3080 ftw3 pcb
MTI specializes in turn-key electronics manufacturing manufacturing service, providing comprehensive solutions from product documentation to high-quality product delivery worldwide.
With a wide range, good quality, reasonable prices and stylish designs, our products are extensively used in communications.Our products are widely recognized and trusted by users and can meet continuously changing economic and social needs.We welcome new and old customers from all walks of life to contact us for future business relationships and mutual success!
| Product name | 3080 ftw3 pcb |
| Keyword | automated circuit board assembly,30a pcb,12v battery charger pcb board,printed circuits assembly corp |
| Place of Origin | China |
| Board Thickness | 1~3.2mm |
| Applicable Industries | new energy, etc. |
| Service | OEM/ODM manufacturing |
| Certificate | ISO-9001:2015, ISO-14001:2015,ISO-13485:2012.UL/CSA |
| Solder Mask Color | Red |
| Advantage | We keep good quality and competitive price to ensure our customers benefit |
| Sales country | All over the world for example:Madagascar,Mayotte,Chad,Canada,Uruguay,Slovakia,Mali,Guernsey,Palau |
One of our Hardware Design Services is small-batch manufacturing, which allows you to test your idea quickly and verify the functionality of the hardware design and PCB board.
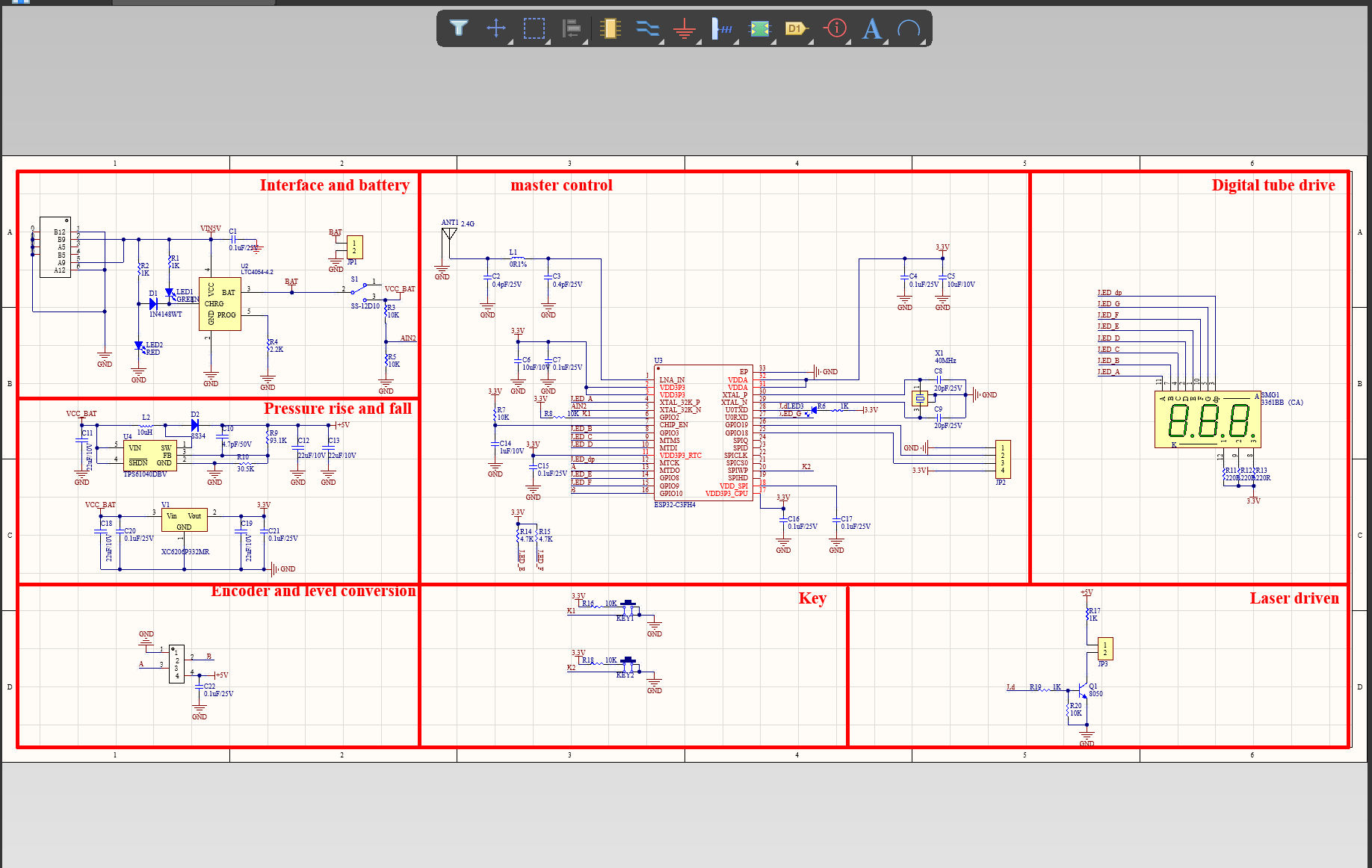
We have rich experience engineer to create a layout using a software platform like Altium Designer. This layout shows you the exact appearance and placement of the components on your board.
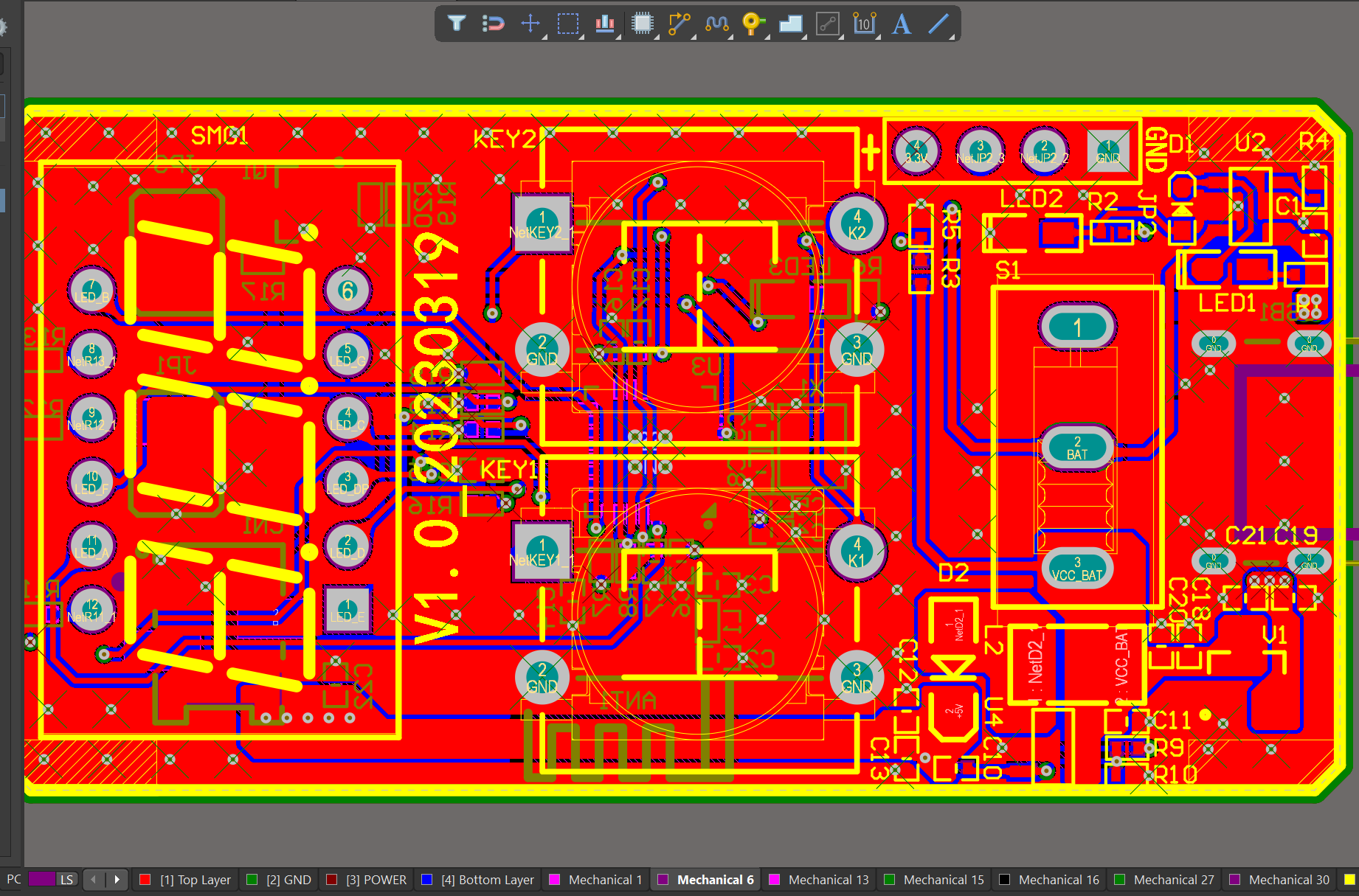
Your deliverables are always ahead of schedule and of the highest quality.
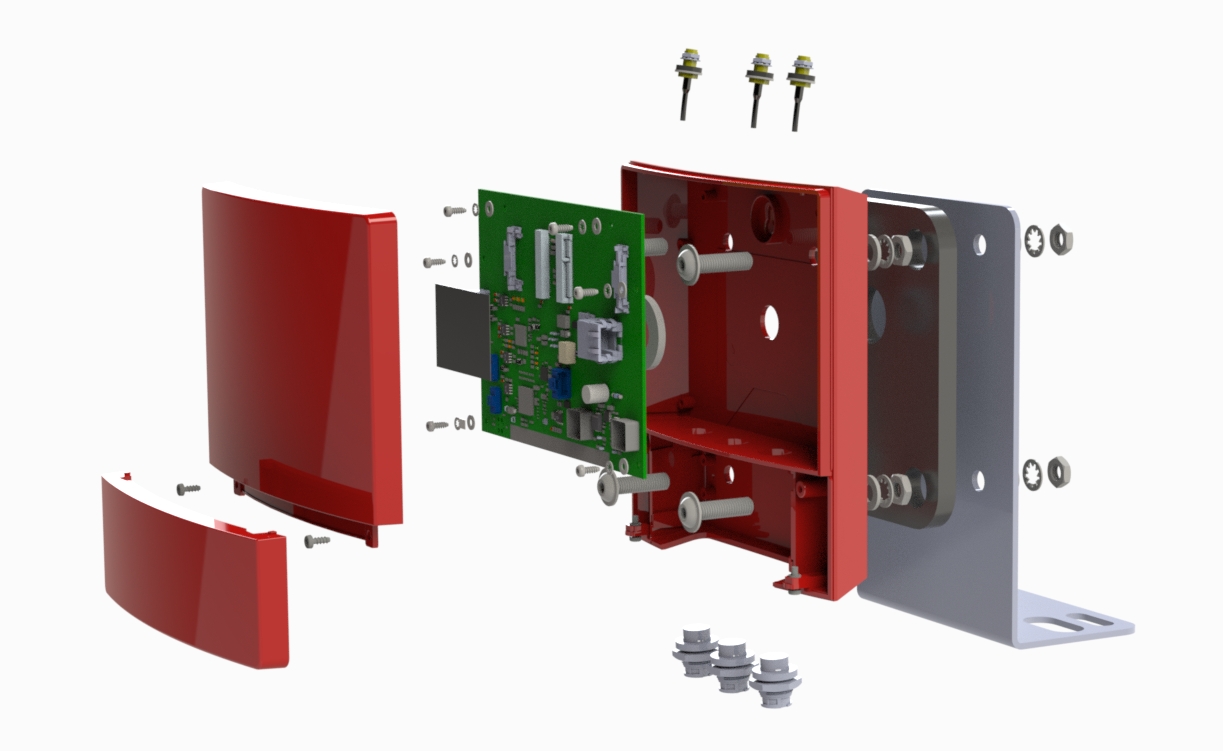
FAQs Guide
2.Can PCBs have multiple power planes?
3.How does the type of vias used affect the performance of a PCB?
4.How does the type of signal layers (analog, digital, power) impact the PCB design?
5.How does the type of laminate material used impact the PCB design?
6.How do surface mount components differ from through-hole components in a PCB?
1.What are the different types of through-hole mounting techniques used in PCBs?
We have flexible production capacity. Whether you are large orders or small orders, you can produce and release goods in a timely manner to meet customer needs.
1. Through-Hole Plating: This is the most common through-hole mounting technique, where the holes in the PCB are plated with a conductive material, usually copper, to create a connection between the layers of the board.
2. Through-Hole Soldering: In this technique, the components are inserted into the plated holes and then soldered to the pads on the opposite side of the board. This provides a strong mechanical connection and good electrical conductivity.
3. Through-Hole Riveting: In this method, the components are inserted into the plated holes and then secured with a rivet or pin. This is commonly used for high-power components or in applications where the board may experience high levels of vibration.
4. Through-Hole Press-Fit: This technique involves inserting the component leads into the plated holes and then pressing them into place using a specialized tool. This provides a strong mechanical connection without the need for soldering.
5. Through-Hole Wave Soldering: In this method, the components are inserted into the plated holes and then passed over a wave of molten solder, which creates a strong solder joint between the component leads and the PCB pads.
6. Through-Hole Reflow Soldering: This technique is similar to wave soldering, but instead of passing over a wave of molten solder, the board is heated in a controlled environment to melt the solder and create a strong joint.
7. Through-Hole Hand Soldering: This is a manual method of soldering where the components are inserted into the plated holes and then soldered by hand using a soldering iron. This is commonly used for small-scale production or for repairs.
8. Through-Hole Pin-in-Paste: This technique involves inserting the component leads into the plated holes and then applying solder paste to the holes before reflow soldering. This provides a strong mechanical connection and good solder joints.
9. Through-Hole Pin-in-Hole: In this method, the component leads are inserted into the plated holes and then bent to form a right angle, creating a secure mechanical connection. This is commonly used for components with large leads, such as electrolytic capacitors.
10. Through-Hole Hand Assembly: This is a manual method of assembly where the components are inserted into the plated holes and then secured with hand tools, such as screws or nuts. This is commonly used for large or heavy components that require additional support.
2.Can PCBs have multiple power planes?
We maintain a stable growth through reasonable capital operations, focus on industry development trends and cutting -edge technologies, and focus on product quality and safety performance.
Yes, PCBs can have multiple power planes. Power planes are layers of copper on a PCB that are used to distribute power and ground signals throughout the board. Multiple power planes can be used to provide different voltages or to separate sensitive analog signals from noisy digital signals. They can also be used to increase the current carrying capacity of the board. The number and arrangement of power planes on a PCB will depend on the specific design requirements and can vary greatly.

3.How does the type of vias used affect the performance of a PCB?
Being one of the top 3080 ftw3 pcb manufacturers in China, We attach great importance to this detail.
The type of vias used can affect the performance of a PCB in several ways:
1. Signal Integrity: Vias can act as discontinuities in the signal path, causing reflections and signal degradation. The type of via used can impact the impedance and signal integrity of the PCB. For high-speed signals, it is important to use controlled impedance vias to maintain signal integrity.
2. Electrical Performance: The type of via used can also affect the electrical performance of the PCB. For example, through-hole vias have lower resistance and inductance compared to blind or buried vias, which can affect the power delivery and signal transmission on the PCB.
3. Thermal Performance: Vias can also play a role in the thermal performance of a PCB. Through-hole vias can act as thermal vias, allowing heat to dissipate from one layer to another. Blind and buried vias, on the other hand, can trap heat and affect the overall thermal management of the PCB.
4. Manufacturing Cost: The type of via used can also impact the cost of manufacturing the PCB. Blind and buried vias require more complex and expensive processes, while through-hole vias are relatively simpler and cheaper to manufacture.
5. PCB Size and Density: The type of via used can also affect the size and density of the PCB. Blind and buried vias take up less space on the surface of the PCB, allowing for higher density designs. This can be beneficial for smaller and more compact PCBs.
Overall, the type of vias used can have a significant impact on the performance, cost, and design of a PCB. It is important to carefully consider the type of vias needed for a specific application to ensure optimal performance and functionality of the PCB.
4.How does the type of signal layers (analog, digital, power) impact the PCB design?
As one of the 3080 ftw3 pcb market leaders, we are known for innovation and reliability.
The type of signal layers on a PCB (analog, digital, power) can impact the design in several ways:
1. Routing: The type of signal layers will determine how the traces are routed on the PCB. Analog signals require careful routing to minimize noise and interference, while digital signals can tolerate more noise. Power signals require wider traces to handle higher currents.
2. Grounding: Analog signals require a solid ground plane to minimize noise and interference, while digital signals can use a split ground plane to isolate sensitive components. Power signals may require multiple ground planes to handle high currents.
3. Component placement: The type of signal layers can also affect the placement of components on the PCB. Analog components should be placed away from digital components to avoid interference, while power components should be placed close to the power source to minimize voltage drops.
4. Signal integrity: The type of signal layers can also impact the signal integrity of the PCB. Analog signals are more susceptible to noise and interference, so the design must take this into account to ensure accurate signal transmission. Digital signals are less sensitive to noise, but the design must still consider signal integrity to avoid timing issues.
5. EMI/EMC: The type of signal layers can also affect the electromagnetic interference (EMI) and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) of the PCB. Analog signals are more likely to cause EMI/EMC issues, so the design must include measures to reduce these effects. Digital signals are less likely to cause EMI/EMC issues, but the design must still consider these factors to ensure compliance with regulations.
Overall, the type of signal layers on a PCB can significantly impact the design and must be carefully considered to ensure optimal performance and functionality of the circuit.

5.How does the type of laminate material used impact the PCB design?
As one of the top 3080 ftw3 pcb manufacturers in China, we take this very seriously.
The type of laminate material used can impact the PCB design in several ways:
1. Electrical properties: Different laminate materials have different electrical properties, such as dielectric constant, loss tangent, and insulation resistance. These properties can affect the signal integrity and impedance of the PCB, which can impact the performance of the circuit.
2. Thermal properties: Some laminate materials have better thermal conductivity than others, which can affect the heat dissipation of the PCB. This is especially important for high-power applications where heat management is crucial.
3. Mechanical properties: The mechanical properties of the laminate material, such as stiffness and flexibility, can impact the overall durability and reliability of the PCB. This is important for applications where the PCB may be subjected to physical stress or vibration.
4. Cost: Different laminate materials have different costs, which can impact the overall cost of the PCB. Some materials may be more expensive but offer better performance, while others may be more cost-effective but have lower performance.
5. Manufacturing process: The type of laminate material used can also impact the manufacturing process of the PCB. Some materials may require specialized equipment or processes, which can affect the production time and cost.
6. Compatibility with components: Certain laminate materials may not be compatible with certain components, such as high-frequency components or components that require specific soldering temperatures. This can limit the design options and affect the functionality of the PCB.
Overall, the type of laminate material used can significantly impact the design, performance, and cost of a PCB. It is important to carefully consider the requirements of the circuit and choose a suitable laminate material to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
6.How do surface mount components differ from through-hole components in a PCB?
We pay attention to user experience and product quality, and provide the best product quality and lowest production cost for cooperative customers.
Surface mount components (SMD) and through-hole components (THD) are two different types of electronic components used in printed circuit boards (PCBs). The main difference between them lies in their method of mounting onto the PCB.
1. Mounting Method:
The main difference between SMD and THD components is their mounting method. SMD components are mounted directly onto the surface of the PCB, while THD components are inserted into holes drilled into the PCB and soldered on the other side.
2. Size:
SMD components are generally smaller in size compared to THD components. This is because SMD components do not require leads or pins for mounting, allowing for a more compact design. THD components, on the other hand, have leads or pins that need to be inserted into the PCB, making them larger in size.
3. Space Efficiency:
Due to their smaller size, SMD components allow for a more space-efficient design on the PCB. This is especially important in modern electronic devices where space is limited. THD components take up more space on the PCB due to their larger size and the need for holes to be drilled.
4. Cost:
SMD components are generally more expensive than THD components. This is because SMD components require more advanced manufacturing techniques and equipment, making them costlier to produce.
5. Assembly Process:
The assembly process for SMD components is automated, using pick-and-place machines to accurately place the components onto the PCB. This makes the process faster and more efficient compared to THD components, which require manual insertion and soldering.
6. Electrical Performance:
SMD components have better electrical performance compared to THD components. This is because SMD components have shorter leads, resulting in less parasitic capacitance and inductance, leading to better signal integrity.
In summary, SMD components offer a more compact design, better electrical performance, and a faster assembly process, but at a higher cost. THD components, on the other hand, are larger in size, less expensive, and can handle higher power and voltage ratings. The choice between SMD and THD components depends on the specific requirements of the PCB design and the intended use of the electronic device.
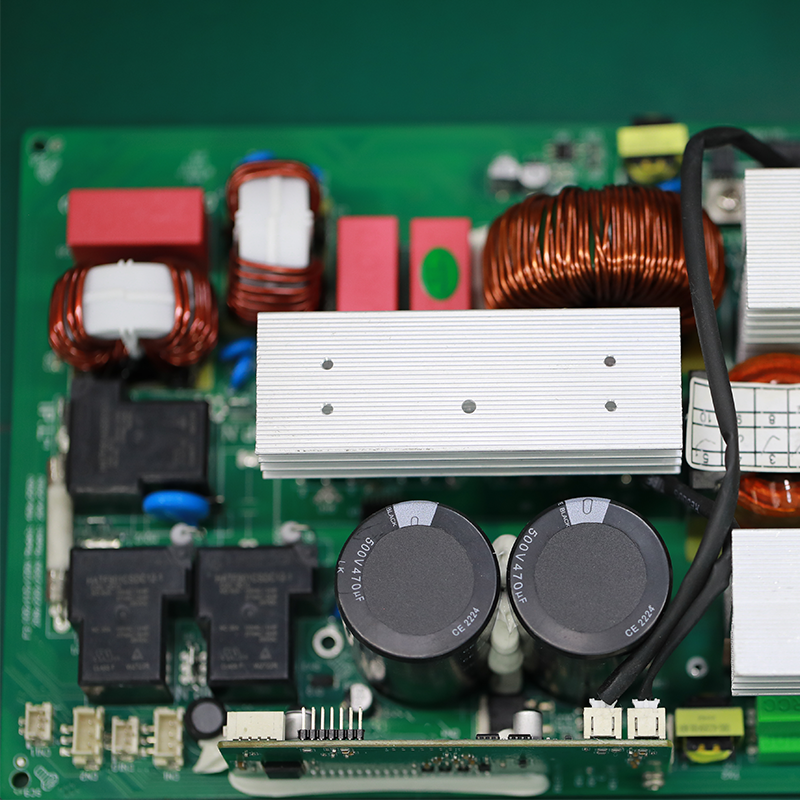
Tags:printed circuit board assemblies,pcb production and assembly



