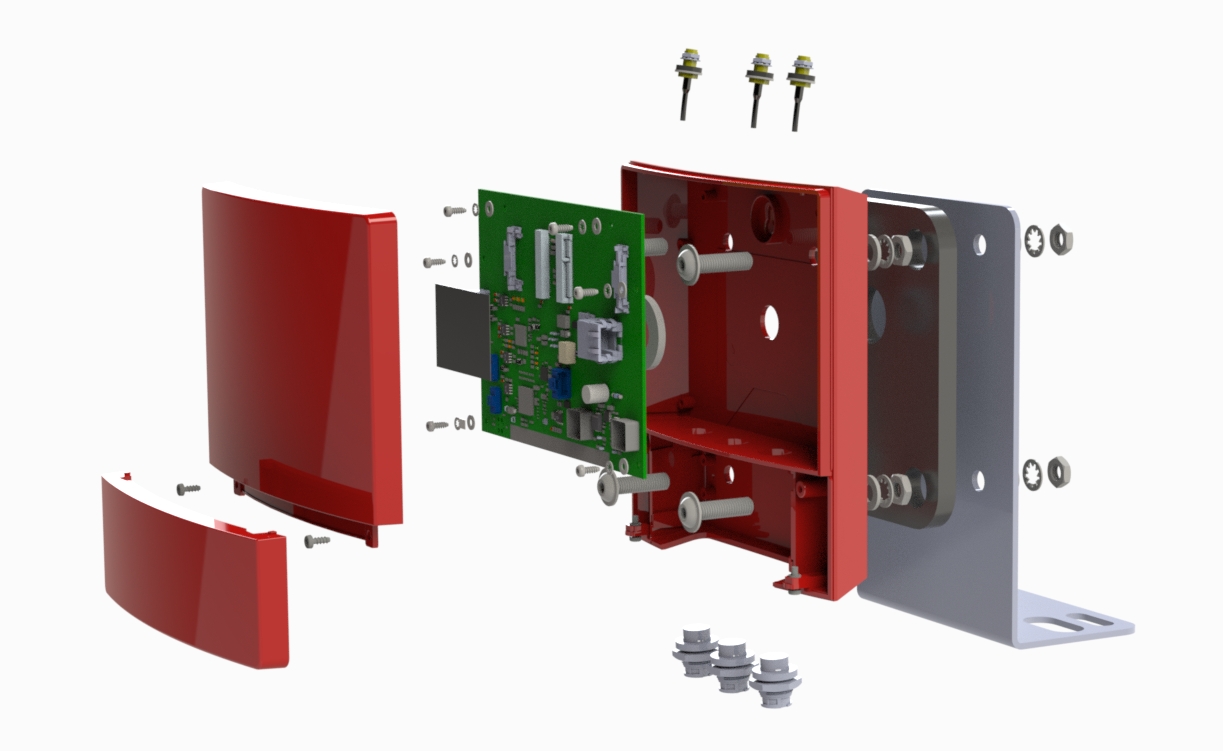
One of our Hardware Design Services is small-batch manufacturing, which allows you to test your idea quickly and verify the functionality of the hardware design and PCB board.
FAQs Guide
2.How does the type of solder mask used affect the PCB’s performance?
3.How do PCBs support the integration of different electronic components?
4.What is the difference between single-sided and double-sided PCBs?
5.Is it possible to have different components on each side of a PCB?
6.How does the number of layers in a PCB affect its functionality?
1.What are the key features of a PCB?
We are committed to providing personalized solutions and established long -term strategic cooperative relationships with customers.
1. Substrate: The base material on which the circuit is printed, usually made of fiberglass or composite epoxy.
2. Conductive Traces: Thin copper lines that connect the components on the PCB.
3. Pads: Small copper areas on the PCB surface where components are soldered.
4. Vias: Holes drilled through the PCB to connect the different layers of the circuit.
5. Solder Mask: A layer of protective material that covers the copper traces and pads, preventing accidental short circuits.
6. Silkscreen: A layer of ink that is printed on the PCB to label the components and provide other useful information.
7. Components: Electronic devices such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits that are mounted on the PCB.
8. Mounting Holes: Holes drilled on the PCB to allow it to be securely attached to a larger device or enclosure.
9. Copper Pour: Large areas of copper that are used to provide a common ground or power plane for the circuit.
10. Edge Connectors: Metal contacts on the edge of the PCB that allow it to be connected to other circuits or devices.
11. Solder Bridges: Small areas of exposed copper that allow for the connection of two or more traces.
12. Test Points: Small pads or holes on the PCB that allow for testing and troubleshooting of the circuit.
13. Silkscreen Legend: Printed text or symbols on the silkscreen layer that provide additional information about the PCB and its components.
14. Designators: Letters or numbers printed on the silkscreen layer to identify specific components on the PCB.
15. Reference Designators: A combination of letters and numbers that identify the location of a component on the PCB according to the schematic diagram.
2.How does the type of solder mask used affect the PCB’s performance?
We have broad development space in domestic and foreign markets. 3070 pcbs have great advantages in terms of price, quality, and delivery date.
The type of solder mask used can affect the PCB’s performance in several ways:
1. Insulation: Solder mask is used to insulate the copper traces on a PCB, preventing them from coming into contact with each other and causing a short circuit. The type of solder mask used can affect the level of insulation provided, which can impact the overall reliability and functionality of the PCB.
2. Solderability: Solder mask also plays a crucial role in the soldering process. The type of solder mask used can affect the surface tension and wetting properties of the solder, which can impact the quality of the solder joints and the overall reliability of the PCB.
3. Thermal resistance: Solder mask can also act as a thermal barrier, protecting the PCB from excessive heat. The type of solder mask used can affect the thermal resistance of the PCB, which can impact its ability to dissipate heat and its overall thermal performance.
4. Chemical resistance: Solder mask is also exposed to various chemicals during the PCB manufacturing process, such as flux and cleaning agents. The type of solder mask used can affect its resistance to these chemicals, which can impact the overall durability and reliability of the PCB.
5. Electrical properties: The type of solder mask used can also affect the electrical properties of the PCB, such as its dielectric constant and dissipation factor. These properties can impact the performance of high-frequency circuits and signal integrity.
Overall, the type of solder mask used can have a significant impact on the performance, reliability, and durability of a PCB. It is essential to carefully select the appropriate solder mask for a specific application to ensure optimal performance.
3.How do PCBs support the integration of different electronic components?
We actively participate in the 3070 pcb industry associations and organization activities. The corporate social responsibility performed well, and the focus of brand building and promotion.
PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) are essential for the integration of different electronic components in electronic devices. They provide a platform for connecting and supporting the various components, allowing them to work together seamlessly. Here are some ways in which PCBs support the integration of different electronic components:
1. Electrical connections: PCBs have a network of copper traces that connect the different electronic components on the board. These traces act as conductors, allowing electricity to flow between the components and enabling them to communicate and work together.
2. Mounting surface: PCBs provide a stable and secure mounting surface for electronic components. The components are soldered onto the board, ensuring that they are firmly attached and will not move or become loose during operation.
3. Space-saving: PCBs are designed to be compact and space-saving, allowing for the integration of multiple components on a single board. This is especially useful in small electronic devices where space is limited.
4. Customization: PCBs can be customized to accommodate different types and sizes of electronic components. This allows for flexibility in design and the integration of a wide range of components, making it easier to create complex electronic devices.
5. Signal routing: PCBs have multiple layers, with each layer dedicated to a specific function. This allows for efficient routing of signals between components, reducing interference and ensuring that the components can communicate effectively.
6. Power distribution: PCBs have dedicated power planes that distribute power to the different components on the board. This ensures that each component receives the required amount of power, preventing damage and ensuring proper functioning.
7. Thermal management: PCBs also play a crucial role in managing the heat generated by electronic components. They have copper layers that act as heat sinks, dissipating heat and preventing the components from overheating.
In summary, PCBs provide a robust and efficient platform for integrating different electronic components. They enable the components to work together seamlessly, ensuring the proper functioning of electronic devices.

4.What is the difference between single-sided and double-sided PCBs?
Our mission is to provide customers with the best solutions for 3070 pcb.
Single-sided PCBs have copper traces and components on only one side of the board, while double-sided PCBs have copper traces and components on both sides of the board. This allows for more complex circuit designs and a higher density of components on a double-sided PCB. Single-sided PCBs are typically used for simpler circuits and are less expensive to manufacture, while double-sided PCBs are used for more complex circuits and are more expensive to manufacture.
5.Is it possible to have different components on each side of a PCB?
We focus on innovation and continuous improvement to maintain a competitive advantage.
Yes, it is possible to have different components on each side of a PCB. This is known as a double-sided PCB or a two-layer PCB. The components on each side can be connected through vias, which are small holes drilled through the PCB that allow for electrical connections between the layers. This allows for more compact and complex circuit designs. However, it also adds complexity to the manufacturing process and may increase the cost of the PCB.
6.How does the number of layers in a PCB affect its functionality?
We should have a stable supply chain and logistics capabilities, and provide customers with high -quality, low -priced 3070 pcb products.
The number of layers in a PCB (Printed Circuit Board) can affect its functionality in several ways:
1. Complexity: The number of layers in a PCB determines the complexity of the circuit design that can be implemented. More layers allow for more components and connections to be included in the design, making it more complex and versatile.
2. Size: A PCB with more layers can be smaller in size compared to a PCB with fewer layers, as it allows for a more compact layout of components and connections. This is especially important in devices with limited space, such as smartphones and wearables.
3. Signal Integrity: The number of layers in a PCB can also affect the signal integrity of the circuit. More layers allow for better routing of signals, reducing the chances of interference and crosstalk between different components.
4. Power Distribution: PCBs with more layers can have dedicated power and ground planes, which help in distributing power evenly across the circuit. This improves the overall performance and stability of the circuit.
5. Cost: The number of layers in a PCB can also affect its cost. More layers mean more materials and manufacturing processes, which can increase the overall cost of the PCB.
6. Thermal Management: PCBs with more layers can have better thermal management, as they allow for the placement of thermal vias and heat sinks to dissipate heat more efficiently. This is important for high-power applications that generate a lot of heat.
In summary, the number of layers in a PCB can significantly impact its functionality, complexity, size, signal integrity, power distribution, cost, and thermal management. Designers must carefully consider the number of layers required for a PCB based on the specific requirements of the circuit and the device it will be used in.

Tags:1 pin pcb connector , 1.2mm pcb , 12 volt pcb led



