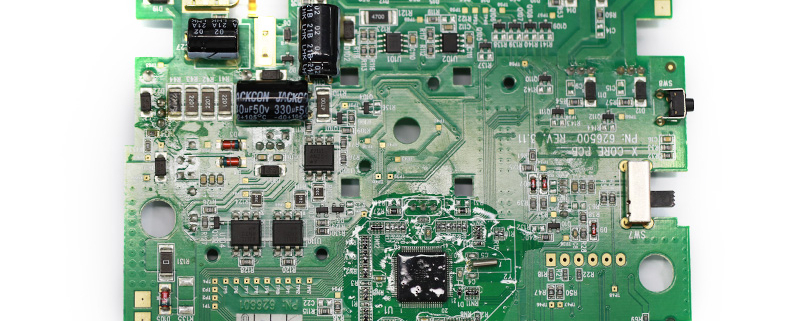
10 layer pcb fabrication
For over two decades, MTI has been dedicated to providing comprehensive OEM/ODM manufacturing services to customers worldwide. With our extensive expertise in PCB assembly, we have established strong collaborative relationships with authorized component distributors. This allows us to source any required components at competitive prices, ensuring cost-effectiveness for our clients.
| Product name | 10 layer pcb fabrication |
| Keyword | 2.4g pcb antenna,1.6t pcb,10 layer pcb stack up,104 keyboard pcb |
| Place of Origin | China |
| Board Thickness | 2~3.2mm |
| Applicable Industries | industrial control, etc. |
| Service | OEM/ODM manufacturing |
| Certificate | ISO-9001:2015, ISO-14001:2015,ISO-13485:2012.UL/CSA |
| Solder Mask Color | Green |
| Advantage | We keep good quality and competitive price to ensure our customers benefit |
| Sales country | All over the world for example:Kiribati,Azerbaijan,Vanuatu,Bhutan,Japan,Portugal,Finland,Chad |
Your deliverables are always ahead of schedule and of the highest quality.
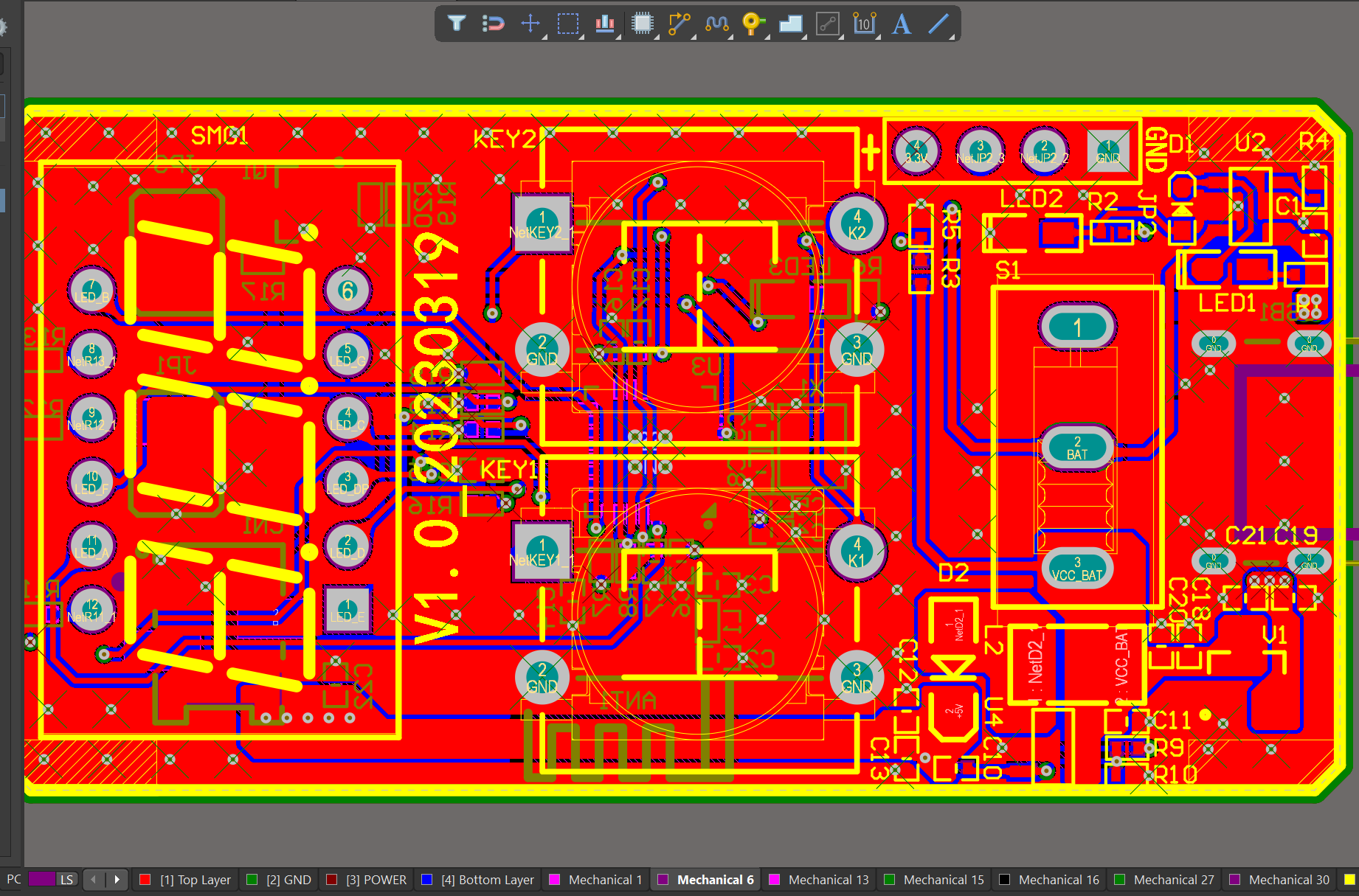
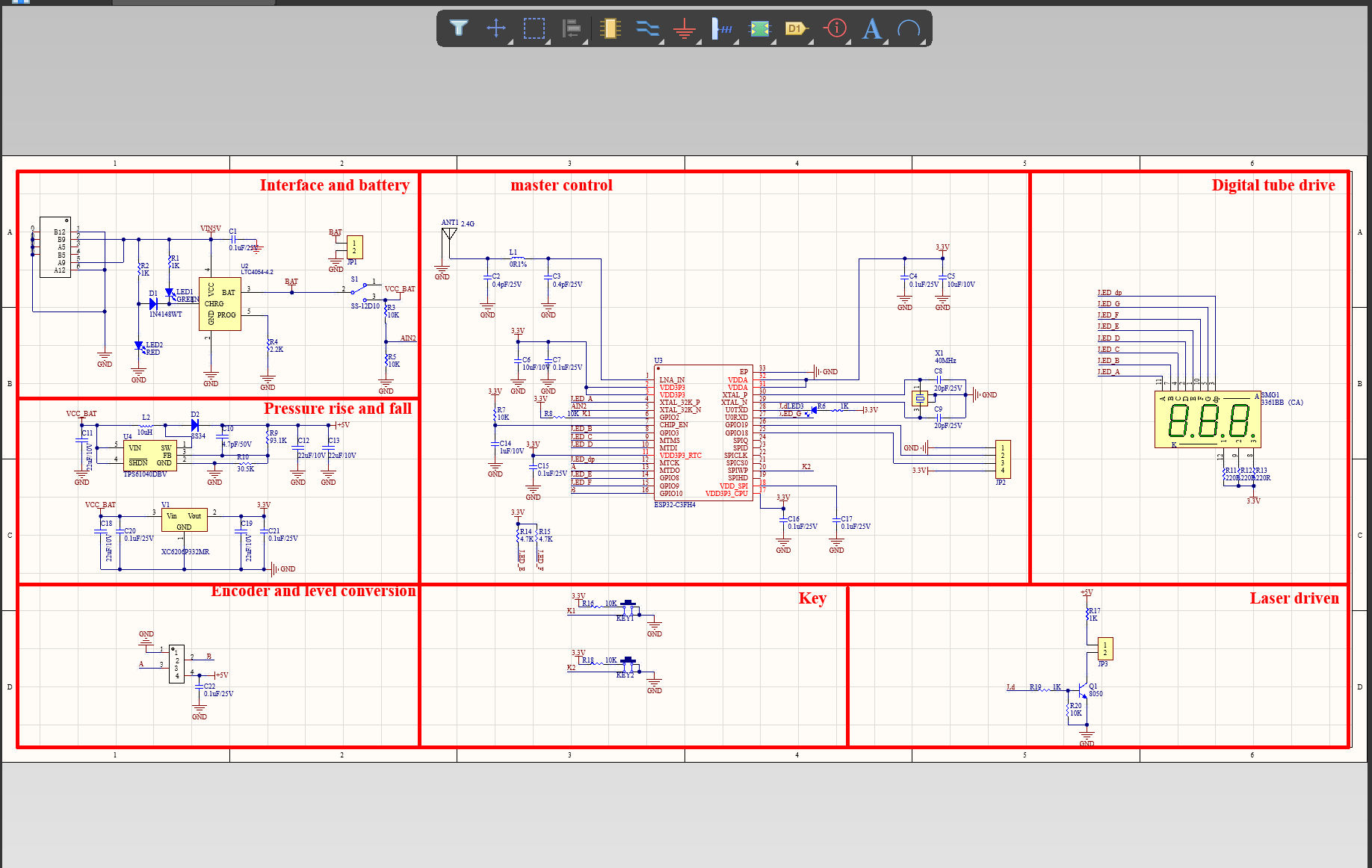
We have rich experience engineer to create a layout using a software platform like Altium Designer. This layout shows you the exact appearance and placement of the components on your board.
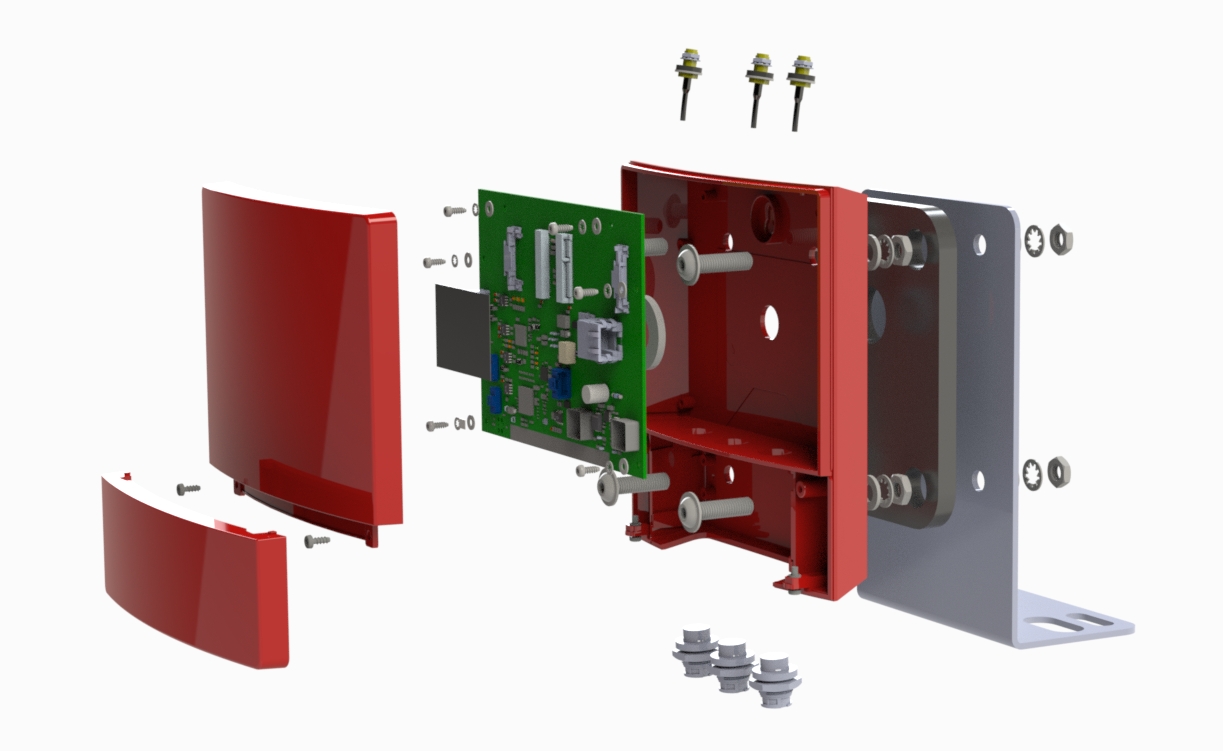
One of our Hardware Design Services is small-batch manufacturing, which allows you to test your idea quickly and verify the functionality of the hardware design and PCB board.
FAQs Guide
2.How important is the trace width and spacing in a PCB design?
3.How does component placement affect signal integrity in a PCB design?
4.What makes a PCB resistant to environmental factors such as moisture and temperature?
5.Can PCBs have multiple power planes?
6.What is the minimum distance required between components on a PCB?
7.How do surface mount components differ from through-hole components in a PCB?
1.What is impedance control and why is it important in PCBs?
We enjoy high authority and influence in the industry and continue to innovate products and service models.
Impedance control is the ability to maintain a consistent electrical impedance throughout a printed circuit board (PCB). It is important in PCBs because it ensures that signals can travel through the board without distortion or loss of quality.
Impedance control is particularly important in high-speed digital and analog circuits, where even small variations in impedance can cause signal reflections and distortions. This can lead to errors in data transmission and affect the overall performance of the circuit.
In addition, impedance control is crucial in ensuring signal integrity and reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI). By maintaining a consistent impedance, the PCB can effectively filter out unwanted signals and prevent them from interfering with the desired signals.
Overall, impedance control is essential for achieving reliable and high-quality performance in PCBs, especially in complex and sensitive electronic systems. It requires careful design and manufacturing techniques, such as controlled trace widths and spacing, to achieve the desired impedance levels.
2.How important is the trace width and spacing in a PCB design?
Our 10 layer pcb fabrication products have competitive and differentiated advantages, and actively promote digital transformation and innovation.
The trace width and spacing in a PCB design are crucial factors that can greatly affect the performance and reliability of the circuit. Here are some reasons why:
1. Current carrying capacity: The trace width determines the amount of current that can flow through the trace without causing excessive heating. If the trace width is too narrow, it can lead to overheating and damage to the circuit.
2. Voltage drop: The trace width also affects the voltage drop across the trace. A narrow trace will have a higher resistance, resulting in a higher voltage drop. This can cause a decrease in the voltage level at the end of the trace, affecting the performance of the circuit.
3. Signal integrity: The spacing between traces is critical for maintaining signal integrity. If the spacing is too narrow, it can lead to crosstalk and interference between signals, resulting in errors and malfunctions in the circuit.
4. Thermal management: The spacing between traces also plays a role in thermal management. Adequate spacing between traces allows for better air circulation, which helps dissipate heat from the circuit. This is especially important for high-power circuits.
5. Manufacturing constraints: The trace width and spacing also need to be considered in the manufacturing process. If the traces are too close together, it can be challenging to etch and inspect the PCB, leading to manufacturing defects.
In summary, the trace width and spacing are critical parameters that need to be carefully considered in PCB design to ensure proper functioning and reliability of the circuit.
3.How does component placement affect signal integrity in a PCB design?
We pay attention to the transformation of intellectual property protection and innovation achievements. Your OEM or ODM order design we have a complete confidentiality system.
Component placement plays a crucial role in determining the signal integrity of a PCB design. The placement of components affects the routing of traces, which in turn affects the impedance, crosstalk, and signal integrity of the PCB.
1. Impedance: The placement of components affects the impedance of the traces. If components are placed too far apart, the traces will be longer, resulting in higher impedance. This can lead to signal reflections and degradation of the signal.
2. Crosstalk: Crosstalk is the interference between two traces on a PCB. The placement of components can affect the distance between traces, which can increase or decrease crosstalk. If components are placed too close together, the crosstalk between traces can increase, leading to signal distortion.
3. Signal routing: The placement of components also affects the routing of traces. If components are placed in a way that requires traces to make sharp turns or cross over each other, it can result in signal degradation. This can be avoided by carefully placing components in a way that allows for smooth and direct routing of traces.
4. Grounding: Proper grounding is essential for maintaining signal integrity. The placement of components can affect the grounding scheme of the PCB. If components are placed too far from the ground plane, it can result in a longer return path for signals, leading to ground bounce and noise.
5. Thermal considerations: The placement of components can also affect the thermal performance of the PCB. If components that generate a lot of heat are placed too close together, it can result in hot spots and affect the performance of the PCB.
To ensure good signal integrity, it is important to carefully consider the placement of components during the PCB design process. Components should be placed in a way that minimizes trace length, reduces crosstalk, allows for direct routing of traces, and ensures proper grounding and thermal management.
4.What makes a PCB resistant to environmental factors such as moisture and temperature?
We should perform well in market competition, and the prices of 10 layer pcb fabrication products have a great competitive advantage.
1. Material Selection: The choice of materials used in the PCB can greatly affect its resistance to environmental factors. Materials such as FR-4, polyimide, and ceramic are known for their high resistance to moisture and temperature.
2. Conformal Coating: Applying a conformal coating to the PCB can provide an additional layer of protection against moisture and temperature. This coating acts as a barrier between the PCB and the environment, preventing any moisture or contaminants from reaching the components.
3. Solder Mask: The solder mask used on the PCB can also play a role in its resistance to environmental factors. A high-quality solder mask can provide a protective layer against moisture and temperature, preventing any damage to the components.
4. Component Placement: Proper placement of components on the PCB can also contribute to its resistance to environmental factors. Components that are sensitive to moisture or temperature should be placed away from areas that are prone to these factors, such as near heat sources or in areas with high humidity.
5. Thermal Management: Adequate thermal management is crucial for maintaining the temperature of the PCB within safe limits. This can be achieved through the use of heat sinks, thermal vias, and proper ventilation.
6. Design Considerations: The design of the PCB can also impact its resistance to environmental factors. Factors such as trace width, spacing, and routing can affect the PCB’s ability to withstand temperature changes and moisture exposure.
7. Testing and Quality Control: Proper testing and quality control measures can ensure that the PCB is built to withstand environmental factors. This includes testing for moisture resistance, thermal cycling, and other environmental stressors.
8. Compliance with Standards: Following industry standards and regulations for PCB design and manufacturing can also contribute to its resistance to environmental factors. These standards often include guidelines for material selection, component placement, and testing procedures.

5.Can PCBs have multiple power planes?
We maintain a stable growth through reasonable capital operations, focus on industry development trends and cutting -edge technologies, and focus on product quality and safety performance.
Yes, PCBs can have multiple power planes. Power planes are layers of copper on a PCB that are used to distribute power and ground signals throughout the board. Multiple power planes can be used to provide different voltages or to separate sensitive analog signals from noisy digital signals. They can also be used to increase the current carrying capacity of the board. The number and arrangement of power planes on a PCB will depend on the specific design requirements and can vary greatly.
6.What is the minimum distance required between components on a PCB?
We have advanced production equipment and technology to meet the needs of customers, and can provide customers with high quality, low priced 10 layer pcb fabrication products.
The minimum distance required between components on a PCB depends on various factors such as the type of components, their size, and the manufacturing process used. Generally, the minimum distance between components is determined by the manufacturer’s design rules and guidelines.
For surface mount components, the minimum distance between components is typically 0.2mm to 0.3mm. This distance is necessary to ensure that the solder paste does not bridge between the pads during the reflow process.
For through-hole components, the minimum distance between components is typically 1mm to 2mm. This distance is necessary to ensure that the components do not interfere with each other during the assembly process.
In high-speed and high-frequency applications, the minimum distance between components may need to be increased to avoid signal interference and crosstalk. In these cases, the manufacturer’s design rules and guidelines should be followed closely.
Overall, the minimum distance between components on a PCB should be determined based on the specific requirements of the design and the capabilities of the manufacturing process.
7.How do surface mount components differ from through-hole components in a PCB?
We pay attention to user experience and product quality, and provide the best product quality and lowest production cost for cooperative customers.
Surface mount components (SMD) and through-hole components (THD) are two different types of electronic components used in printed circuit boards (PCBs). The main difference between them lies in their method of mounting onto the PCB.
1. Mounting Method:
The main difference between SMD and THD components is their mounting method. SMD components are mounted directly onto the surface of the PCB, while THD components are inserted into holes drilled into the PCB and soldered on the other side.
2. Size:
SMD components are generally smaller in size compared to THD components. This is because SMD components do not require leads or pins for mounting, allowing for a more compact design. THD components, on the other hand, have leads or pins that need to be inserted into the PCB, making them larger in size.
3. Space Efficiency:
Due to their smaller size, SMD components allow for a more space-efficient design on the PCB. This is especially important in modern electronic devices where space is limited. THD components take up more space on the PCB due to their larger size and the need for holes to be drilled.
4. Cost:
SMD components are generally more expensive than THD components. This is because SMD components require more advanced manufacturing techniques and equipment, making them costlier to produce.
5. Assembly Process:
The assembly process for SMD components is automated, using pick-and-place machines to accurately place the components onto the PCB. This makes the process faster and more efficient compared to THD components, which require manual insertion and soldering.
6. Electrical Performance:
SMD components have better electrical performance compared to THD components. This is because SMD components have shorter leads, resulting in less parasitic capacitance and inductance, leading to better signal integrity.
In summary, SMD components offer a more compact design, better electrical performance, and a faster assembly process, but at a higher cost. THD components, on the other hand, are larger in size, less expensive, and can handle higher power and voltage ratings. The choice between SMD and THD components depends on the specific requirements of the PCB design and the intended use of the electronic device.
Tags:rigid flex electronic pcba , 3018 cnc pcb , 2.4g pcb antenna