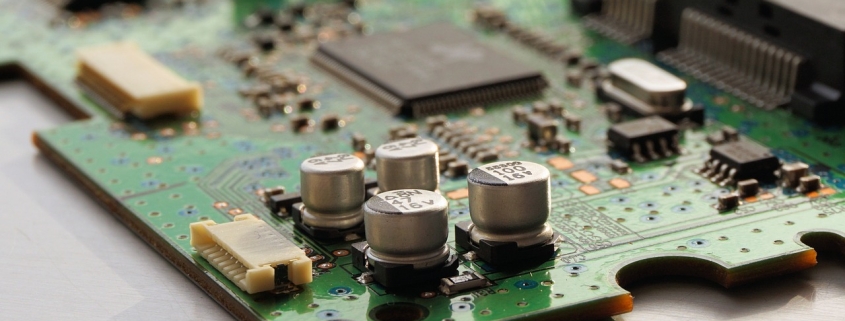
06141 pcb 305
MTI is a manufacturer of high-precision printed circuit board (PCB).We specialize in the manufacture of high precision double-sided and multilayer printed circuit boards, We provide high quality products and faster service for high-tech companies.
We have a group of experienced staff and high-quality management team, set up a complete quality assurance system. Products include FR-4 PCB, Metal PCB and RFPCB (ceramic PCB, PTFE PCB), etc. Have rich experience in the production of thick copper PCB, RF PCB, high Tg PCB, HDI PCB.With ISO9001, ISO14001, TS16949, ISO 13485, RoHS certifications.
| Product name | 06141 pcb 305 |
| Keyword | 120mm pcb,16 layer pcb stackup |
| Place of Origin | China |
| Board Thickness | 1~3.2mm |
| Applicable Industries | testing instruments, etc. |
| Service | OEM/ODM manufacturing |
| Certificate | ISO-9001:2015, ISO-14001:2015,ISO-13485:2012.UL/CSA |
| Solder Mask Color | Blue |
| Advantage | We keep good quality and competitive price to ensure our customers benefit |
| Sales country | All over the world for example:Thailand,Niger,Rwanda,Guinea-Bissau,Niue |
We have rich experience engineer to create a layout using a software platform like Altium Designer. This layout shows you the exact appearance and placement of the components on your board.
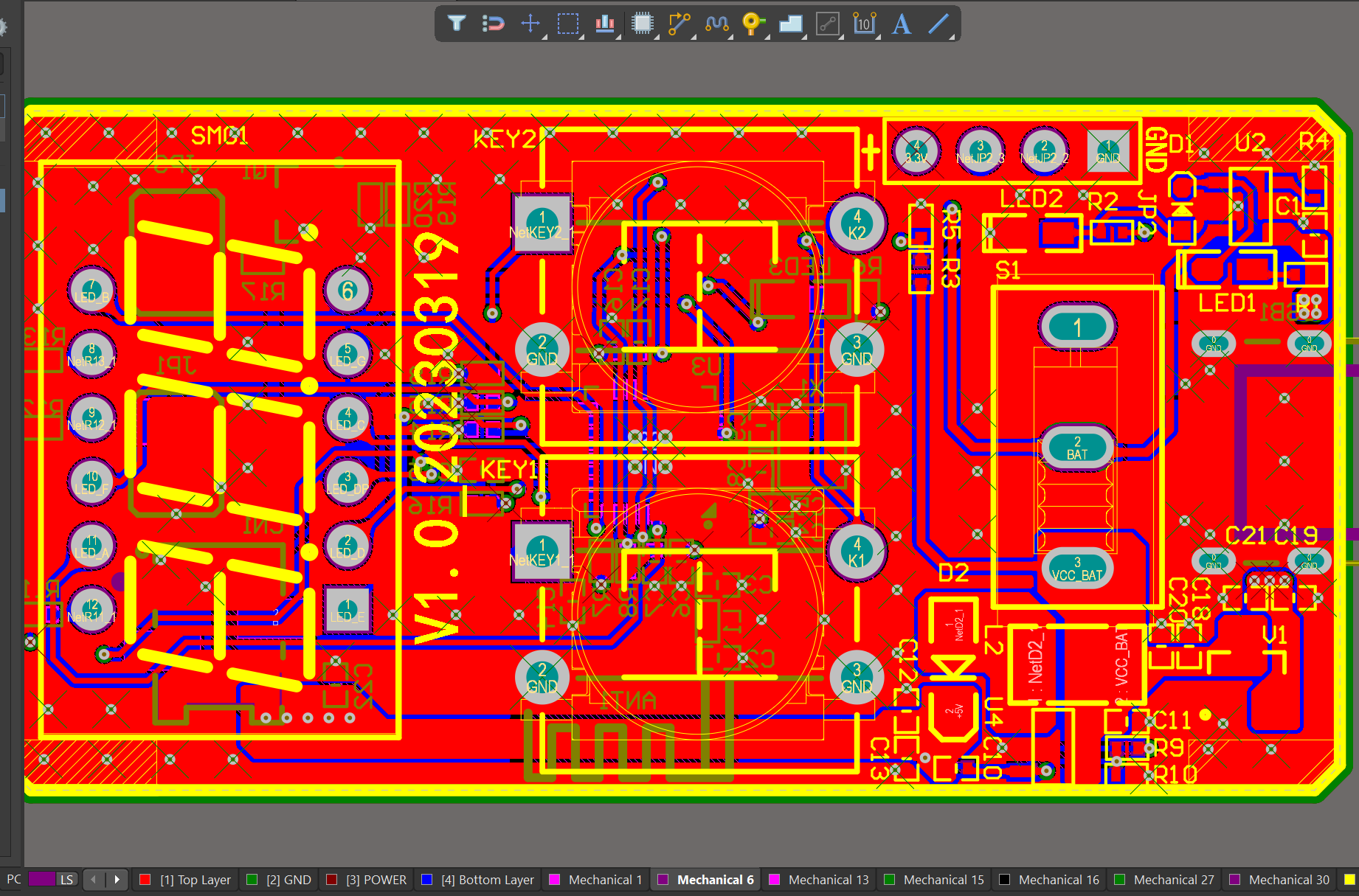
Your deliverables are always ahead of schedule and of the highest quality.
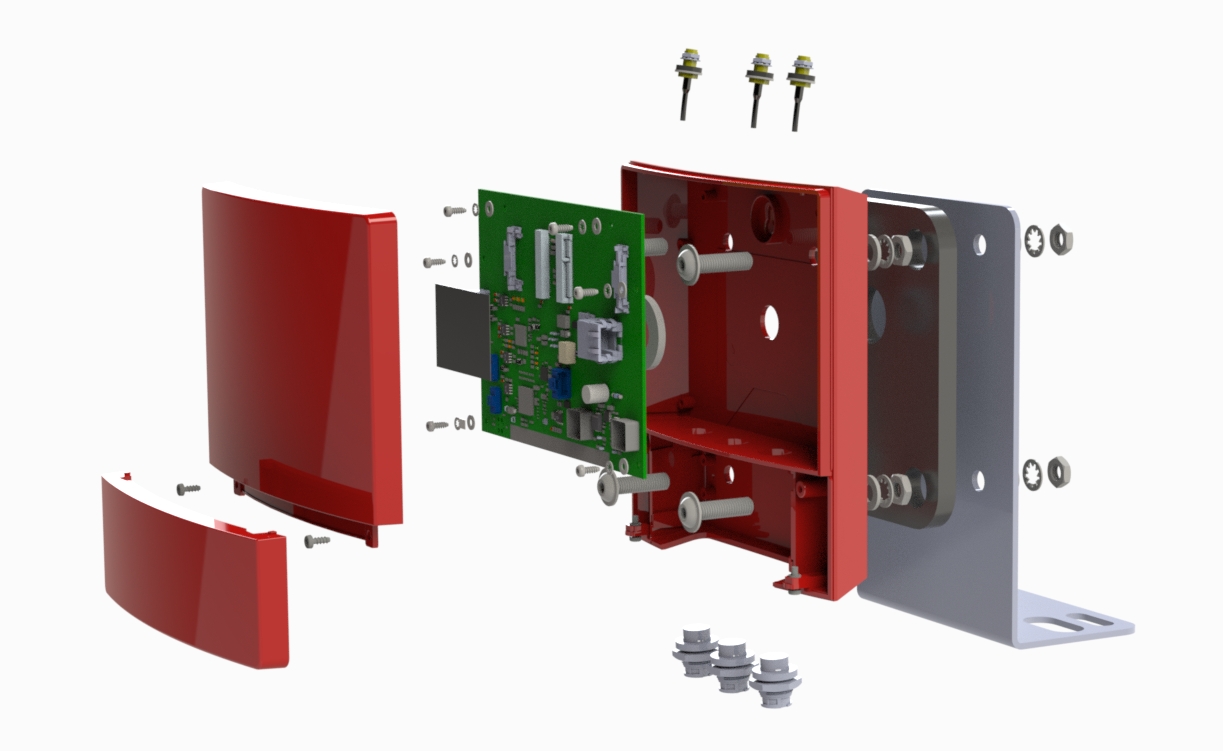
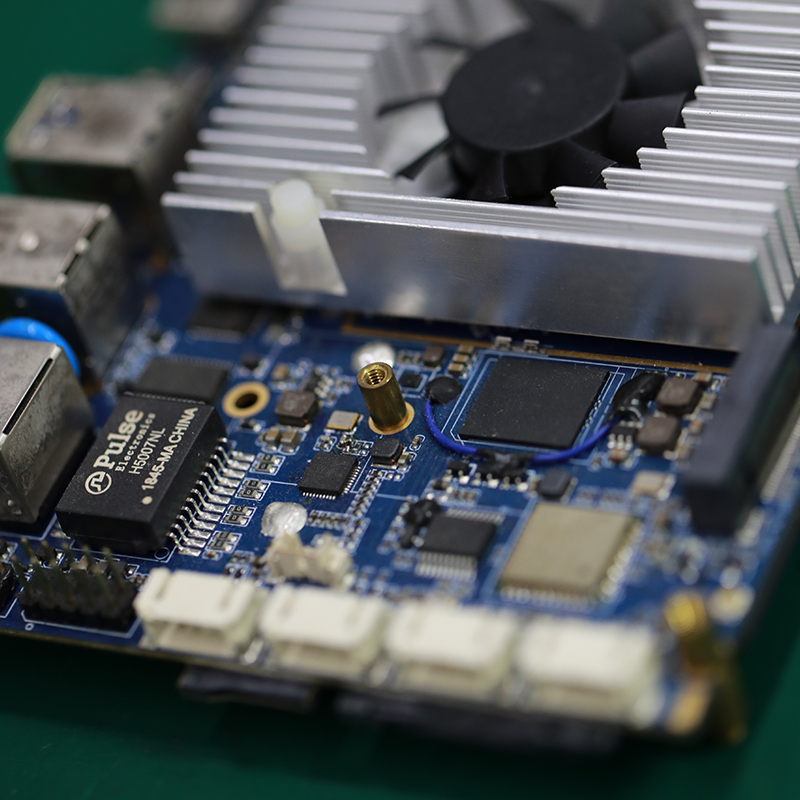
One of our Hardware Design Services is small-batch manufacturing, which allows you to test your idea quickly and verify the functionality of the hardware design and PCB board.
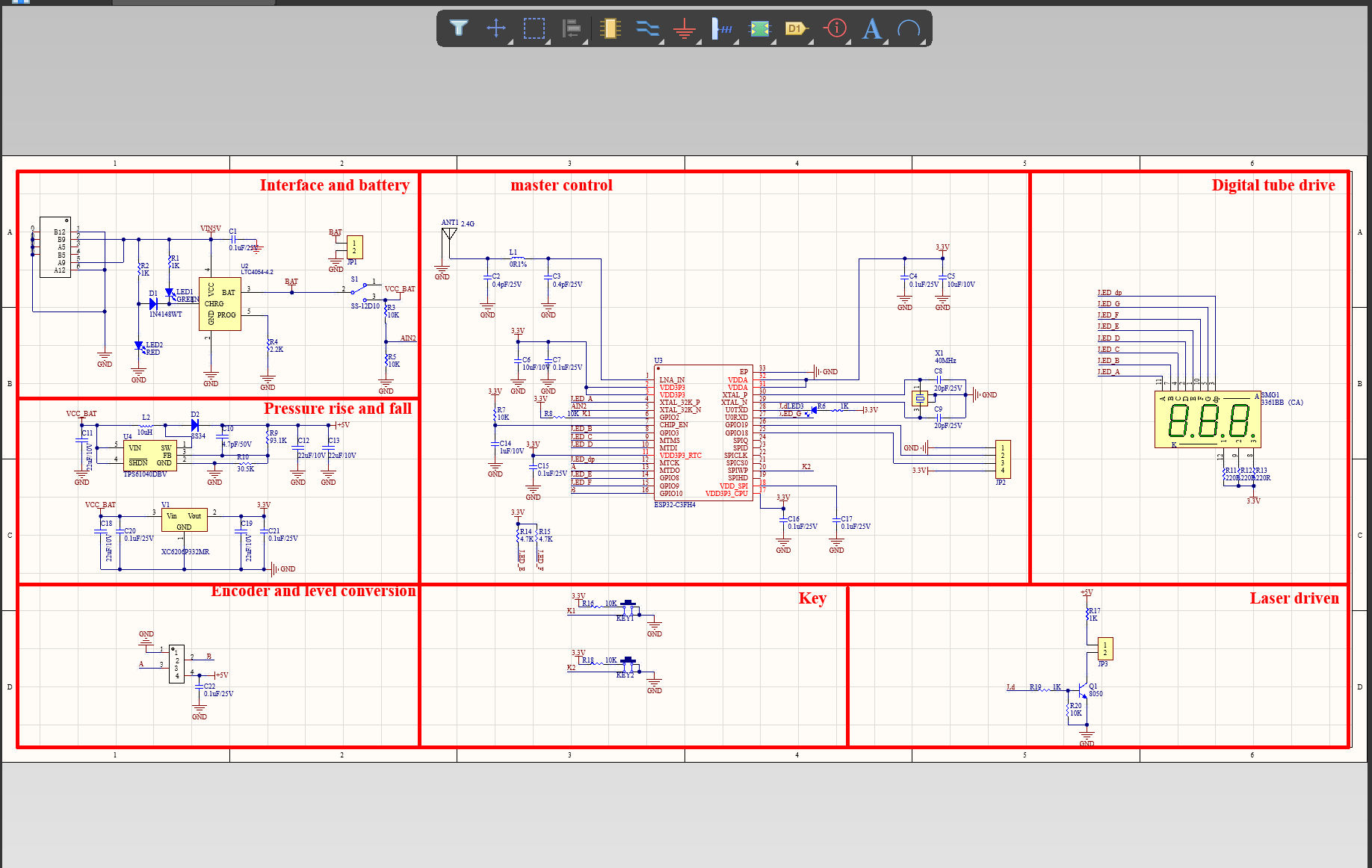
FAQs Guide
2.Can PCBs be designed with high-speed and high-frequency applications in mind?
3.How do PCBs handle overcurrent and short circuits?
4.What are the key features of a PCB?
5.Can PCBs be made with different thicknesses?
1.How does the type of solder mask used affect the PCB’s performance?
We have broad development space in domestic and foreign markets. 06141 pcb 305s have great advantages in terms of price, quality, and delivery date.
The type of solder mask used can affect the PCB’s performance in several ways:
1. Insulation: Solder mask is used to insulate the copper traces on a PCB, preventing them from coming into contact with each other and causing a short circuit. The type of solder mask used can affect the level of insulation provided, which can impact the overall reliability and functionality of the PCB.
2. Solderability: Solder mask also plays a crucial role in the soldering process. The type of solder mask used can affect the surface tension and wetting properties of the solder, which can impact the quality of the solder joints and the overall reliability of the PCB.
3. Thermal resistance: Solder mask can also act as a thermal barrier, protecting the PCB from excessive heat. The type of solder mask used can affect the thermal resistance of the PCB, which can impact its ability to dissipate heat and its overall thermal performance.
4. Chemical resistance: Solder mask is also exposed to various chemicals during the PCB manufacturing process, such as flux and cleaning agents. The type of solder mask used can affect its resistance to these chemicals, which can impact the overall durability and reliability of the PCB.
5. Electrical properties: The type of solder mask used can also affect the electrical properties of the PCB, such as its dielectric constant and dissipation factor. These properties can impact the performance of high-frequency circuits and signal integrity.
Overall, the type of solder mask used can have a significant impact on the performance, reliability, and durability of a PCB. It is essential to carefully select the appropriate solder mask for a specific application to ensure optimal performance.
2.Can PCBs be designed with high-speed and high-frequency applications in mind?
We attach importance to the innovation ability and team spirit of employees, have advanced R & D facilities and laboratories, and have a good quality management system.
Yes, PCBs can be designed with high-speed and high-frequency applications in mind. This involves careful consideration of the layout, trace routing, and component placement to minimize signal loss and interference. Specialized materials and techniques, such as controlled impedance routing and differential pairs, can also be used to improve signal integrity and reduce noise. Additionally, the use of advanced simulation and analysis tools can help optimize the design for high-speed and high-frequency performance.
3.How do PCBs handle overcurrent and short circuits?
We have a first -class management team, and we pay attention to teamwork to achieve common goals.
PCBs (printed circuit boards) have several mechanisms in place to handle overcurrent and short circuits:
1. Fuses: Fuses are the most common protection mechanism used on PCBs. They are designed to break the circuit when the current exceeds a certain threshold, preventing damage to the components and the board.
2. Circuit breakers: Similar to fuses, circuit breakers are designed to break the circuit when the current exceeds a certain threshold. However, unlike fuses, circuit breakers can be reset and reused.
3. Overcurrent protection devices: These devices, such as overcurrent protection diodes, are designed to limit the amount of current flowing through the circuit. They act as a safety valve, preventing excessive current from damaging the components.
4. Thermal protection: Some PCBs have thermal protection mechanisms, such as thermal fuses or thermal cutoffs, which are designed to break the circuit when the temperature of the board exceeds a certain threshold. This helps prevent damage to the board and components due to overheating.
5. Short circuit protection: PCBs may also have short circuit protection mechanisms, such as polymeric positive temperature coefficient (PPTC) devices, which are designed to limit the current in the event of a short circuit. These devices have a high resistance at normal operating temperatures, but their resistance increases significantly when the temperature rises due to a short circuit, limiting the current flow.
Overall, PCBs use a combination of these protection mechanisms to handle overcurrent and short circuits, ensuring the safety and reliability of the board and its components.
4.What are the key features of a PCB?
We are committed to providing personalized solutions and established long -term strategic cooperative relationships with customers.
1. Substrate: The base material on which the circuit is printed, usually made of fiberglass or composite epoxy.
2. Conductive Traces: Thin copper lines that connect the components on the PCB.
3. Pads: Small copper areas on the PCB surface where components are soldered.
4. Vias: Holes drilled through the PCB to connect the different layers of the circuit.
5. Solder Mask: A layer of protective material that covers the copper traces and pads, preventing accidental short circuits.
6. Silkscreen: A layer of ink that is printed on the PCB to label the components and provide other useful information.
7. Components: Electronic devices such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits that are mounted on the PCB.
8. Mounting Holes: Holes drilled on the PCB to allow it to be securely attached to a larger device or enclosure.
9. Copper Pour: Large areas of copper that are used to provide a common ground or power plane for the circuit.
10. Edge Connectors: Metal contacts on the edge of the PCB that allow it to be connected to other circuits or devices.
11. Solder Bridges: Small areas of exposed copper that allow for the connection of two or more traces.
12. Test Points: Small pads or holes on the PCB that allow for testing and troubleshooting of the circuit.
13. Silkscreen Legend: Printed text or symbols on the silkscreen layer that provide additional information about the PCB and its components.
14. Designators: Letters or numbers printed on the silkscreen layer to identify specific components on the PCB.
15. Reference Designators: A combination of letters and numbers that identify the location of a component on the PCB according to the schematic diagram.

5.Can PCBs be made with different thicknesses?
We operate our 06141 pcb 305 business with integrity and honesty.
Yes, PCBs (printed circuit boards) can be made with different thicknesses. The thickness of a PCB is determined by the thickness of the copper layer and the thickness of the substrate material. The copper layer thickness can range from 0.5 oz to 3 oz, while the substrate material thickness can range from 0.2 mm to 3.2 mm. The most common thicknesses for PCBs are 1.6 mm and 0.8 mm, but custom thicknesses can be requested from PCB manufacturers. The thickness of a PCB can affect its mechanical strength, thermal properties, and electrical performance.
Tags:1 oz pcb copper thickness