3080 pcb
MTI is a professional manufacturer of PCB and PCBA , we supply one-stop service. The company’s main services include PCB production, PCB Assembly and electronic materials purchasing, SMT patch, circuit board welding, circuit board plug-in.
Our clientele spans across major continents (Asia,Europe,Africa,America,Oceania)and encompasses various industries, including healthcare,new energy
| Product name | 3080 pcb |
| Keyword | 1000w amplifier pcb board,pcb boards,06141 pcb 305,pcb assembly manufacturer,16 layer pcb manufacturer |
| Place of Origin | China |
| Board Thickness | 1~3.2mm |
| Applicable Industries | aerospace, etc. |
| Service | OEM/ODM manufacturing |
| Certificate | ISO-9001:2015, ISO-14001:2015,ISO-13485:2012.UL/CSA |
| Solder Mask Color | Red |
| Advantage | We keep good quality and competitive price to ensure our customers benefit |
| Sales country | All over the world for example:Malaysia,Rwanda,Armenia,Guinea,Jordan,Portugal,Bermuda |
Your deliverables are always ahead of schedule and of the highest quality.
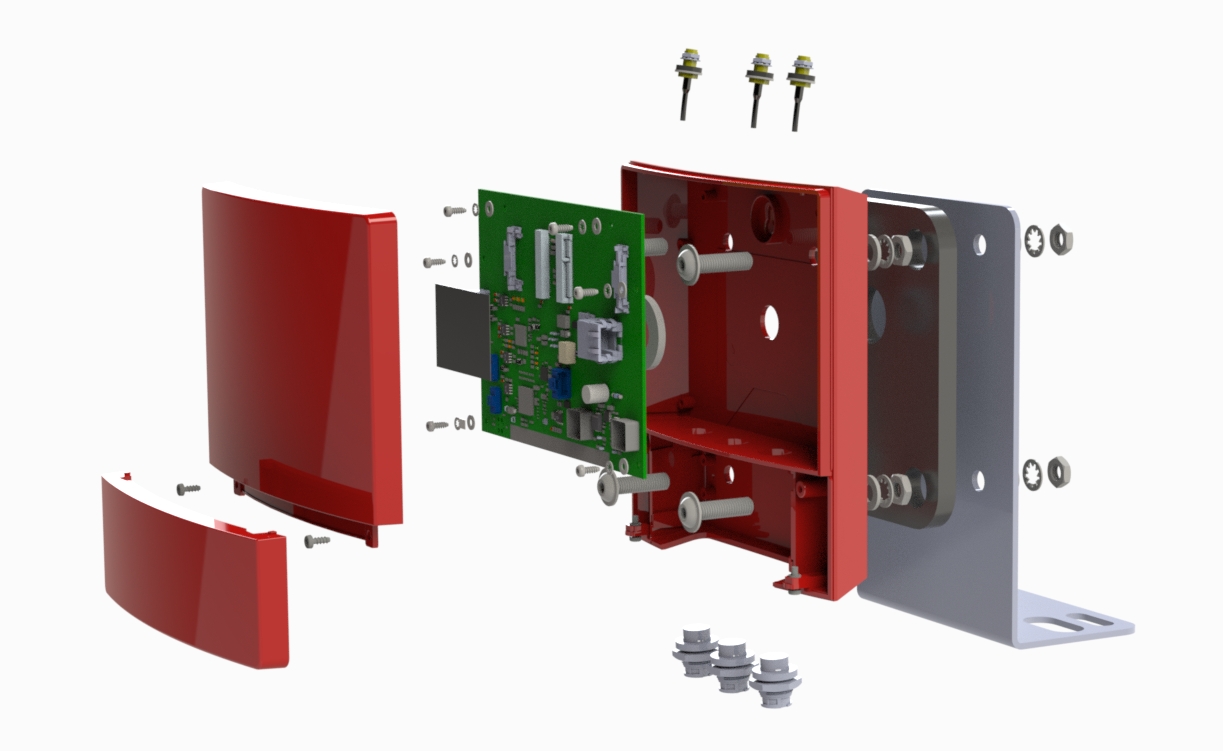
We have rich experience engineer to create a layout using a software platform like Altium Designer. This layout shows you the exact appearance and placement of the components on your board.
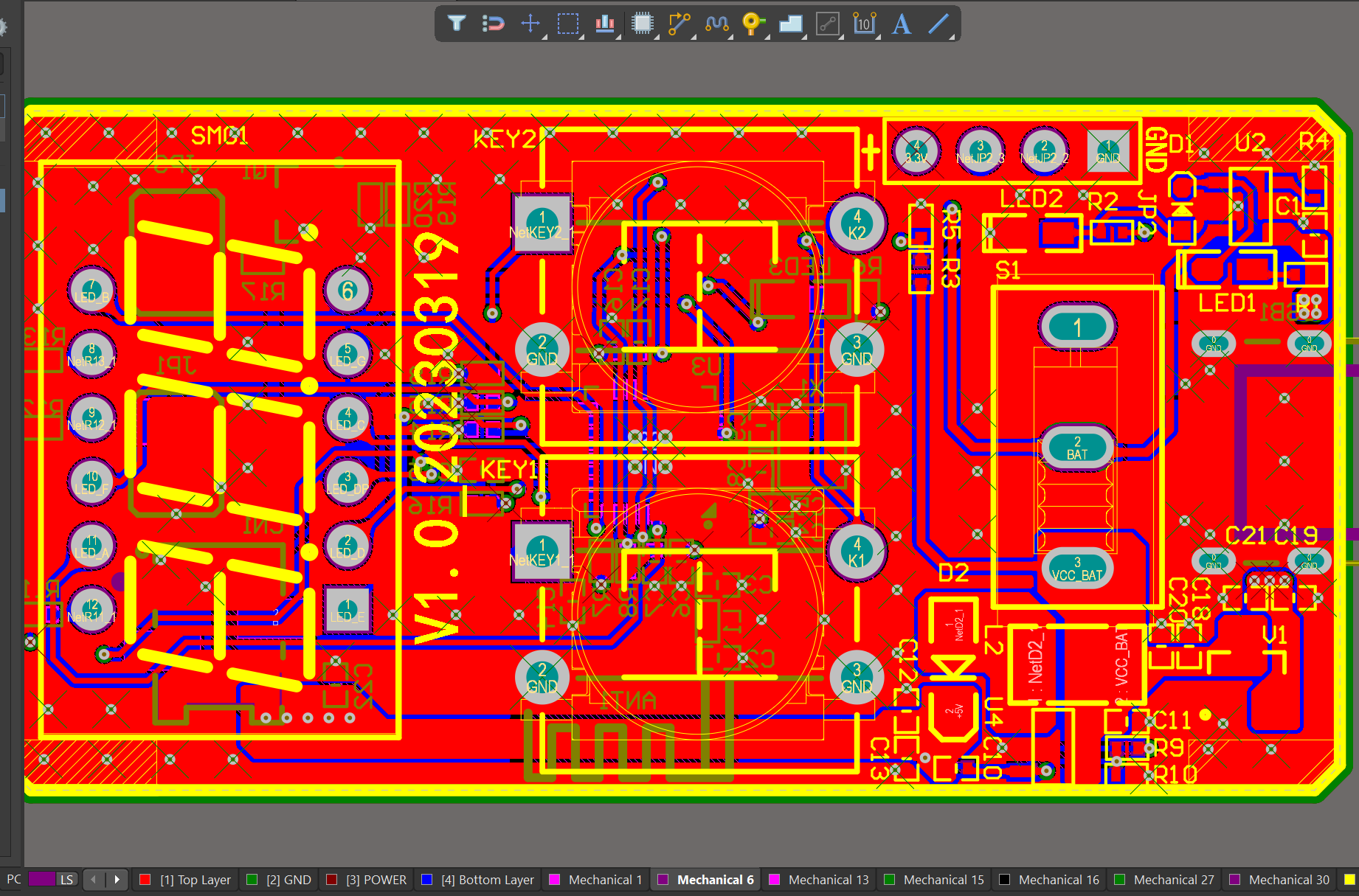
One of our Hardware Design Services is small-batch manufacturing, which allows you to test your idea quickly and verify the functionality of the hardware design and PCB board.
FAQs Guide
2.How do PCBs support the integration of different electronic components?
3.What makes a PCB resistant to environmental factors such as moisture and temperature?
4.What are the factors to consider when choosing the right PCB material for a specific application?
5.Can PCBs be designed with high-speed and high-frequency applications in mind?
6.Can PCBs have different shapes and sizes?
7.How does the type of signal layers (analog, digital, power) impact the PCB design?
1.How does the type of solder mask used affect the PCB’s performance?
We have broad development space in domestic and foreign markets. 3080 pcbs have great advantages in terms of price, quality, and delivery date.
The type of solder mask used can affect the PCB’s performance in several ways:
1. Insulation: Solder mask is used to insulate the copper traces on a PCB, preventing them from coming into contact with each other and causing a short circuit. The type of solder mask used can affect the level of insulation provided, which can impact the overall reliability and functionality of the PCB.
2. Solderability: Solder mask also plays a crucial role in the soldering process. The type of solder mask used can affect the surface tension and wetting properties of the solder, which can impact the quality of the solder joints and the overall reliability of the PCB.
3. Thermal resistance: Solder mask can also act as a thermal barrier, protecting the PCB from excessive heat. The type of solder mask used can affect the thermal resistance of the PCB, which can impact its ability to dissipate heat and its overall thermal performance.
4. Chemical resistance: Solder mask is also exposed to various chemicals during the PCB manufacturing process, such as flux and cleaning agents. The type of solder mask used can affect its resistance to these chemicals, which can impact the overall durability and reliability of the PCB.
5. Electrical properties: The type of solder mask used can also affect the electrical properties of the PCB, such as its dielectric constant and dissipation factor. These properties can impact the performance of high-frequency circuits and signal integrity.
Overall, the type of solder mask used can have a significant impact on the performance, reliability, and durability of a PCB. It is essential to carefully select the appropriate solder mask for a specific application to ensure optimal performance.
2.How do PCBs support the integration of different electronic components?
We actively participate in the 3080 pcb industry associations and organization activities. The corporate social responsibility performed well, and the focus of brand building and promotion.
PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) are essential for the integration of different electronic components in electronic devices. They provide a platform for connecting and supporting the various components, allowing them to work together seamlessly. Here are some ways in which PCBs support the integration of different electronic components:
1. Electrical connections: PCBs have a network of copper traces that connect the different electronic components on the board. These traces act as conductors, allowing electricity to flow between the components and enabling them to communicate and work together.
2. Mounting surface: PCBs provide a stable and secure mounting surface for electronic components. The components are soldered onto the board, ensuring that they are firmly attached and will not move or become loose during operation.
3. Space-saving: PCBs are designed to be compact and space-saving, allowing for the integration of multiple components on a single board. This is especially useful in small electronic devices where space is limited.
4. Customization: PCBs can be customized to accommodate different types and sizes of electronic components. This allows for flexibility in design and the integration of a wide range of components, making it easier to create complex electronic devices.
5. Signal routing: PCBs have multiple layers, with each layer dedicated to a specific function. This allows for efficient routing of signals between components, reducing interference and ensuring that the components can communicate effectively.
6. Power distribution: PCBs have dedicated power planes that distribute power to the different components on the board. This ensures that each component receives the required amount of power, preventing damage and ensuring proper functioning.
7. Thermal management: PCBs also play a crucial role in managing the heat generated by electronic components. They have copper layers that act as heat sinks, dissipating heat and preventing the components from overheating.
In summary, PCBs provide a robust and efficient platform for integrating different electronic components. They enable the components to work together seamlessly, ensuring the proper functioning of electronic devices.
3.What makes a PCB resistant to environmental factors such as moisture and temperature?
We should perform well in market competition, and the prices of 3080 pcb products have a great competitive advantage.
1. Material Selection: The choice of materials used in the PCB can greatly affect its resistance to environmental factors. Materials such as FR-4, polyimide, and ceramic are known for their high resistance to moisture and temperature.
2. Conformal Coating: Applying a conformal coating to the PCB can provide an additional layer of protection against moisture and temperature. This coating acts as a barrier between the PCB and the environment, preventing any moisture or contaminants from reaching the components.
3. Solder Mask: The solder mask used on the PCB can also play a role in its resistance to environmental factors. A high-quality solder mask can provide a protective layer against moisture and temperature, preventing any damage to the components.
4. Component Placement: Proper placement of components on the PCB can also contribute to its resistance to environmental factors. Components that are sensitive to moisture or temperature should be placed away from areas that are prone to these factors, such as near heat sources or in areas with high humidity.
5. Thermal Management: Adequate thermal management is crucial for maintaining the temperature of the PCB within safe limits. This can be achieved through the use of heat sinks, thermal vias, and proper ventilation.
6. Design Considerations: The design of the PCB can also impact its resistance to environmental factors. Factors such as trace width, spacing, and routing can affect the PCB’s ability to withstand temperature changes and moisture exposure.
7. Testing and Quality Control: Proper testing and quality control measures can ensure that the PCB is built to withstand environmental factors. This includes testing for moisture resistance, thermal cycling, and other environmental stressors.
8. Compliance with Standards: Following industry standards and regulations for PCB design and manufacturing can also contribute to its resistance to environmental factors. These standards often include guidelines for material selection, component placement, and testing procedures.
4.What are the factors to consider when choosing the right PCB material for a specific application?
We are centered on customers and always pay attention to customers’ needs for 3080 pcb products.
1. Electrical properties: The electrical properties of the PCB material, such as dielectric constant, loss tangent, and insulation resistance, should be carefully considered to ensure optimal performance for the specific application.
2. Thermal properties: The thermal conductivity and coefficient of thermal expansion of the PCB material are important factors to consider, especially for applications that require high power or operate in extreme temperatures.
3. Mechanical properties: The mechanical strength, stiffness, and flexibility of the PCB material should be evaluated to ensure it can withstand the physical stresses and strains of the application.
4. Chemical resistance: The PCB material should be resistant to any chemicals or solvents that it may come into contact with during its use.
5. Cost: The cost of the PCB material should be considered, as it can vary significantly depending on the type and quality of the material.
6. Availability: Some PCB materials may be more readily available than others, which can affect production timelines and costs.
7. Manufacturing process: The chosen PCB material should be compatible with the manufacturing process, such as etching, drilling, and plating, to ensure efficient and reliable production.
8. Environmental factors: The application environment, such as humidity, moisture, and exposure to UV light, should be taken into account when selecting a PCB material to ensure it can withstand these conditions.
9. Signal integrity: For high-frequency applications, the PCB material should have low signal loss and good signal integrity to prevent interference and ensure accurate signal transmission.
10. RoHS compliance: If the application requires compliance with environmental regulations, such as the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive, the PCB material should be chosen accordingly.
5.Can PCBs be designed with high-speed and high-frequency applications in mind?
We attach importance to the innovation ability and team spirit of employees, have advanced R & D facilities and laboratories, and have a good quality management system.
Yes, PCBs can be designed with high-speed and high-frequency applications in mind. This involves careful consideration of the layout, trace routing, and component placement to minimize signal loss and interference. Specialized materials and techniques, such as controlled impedance routing and differential pairs, can also be used to improve signal integrity and reduce noise. Additionally, the use of advanced simulation and analysis tools can help optimize the design for high-speed and high-frequency performance.
6.Can PCBs have different shapes and sizes?
Our company has many years of 3080 pcb experience and expertise.
Yes, PCBs (printed circuit boards) can have different shapes and sizes depending on the specific design and purpose of the circuit. They can range from small and compact to large and complex, and can be rectangular, circular, or even irregularly shaped. The shape and size of a PCB is determined by the layout of the components and the desired functionality of the circuit.
7.How does the type of signal layers (analog, digital, power) impact the PCB design?
As one of the 3080 pcb market leaders, we are known for innovation and reliability.
The type of signal layers on a PCB (analog, digital, power) can impact the design in several ways:
1. Routing: The type of signal layers will determine how the traces are routed on the PCB. Analog signals require careful routing to minimize noise and interference, while digital signals can tolerate more noise. Power signals require wider traces to handle higher currents.
2. Grounding: Analog signals require a solid ground plane to minimize noise and interference, while digital signals can use a split ground plane to isolate sensitive components. Power signals may require multiple ground planes to handle high currents.
3. Component placement: The type of signal layers can also affect the placement of components on the PCB. Analog components should be placed away from digital components to avoid interference, while power components should be placed close to the power source to minimize voltage drops.
4. Signal integrity: The type of signal layers can also impact the signal integrity of the PCB. Analog signals are more susceptible to noise and interference, so the design must take this into account to ensure accurate signal transmission. Digital signals are less sensitive to noise, but the design must still consider signal integrity to avoid timing issues.
5. EMI/EMC: The type of signal layers can also affect the electromagnetic interference (EMI) and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) of the PCB. Analog signals are more likely to cause EMI/EMC issues, so the design must include measures to reduce these effects. Digital signals are less likely to cause EMI/EMC issues, but the design must still consider these factors to ensure compliance with regulations.
Overall, the type of signal layers on a PCB can significantly impact the design and must be carefully considered to ensure optimal performance and functionality of the circuit.
Tags:3080 ftw3 pcb , printed circuit board assemblies