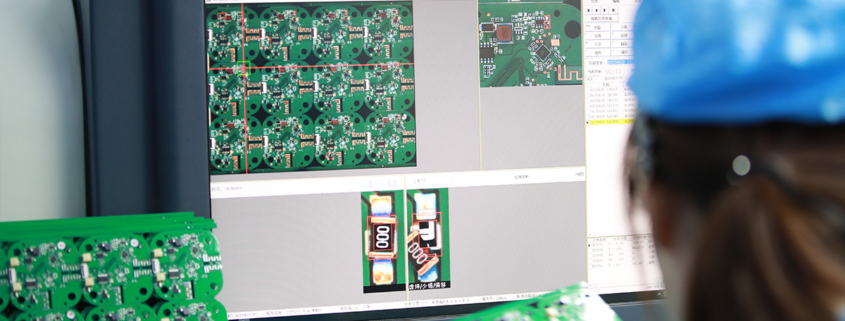
pcb assembling
MTI specializes in turn-key electronics manufacturing manufacturing service, providing comprehensive solutions from product documentation to high-quality product delivery worldwide.
With a wide range, good quality, reasonable prices and stylish designs, our products are extensively used in telecommunications.Our products are widely recognized and trusted by users and can meet continuously changing economic and social needs.We welcome new and old customers from all walks of life to contact us for future business relationships and mutual success!
| Product name | pcb assembling |
| Keyword | 3080 fe pcb,3018 pcb,1.2mm pcb,2.4 ghz pcb trace antenna |
| Place of Origin | China |
| Board Thickness | 2~3.2mm |
| Applicable Industries | telecommunications, etc. |
| Service | OEM/ODM manufacturing |
| Certificate | ISO-9001:2015, ISO-14001:2015,ISO-13485:2012.UL/CSA |
| Solder Mask Color | Black |
| Advantage | We keep good quality and competitive price to ensure our customers benefit |
| Sales country | All over the world for example:Solomon Islands,Costa Rica,Saint Pierre and Miquelon,Czech Republic,Benin,Comoros,Navassa Island,Luxembourg,Europa Island |
One of our Hardware Design Services is small-batch manufacturing, which allows you to test your idea quickly and verify the functionality of the hardware design and PCB board.
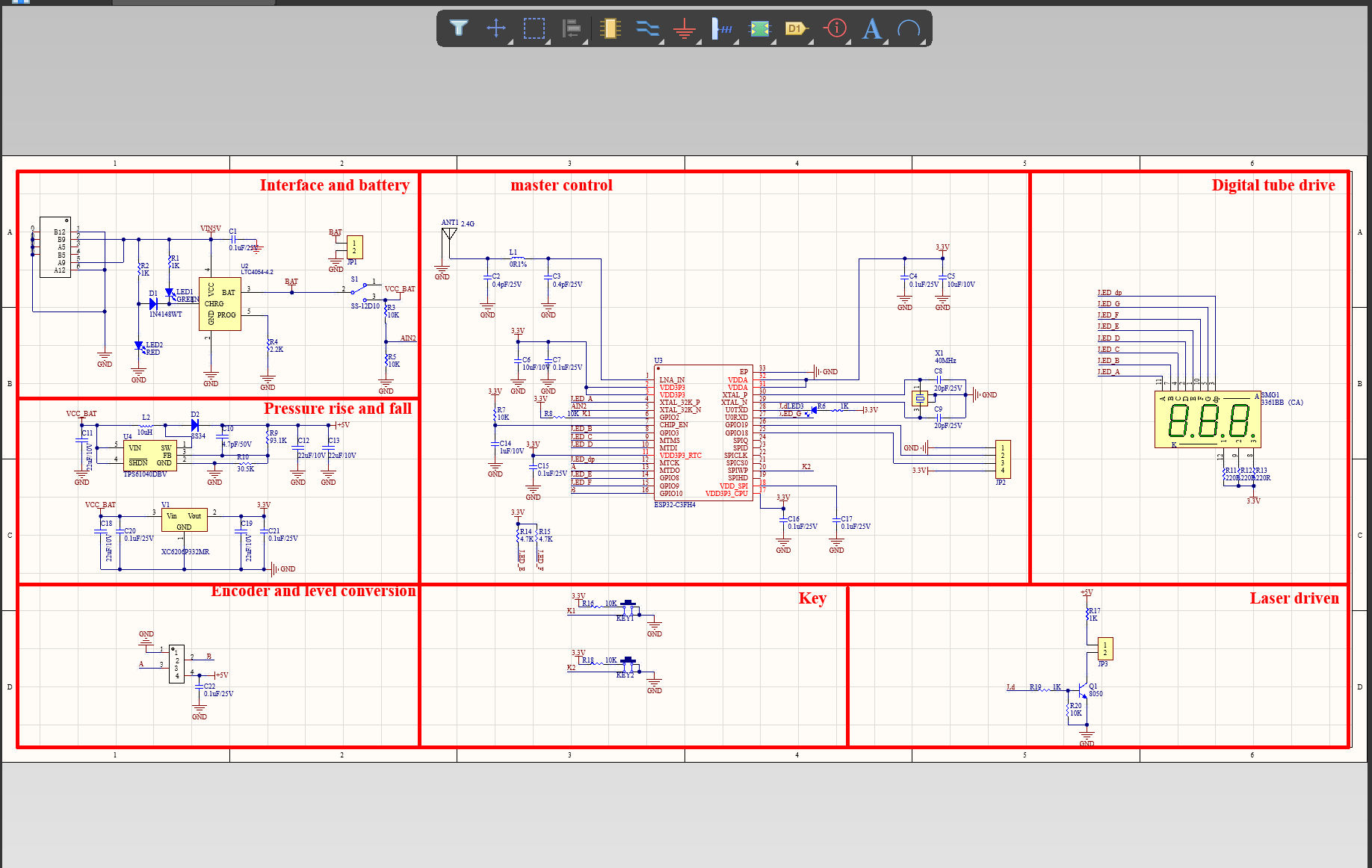
We have rich experience engineer to create a layout using a software platform like Altium Designer. This layout shows you the exact appearance and placement of the components on your board.
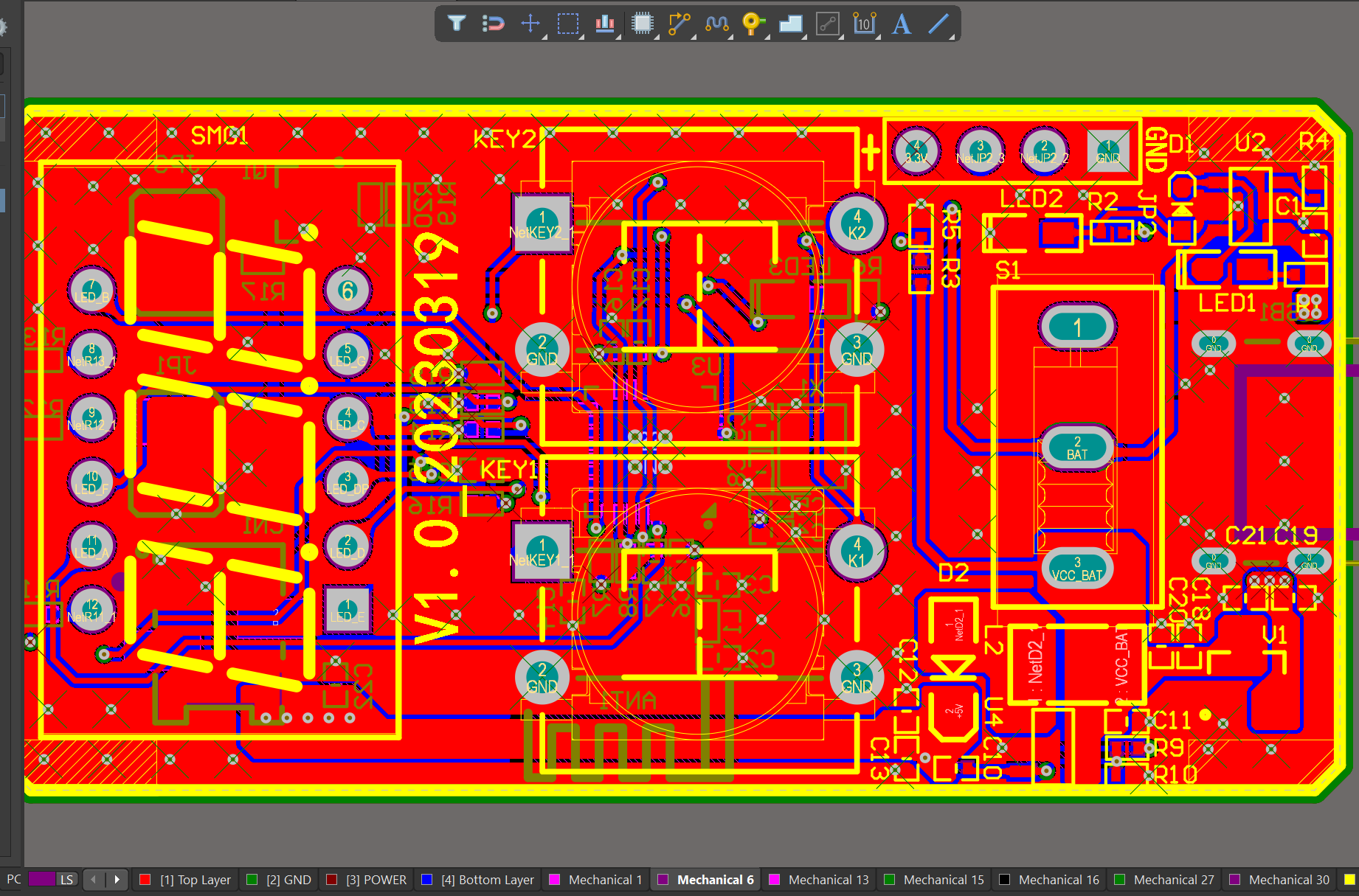
Your deliverables are always ahead of schedule and of the highest quality.
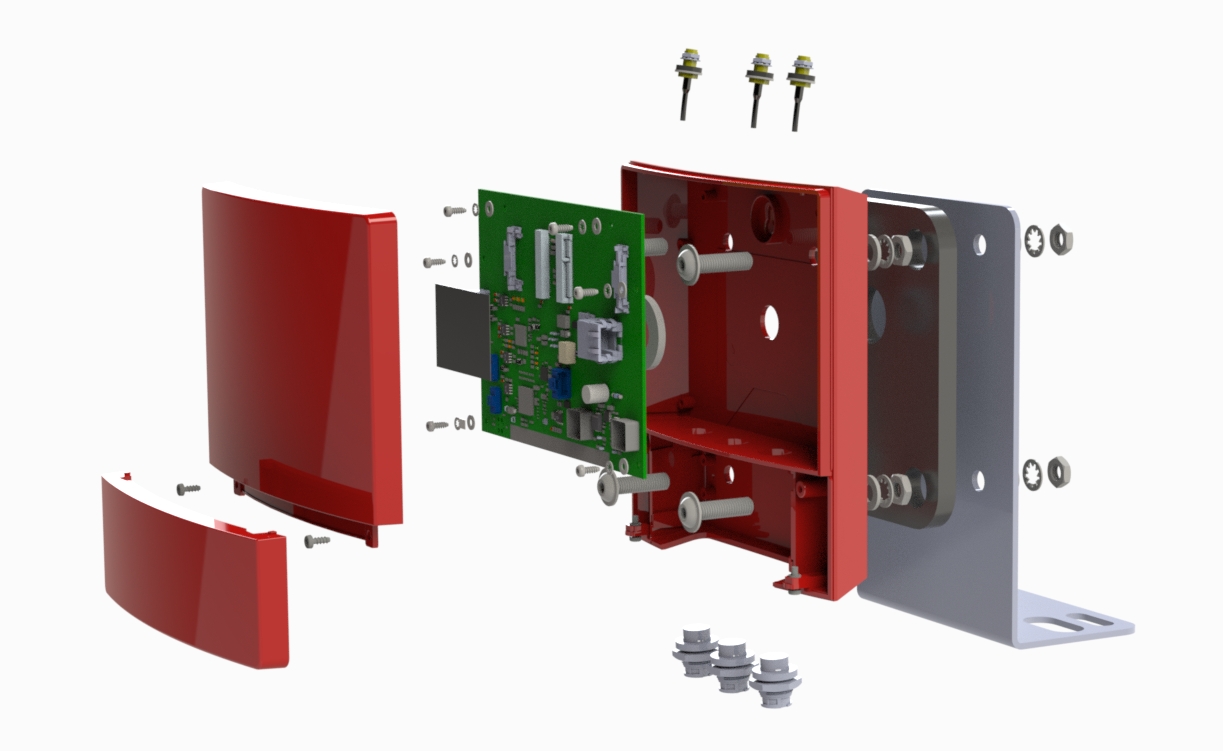
FAQs Guide
2.What is the minimum distance required between components on a PCB?
3.Can PCBs be designed to withstand high vibration or shock?
4.How do surface mount components differ from through-hole components in a PCB?
5.Can PCBs be made with different thicknesses?
6.How does the hole size and shape impact the manufacturing process of a PCB?
1.How does the type of solder mask used affect the PCB’s performance?
We have broad development space in domestic and foreign markets. pcb assemblings have great advantages in terms of price, quality, and delivery date.
The type of solder mask used can affect the PCB’s performance in several ways:
1. Insulation: Solder mask is used to insulate the copper traces on a PCB, preventing them from coming into contact with each other and causing a short circuit. The type of solder mask used can affect the level of insulation provided, which can impact the overall reliability and functionality of the PCB.
2. Solderability: Solder mask also plays a crucial role in the soldering process. The type of solder mask used can affect the surface tension and wetting properties of the solder, which can impact the quality of the solder joints and the overall reliability of the PCB.
3. Thermal resistance: Solder mask can also act as a thermal barrier, protecting the PCB from excessive heat. The type of solder mask used can affect the thermal resistance of the PCB, which can impact its ability to dissipate heat and its overall thermal performance.
4. Chemical resistance: Solder mask is also exposed to various chemicals during the PCB manufacturing process, such as flux and cleaning agents. The type of solder mask used can affect its resistance to these chemicals, which can impact the overall durability and reliability of the PCB.
5. Electrical properties: The type of solder mask used can also affect the electrical properties of the PCB, such as its dielectric constant and dissipation factor. These properties can impact the performance of high-frequency circuits and signal integrity.
Overall, the type of solder mask used can have a significant impact on the performance, reliability, and durability of a PCB. It is essential to carefully select the appropriate solder mask for a specific application to ensure optimal performance.
2.What is the minimum distance required between components on a PCB?
We have advanced production equipment and technology to meet the needs of customers, and can provide customers with high quality, low priced pcb assembling products.
The minimum distance required between components on a PCB depends on various factors such as the type of components, their size, and the manufacturing process used. Generally, the minimum distance between components is determined by the manufacturer’s design rules and guidelines.
For surface mount components, the minimum distance between components is typically 0.2mm to 0.3mm. This distance is necessary to ensure that the solder paste does not bridge between the pads during the reflow process.
For through-hole components, the minimum distance between components is typically 1mm to 2mm. This distance is necessary to ensure that the components do not interfere with each other during the assembly process.
In high-speed and high-frequency applications, the minimum distance between components may need to be increased to avoid signal interference and crosstalk. In these cases, the manufacturer’s design rules and guidelines should be followed closely.
Overall, the minimum distance between components on a PCB should be determined based on the specific requirements of the design and the capabilities of the manufacturing process.
3.Can PCBs be designed to withstand high vibration or shock?
We have established long-term and stable partnerships with our suppliers, so we have great advantages in price and cost and quality assurance.
Yes, PCBs can be designed to withstand high vibration or shock by incorporating certain design features and using appropriate materials. Some ways to make a PCB more resistant to vibration and shock include:
1. Using a thicker and more rigid PCB substrate material, such as FR-4 or ceramic, to provide better structural support and reduce flexing.
2. Adding additional support structures, such as mounting holes or stiffeners, to secure the PCB to the chassis or enclosure.
3. Using smaller and more compact components to reduce the overall weight and size of the PCB, which can help minimize the effects of vibration.
4. Using shock-absorbing materials, such as rubber or foam, between the PCB and the mounting surface to absorb and dampen vibrations.
5. Designing the PCB layout to minimize the length and number of traces and vias, which can reduce the risk of mechanical stress and failure.
6. Using surface mount technology (SMT) components instead of through-hole components, as they are less prone to damage from vibration.
7. Incorporating conformal coating or potting materials to protect the PCB and components from moisture and mechanical stress.
It is important to consider the specific requirements and environment in which the PCB will be used when designing for high vibration or shock resistance. Consulting with a PCB design expert can also help ensure that the PCB is properly designed to withstand these conditions.
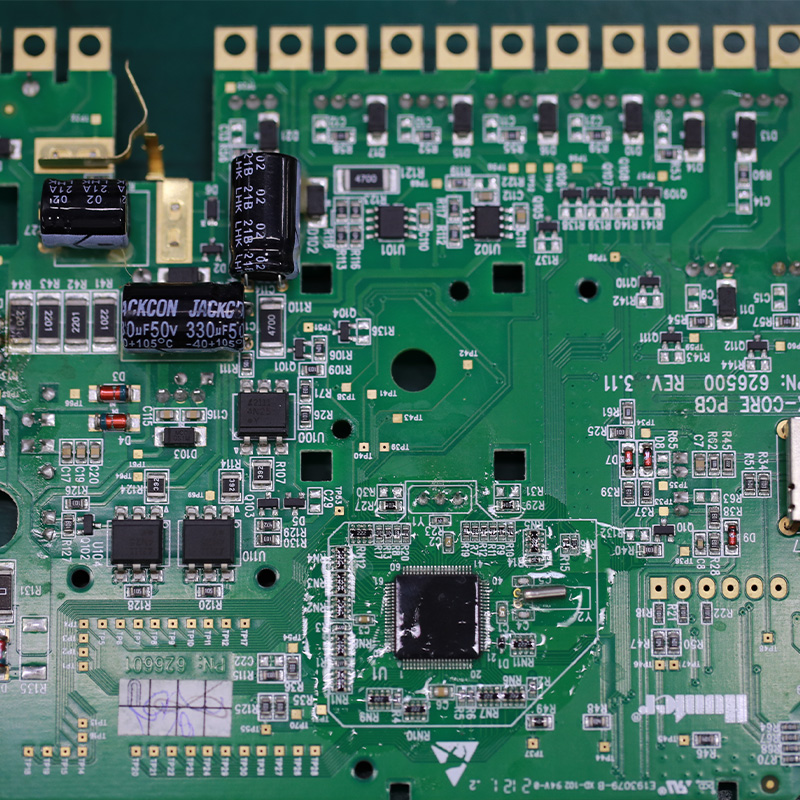
4.How do surface mount components differ from through-hole components in a PCB?
We pay attention to user experience and product quality, and provide the best product quality and lowest production cost for cooperative customers.
Surface mount components (SMD) and through-hole components (THD) are two different types of electronic components used in printed circuit boards (PCBs). The main difference between them lies in their method of mounting onto the PCB.
1. Mounting Method:
The main difference between SMD and THD components is their mounting method. SMD components are mounted directly onto the surface of the PCB, while THD components are inserted into holes drilled into the PCB and soldered on the other side.
2. Size:
SMD components are generally smaller in size compared to THD components. This is because SMD components do not require leads or pins for mounting, allowing for a more compact design. THD components, on the other hand, have leads or pins that need to be inserted into the PCB, making them larger in size.
3. Space Efficiency:
Due to their smaller size, SMD components allow for a more space-efficient design on the PCB. This is especially important in modern electronic devices where space is limited. THD components take up more space on the PCB due to their larger size and the need for holes to be drilled.
4. Cost:
SMD components are generally more expensive than THD components. This is because SMD components require more advanced manufacturing techniques and equipment, making them costlier to produce.
5. Assembly Process:
The assembly process for SMD components is automated, using pick-and-place machines to accurately place the components onto the PCB. This makes the process faster and more efficient compared to THD components, which require manual insertion and soldering.
6. Electrical Performance:
SMD components have better electrical performance compared to THD components. This is because SMD components have shorter leads, resulting in less parasitic capacitance and inductance, leading to better signal integrity.
In summary, SMD components offer a more compact design, better electrical performance, and a faster assembly process, but at a higher cost. THD components, on the other hand, are larger in size, less expensive, and can handle higher power and voltage ratings. The choice between SMD and THD components depends on the specific requirements of the PCB design and the intended use of the electronic device.
5.Can PCBs be made with different thicknesses?
We operate our pcb assembling business with integrity and honesty.
Yes, PCBs (printed circuit boards) can be made with different thicknesses. The thickness of a PCB is determined by the thickness of the copper layer and the thickness of the substrate material. The copper layer thickness can range from 0.5 oz to 3 oz, while the substrate material thickness can range from 0.2 mm to 3.2 mm. The most common thicknesses for PCBs are 1.6 mm and 0.8 mm, but custom thicknesses can be requested from PCB manufacturers. The thickness of a PCB can affect its mechanical strength, thermal properties, and electrical performance.
6.How does the hole size and shape impact the manufacturing process of a PCB?
We continue to invest in research and development and continue to launch innovative products.
The hole size and shape on a PCB can impact the manufacturing process in several ways:
1. Drilling process: The size and shape of the holes determine the type of drill bit and the drilling speed required for creating the holes. Smaller holes require smaller drill bits and slower drilling speeds, while larger holes require larger drill bits and faster drilling speeds. The shape of the hole can also affect the stability of the drill bit and the accuracy of the drilling process.
2. Plating process: After the holes are drilled, they need to be plated with a conductive material to create electrical connections between different layers of the PCB. The size and shape of the holes can affect the plating process, as larger or irregularly shaped holes may require more plating material and longer plating times.
3. Soldering process: The size and shape of the holes can also impact the soldering process. Smaller holes may require more precise placement of components and more careful soldering techniques, while larger holes may allow for easier soldering.
4. Component placement: The size and shape of the holes can also affect the placement of components on the PCB. Smaller holes may limit the size of components that can be used, while larger holes may allow for more flexibility in component placement.
5. PCB design: The size and shape of the holes can also impact the overall design of the PCB. Different hole sizes and shapes may require different routing and layout strategies, which can affect the overall functionality and performance of the PCB.
Overall, the size and shape of the holes on a PCB can significantly impact the manufacturing process and should be carefully considered during the design phase to ensure efficient and accurate production.
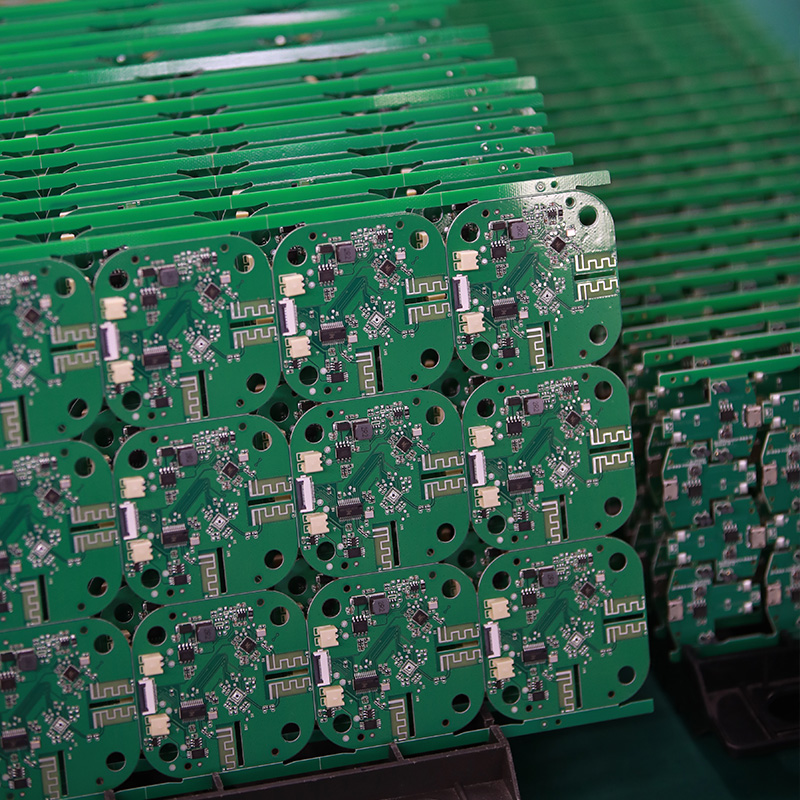

Tags:circuit board assemblies, flex pcba manufacturer