12 layer pcb
MTI is a high-tech company specializing in PCB manufacturing, PCB assembly and parts procurement services with more than 20 years of experience. We are committed to producing various types of printed circuit boards, mainly including single-sided, double-sided, multi-layer circuit boards, high-precision HDI, flexible boards (FPC), rigid-flex boards (including HDI), metal circuit boards and their SMD plugin.Product line application areas include:communications.Fast response, strict quality control, best service, and strong technical support export our PCB products to global markets,including,Finland,Colombia,Wake Island,Ghana,Antigua and Barbuda.
MTI would like to build long and stable business relationship with the customers from all over the world on the basis of mutual benefits and mutual progress;Choose MTI , Drive you Success!
| Product name | 12 layer pcb |
| Keyword | 2.4ghz pcb antenna,104 key keyboard pcb,100 pcb keyboard,30 layer pcb,120 mm pcb |
| Place of Origin | China |
| Board Thickness | 2~3.2mm |
| Applicable Industries | automotive electronics , etc. |
| Service | OEM/ODM manufacturing |
| Certificate | ISO-9001:2015, ISO-14001:2015,ISO-13485:2012.UL/CSA |
| Solder Mask Color | Green |
| Advantage | We keep good quality and competitive price to ensure our customers benefit |
| Sales country | All over the world for example:Finland,Colombia,Wake Island,Ghana,Antigua and Barbuda |
Your deliverables are always ahead of schedule and of the highest quality.
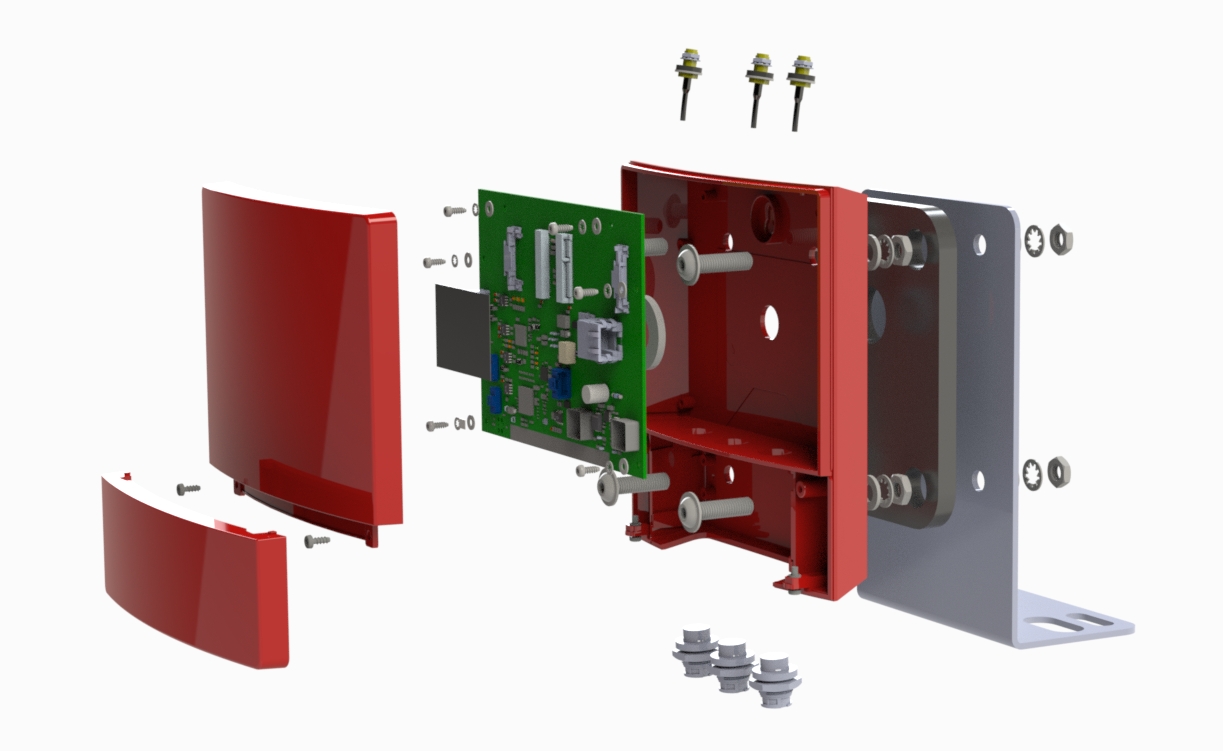
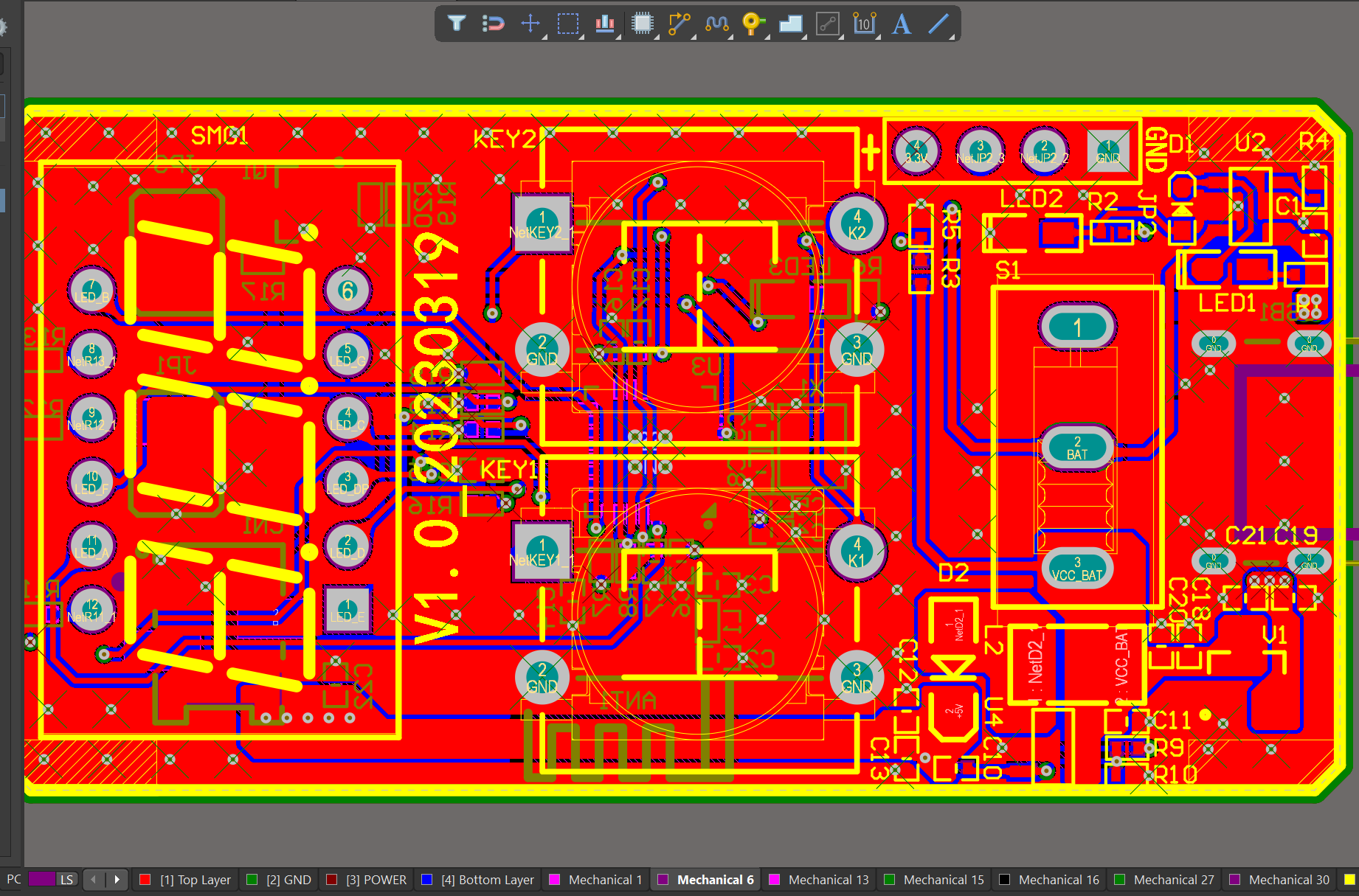
We have rich experience engineer to create a layout using a software platform like Altium Designer. This layout shows you the exact appearance and placement of the components on your board.
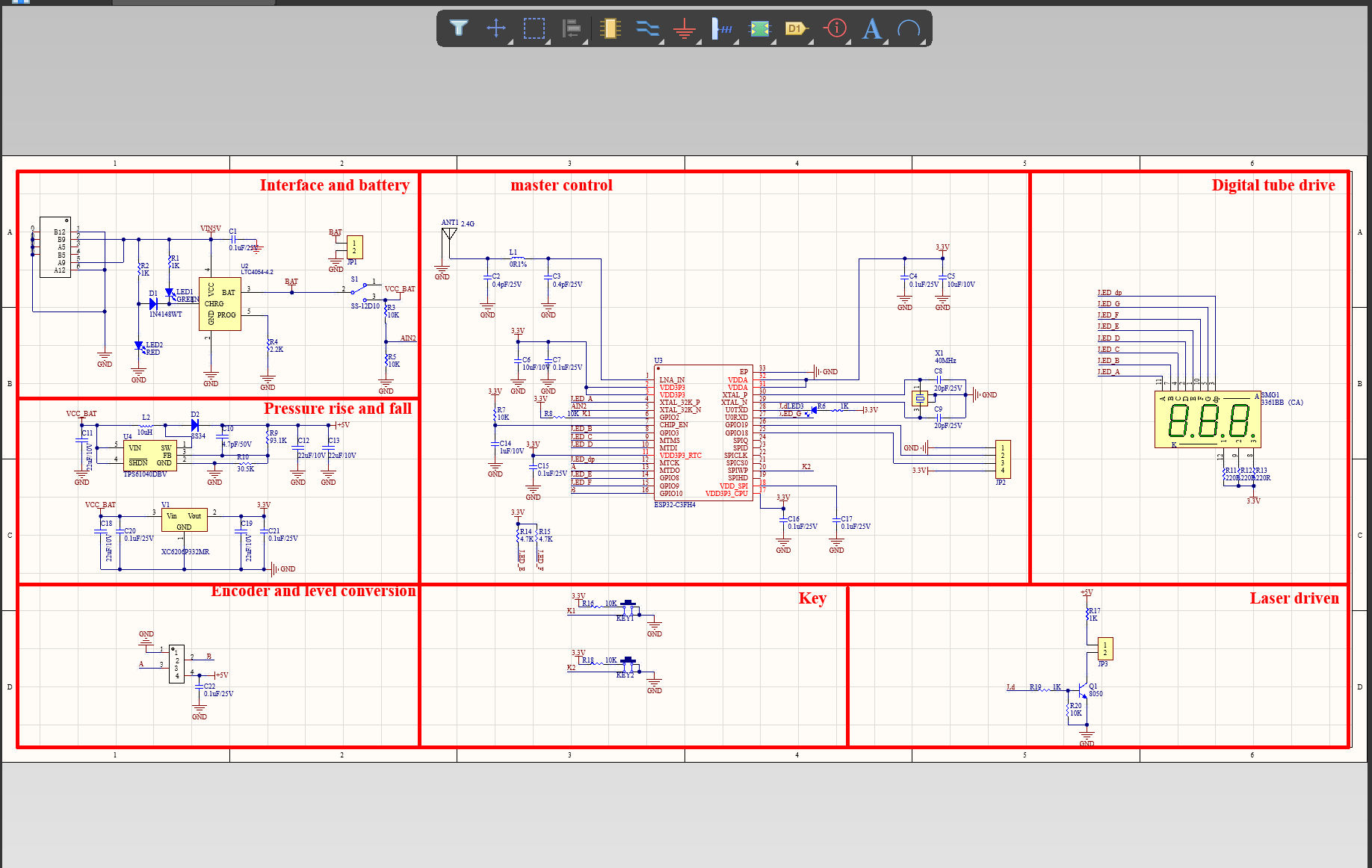
One of our Hardware Design Services is small-batch manufacturing, which allows you to test your idea quickly and verify the functionality of the hardware design and PCB board.
FAQs Guide
2.What is the minimum distance required between components on a PCB?
3.How does the type of laminate material used impact the PCB design?
4.How do surface mount components differ from through-hole components in a PCB?
5.How does the type of PCB connection (wired or wireless) impact its design and features?
6.What is the difference between single-sided and double-sided PCBs?
7.What are the key features of a PCB?
8.Can PCBs be made with different thicknesses?
1.Can a PCB have different levels of flexibility?
We have a wide range of 12 layer pcb customer groups and establishes long -term cooperative relationships with partners.
Yes, a PCB (printed circuit board) can have different levels of flexibility depending on its design and materials used. Some PCBs are rigid and cannot bend or flex at all, while others are designed to be flexible and can bend or twist to a certain degree. There are also PCBs that have a combination of rigid and flexible areas, known as flex-rigid PCBs. The level of flexibility in a PCB is determined by factors such as the type of substrate material, the thickness and number of layers, and the type of circuit design.
2.What is the minimum distance required between components on a PCB?
We have advanced production equipment and technology to meet the needs of customers, and can provide customers with high quality, low priced 12 layer pcb products.
The minimum distance required between components on a PCB depends on various factors such as the type of components, their size, and the manufacturing process used. Generally, the minimum distance between components is determined by the manufacturer’s design rules and guidelines.
For surface mount components, the minimum distance between components is typically 0.2mm to 0.3mm. This distance is necessary to ensure that the solder paste does not bridge between the pads during the reflow process.
For through-hole components, the minimum distance between components is typically 1mm to 2mm. This distance is necessary to ensure that the components do not interfere with each other during the assembly process.
In high-speed and high-frequency applications, the minimum distance between components may need to be increased to avoid signal interference and crosstalk. In these cases, the manufacturer’s design rules and guidelines should be followed closely.
Overall, the minimum distance between components on a PCB should be determined based on the specific requirements of the design and the capabilities of the manufacturing process.
3.How does the type of laminate material used impact the PCB design?
As one of the top 12 layer pcb manufacturers in China, we take this very seriously.
The type of laminate material used can impact the PCB design in several ways:
1. Electrical properties: Different laminate materials have different electrical properties, such as dielectric constant, loss tangent, and insulation resistance. These properties can affect the signal integrity and impedance of the PCB, which can impact the performance of the circuit.
2. Thermal properties: Some laminate materials have better thermal conductivity than others, which can affect the heat dissipation of the PCB. This is especially important for high-power applications where heat management is crucial.
3. Mechanical properties: The mechanical properties of the laminate material, such as stiffness and flexibility, can impact the overall durability and reliability of the PCB. This is important for applications where the PCB may be subjected to physical stress or vibration.
4. Cost: Different laminate materials have different costs, which can impact the overall cost of the PCB. Some materials may be more expensive but offer better performance, while others may be more cost-effective but have lower performance.
5. Manufacturing process: The type of laminate material used can also impact the manufacturing process of the PCB. Some materials may require specialized equipment or processes, which can affect the production time and cost.
6. Compatibility with components: Certain laminate materials may not be compatible with certain components, such as high-frequency components or components that require specific soldering temperatures. This can limit the design options and affect the functionality of the PCB.
Overall, the type of laminate material used can significantly impact the design, performance, and cost of a PCB. It is important to carefully consider the requirements of the circuit and choose a suitable laminate material to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
4.How do surface mount components differ from through-hole components in a PCB?
We pay attention to user experience and product quality, and provide the best product quality and lowest production cost for cooperative customers.
Surface mount components (SMD) and through-hole components (THD) are two different types of electronic components used in printed circuit boards (PCBs). The main difference between them lies in their method of mounting onto the PCB.
1. Mounting Method:
The main difference between SMD and THD components is their mounting method. SMD components are mounted directly onto the surface of the PCB, while THD components are inserted into holes drilled into the PCB and soldered on the other side.
2. Size:
SMD components are generally smaller in size compared to THD components. This is because SMD components do not require leads or pins for mounting, allowing for a more compact design. THD components, on the other hand, have leads or pins that need to be inserted into the PCB, making them larger in size.
3. Space Efficiency:
Due to their smaller size, SMD components allow for a more space-efficient design on the PCB. This is especially important in modern electronic devices where space is limited. THD components take up more space on the PCB due to their larger size and the need for holes to be drilled.
4. Cost:
SMD components are generally more expensive than THD components. This is because SMD components require more advanced manufacturing techniques and equipment, making them costlier to produce.
5. Assembly Process:
The assembly process for SMD components is automated, using pick-and-place machines to accurately place the components onto the PCB. This makes the process faster and more efficient compared to THD components, which require manual insertion and soldering.
6. Electrical Performance:
SMD components have better electrical performance compared to THD components. This is because SMD components have shorter leads, resulting in less parasitic capacitance and inductance, leading to better signal integrity.
In summary, SMD components offer a more compact design, better electrical performance, and a faster assembly process, but at a higher cost. THD components, on the other hand, are larger in size, less expensive, and can handle higher power and voltage ratings. The choice between SMD and THD components depends on the specific requirements of the PCB design and the intended use of the electronic device.
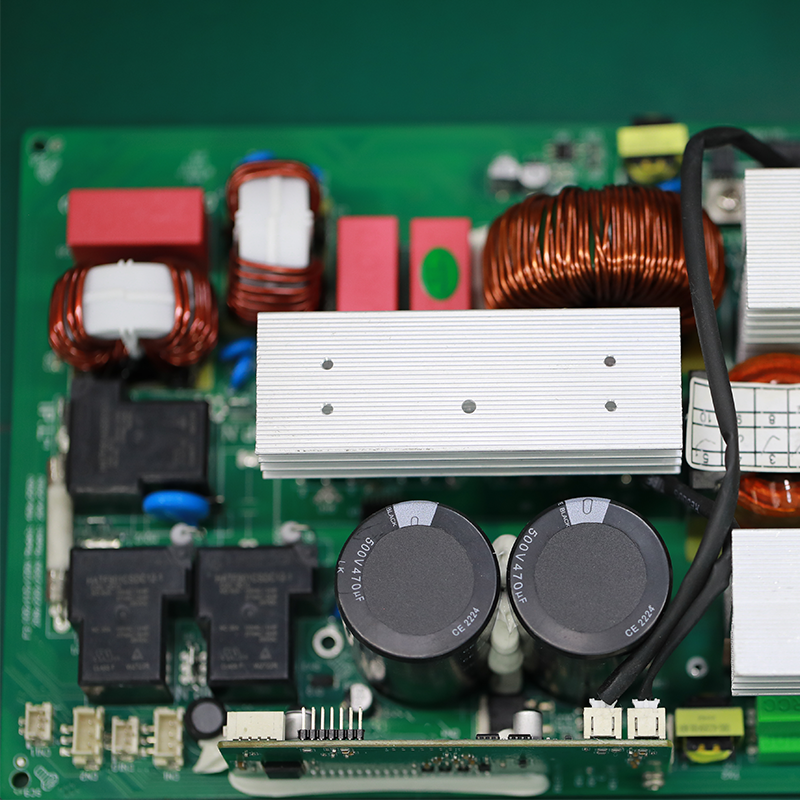
5.How does the type of PCB connection (wired or wireless) impact its design and features?
Our products & services cover a wide range of areas and meet the needs of different fields.
The type of PCB connection, whether wired or wireless, can have a significant impact on the design and features of the PCB. Some of the key ways in which the type of connection can impact the PCB design and features are:
1. Size and form factor: Wired PCBs typically require physical connectors and cables, which can add to the overall size and form factor of the PCB. On the other hand, wireless PCBs do not require physical connectors and cables, allowing for a smaller and more compact design.
2. Power consumption: Wired PCBs require a constant supply of power to function, whereas wireless PCBs can operate on battery power. This can impact the power consumption and battery life of the device, which in turn can affect the overall design and features of the PCB.
3. Flexibility and mobility: Wireless PCBs offer greater flexibility and mobility as they do not have physical connections that restrict movement. This can be advantageous in applications where the device needs to be moved or used in different locations.
4. Data transfer speed: Wired PCBs typically have faster data transfer speeds compared to wireless PCBs. This can impact the design and features of the PCB, as certain applications may require high-speed data transfer.
5. Cost: The type of connection can also impact the cost of the PCB. Wired PCBs may require additional components such as connectors and cables, which can add to the overall cost. Wireless PCBs, on the other hand, may require more advanced technology and components, making them more expensive.
6. Reliability: Wired PCBs are generally considered more reliable as they have a physical connection, which is less prone to interference or signal loss. Wireless PCBs, on the other hand, may be more susceptible to interference and signal loss, which can impact their reliability.
Overall, the type of PCB connection can significantly impact the design and features of the PCB, and it is important to carefully consider the specific requirements of the application when choosing between wired and wireless connections.
6.What is the difference between single-sided and double-sided PCBs?
Our mission is to provide customers with the best solutions for 12 layer pcb.
Single-sided PCBs have copper traces and components on only one side of the board, while double-sided PCBs have copper traces and components on both sides of the board. This allows for more complex circuit designs and a higher density of components on a double-sided PCB. Single-sided PCBs are typically used for simpler circuits and are less expensive to manufacture, while double-sided PCBs are used for more complex circuits and are more expensive to manufacture.
7.What are the key features of a PCB?
We are committed to providing personalized solutions and established long -term strategic cooperative relationships with customers.
1. Substrate: The base material on which the circuit is printed, usually made of fiberglass or composite epoxy.
2. Conductive Traces: Thin copper lines that connect the components on the PCB.
3. Pads: Small copper areas on the PCB surface where components are soldered.
4. Vias: Holes drilled through the PCB to connect the different layers of the circuit.
5. Solder Mask: A layer of protective material that covers the copper traces and pads, preventing accidental short circuits.
6. Silkscreen: A layer of ink that is printed on the PCB to label the components and provide other useful information.
7. Components: Electronic devices such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits that are mounted on the PCB.
8. Mounting Holes: Holes drilled on the PCB to allow it to be securely attached to a larger device or enclosure.
9. Copper Pour: Large areas of copper that are used to provide a common ground or power plane for the circuit.
10. Edge Connectors: Metal contacts on the edge of the PCB that allow it to be connected to other circuits or devices.
11. Solder Bridges: Small areas of exposed copper that allow for the connection of two or more traces.
12. Test Points: Small pads or holes on the PCB that allow for testing and troubleshooting of the circuit.
13. Silkscreen Legend: Printed text or symbols on the silkscreen layer that provide additional information about the PCB and its components.
14. Designators: Letters or numbers printed on the silkscreen layer to identify specific components on the PCB.
15. Reference Designators: A combination of letters and numbers that identify the location of a component on the PCB according to the schematic diagram.
8.Can PCBs be made with different thicknesses?
We operate our 12 layer pcb business with integrity and honesty.
Yes, PCBs (printed circuit boards) can be made with different thicknesses. The thickness of a 12 layer pcb is determined by the thickness of the copper layer and the thickness of the substrate material. The copper layer thickness can range from 0.5 oz to 3 oz, while the substrate material thickness can range from 0.2 mm to 3.2 mm. The most common thicknesses for PCBs are 1.6 mm and 0.8 mm, but custom thicknesses can be requested from PCB manufacturers. The thickness of a PCB can affect its mechanical strength, thermal properties, and electrical performance.

Tags:2.4 ghz pcb antenna design,100 mechanical keyboard pcb,3080 fe pcb



