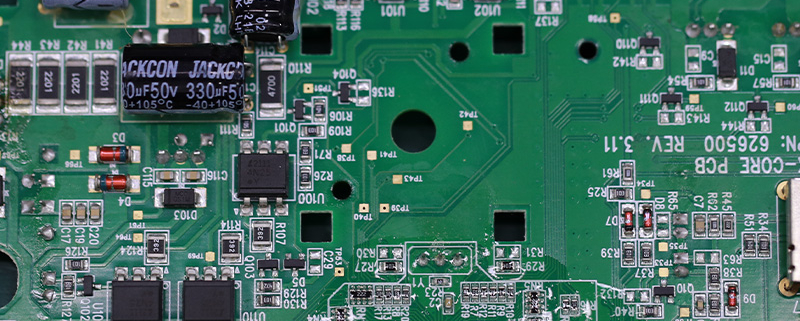
Fast turn printed circuit board assembly
MTI is a manufacturer of high-precision printed circuit board (PCB).We specialize in the manufacture of high precision double-sided and multilayer printed circuit boards, We provide high quality products and faster service for high-tech companies.
We have a group of experienced staff and high-quality management team, set up a complete quality assurance system. Products include FR-4 PCB, Metal PCB and RFPCB (ceramic PCB, PTFE PCB), etc. Have rich experience in the production of thick copper PCB, RF PCB, high Tg PCB, HDI PCB,Fast turn printed circuit board assembly.With ISO9001, ISO14001, TS16949, ISO 13485, RoHS certifications.
| Product name | fast turn printed circuit board assembly |
| Keyword | 1080 pcb,printed circuits assembly corp,16 layer pcb manufacturer,prototype circuit board assembly,pcb manufacturers |
| Place of Origin | China |
| Board Thickness | 2~3.2mm |
| Applicable Industries | new energy, etc. |
| Service | OEM/ODM manufacturing |
| Certificate | ISO-9001:2015, ISO-14001:2015,ISO-13485:2012.UL/CSA |
| Solder Mask Color | Red |
| Advantage | We keep good quality and competitive price to ensure our customers benefit |
| Sales country | All over the world for example:Sweden,United Arab Emirates,Bosnia and Herzegovina,Saint Kitts and Nevis,Cyprus,Navassa Island,Mali,Malawi,Zambia |
We have rich experience engineer to create a layout using a software platform like Altium Designer. This layout shows you the exact appearance and placement of the components on your board.
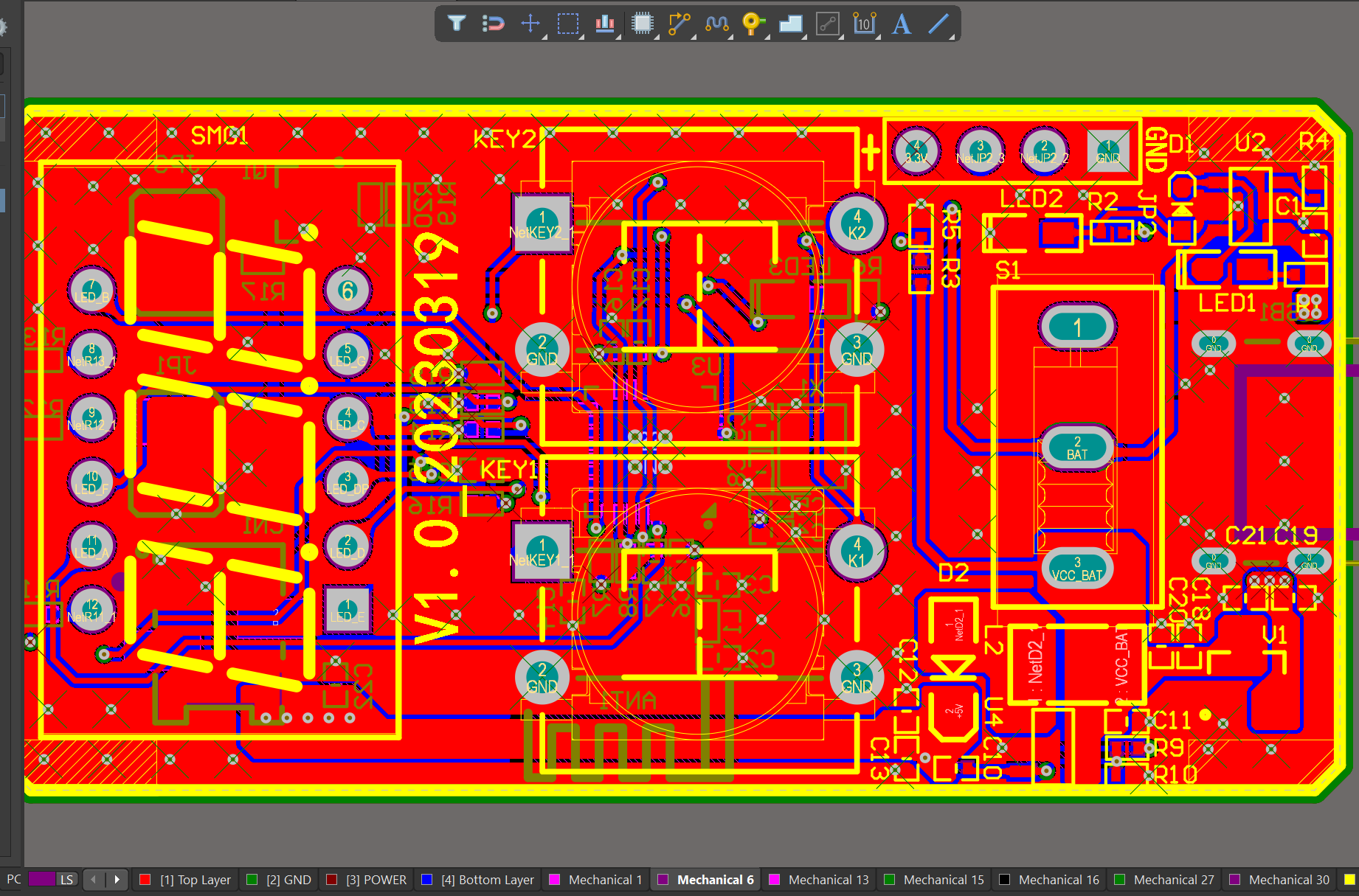
Your deliverables are always ahead of schedule and of the highest quality.
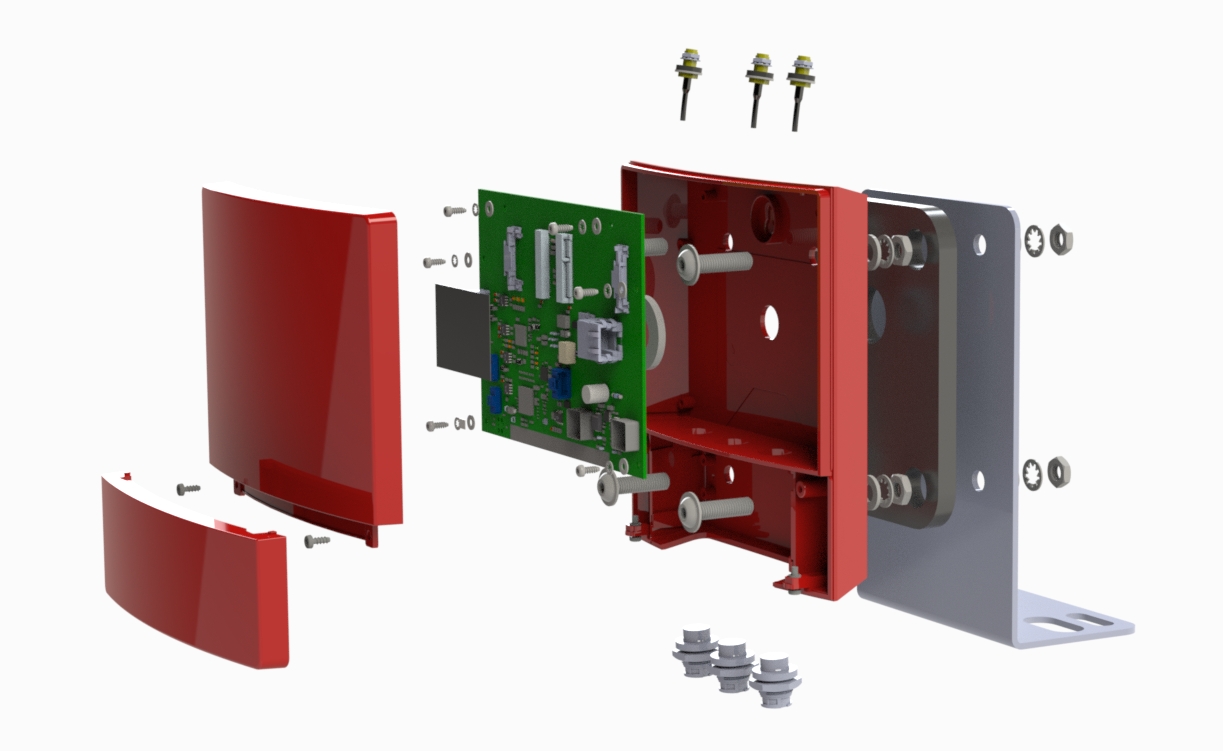
One of our Hardware Design Services is small-batch manufacturing, which allows you to test your idea quickly and verify the functionality of the hardware design and PCB board.
FAQs Guide
2.What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a rigid or flexible PCB?
3.What are the factors to consider when choosing the right PCB material for a specific application?
4.Can PCBs be made with different thicknesses?
5.What is impedance control and why is it important in PCBs?
6.How important is the trace width and spacing in a PCB design?
7.How does component placement affect signal integrity in a PCB design?
1.How does the number of layers in a PCB affect its functionality?
We should have a stable supply chain and logistics capabilities, and provide customers with high -quality, low -priced fast turn printed circuit board assembly products.
The number of layers in a PCB (Printed Circuit Board) can affect its functionality in several ways:
1. Complexity: The number of layers in a PCB determines the complexity of the circuit design that can be implemented. More layers allow for more components and connections to be included in the design, making it more complex and versatile.
2. Size: A PCB with more layers can be smaller in size compared to a PCB with fewer layers, as it allows for a more compact layout of components and connections. This is especially important in devices with limited space, such as smartphones and wearables.
3. Signal Integrity: The number of layers in a PCB can also affect the signal integrity of the circuit. More layers allow for better routing of signals, reducing the chances of interference and crosstalk between different components.
4. Power Distribution: PCBs with more layers can have dedicated power and ground planes, which help in distributing power evenly across the circuit. This improves the overall performance and stability of the circuit.
5. Cost: The number of layers in a PCB can also affect its cost. More layers mean more materials and manufacturing processes, which can increase the overall cost of the PCB.
6. Thermal Management: PCBs with more layers can have better thermal management, as they allow for the placement of thermal vias and heat sinks to dissipate heat more efficiently. This is important for high-power applications that generate a lot of heat.
In summary, the number of layers in a PCB can significantly impact its functionality, complexity, size, signal integrity, power distribution, cost, and thermal management. Designers must carefully consider the number of layers required for a PCB based on the specific requirements of the circuit and the device it will be used in.
2.What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a rigid or flexible PCB?
We have the leading technology and innovation capabilities, and attach importance to employee training and development, and provide promotion opportunities.
Advantages of rigid PCB:
1. Durability: Rigid PCBs are more durable and can withstand higher levels of stress and strain compared to flexible PCBs.
2. Better for high-speed applications: Rigid PCBs are better suited for high-speed applications as they have better signal integrity and lower signal loss.
3. Cost-effective: Rigid PCBs are generally less expensive to manufacture compared to flexible PCBs.
4. Easier to assemble: Rigid PCBs are easier to assemble and can be used with automated assembly processes, making them more efficient for mass production.
5. Higher component density: Rigid PCBs can accommodate a higher number of components and have a higher component density compared to flexible PCBs.
Disadvantages of rigid PCB:
1. Limited flexibility: Rigid PCBs are not flexible and cannot be bent or twisted, making them unsuitable for certain applications.
2. Bulkier: Rigid PCBs are bulkier and take up more space compared to flexible PCBs, which can be a disadvantage in compact electronic devices.
3. Prone to damage: Rigid PCBs are more prone to damage from vibrations and shocks, which can affect their performance.
Advantages of flexible PCB:
1. Flexibility: Flexible PCBs can be bent, twisted, and folded, making them suitable for applications where space is limited or where the PCB needs to conform to a specific shape.
2. Lightweight: Flexible PCBs are lightweight and take up less space compared to rigid PCBs, making them ideal for portable electronic devices.
3. Better for high vibration environments: Flexible PCBs are more resistant to vibrations and shocks, making them suitable for use in high vibration environments.
4. Higher reliability: Flexible PCBs have fewer interconnects and solder joints, reducing the chances of failure and increasing reliability.
Disadvantages of flexible PCB:
1. Higher cost: Flexible PCBs are generally more expensive to manufacture compared to rigid PCBs.
2. Limited component density: Flexible PCBs have a lower component density compared to rigid PCBs, which can limit their use in high-density applications.
3. Difficult to repair: Flexible PCBs are more difficult to repair compared to rigid PCBs, as they require specialized equipment and expertise.
4. Less suitable for high-speed applications: Flexible PCBs have higher signal loss and lower signal integrity compared to rigid PCBs, making them less suitable for high-speed applications.
3.What are the factors to consider when choosing the right PCB material for a specific application?
We are centered on customers and always pay attention to customers’ needs for fast turn printed circuit board assembly products.
1. Electrical properties: The electrical properties of the PCB material, such as dielectric constant, loss tangent, and insulation resistance, should be carefully considered to ensure optimal performance for the specific application.
2. Thermal properties: The thermal conductivity and coefficient of thermal expansion of the PCB material are important factors to consider, especially for applications that require high power or operate in extreme temperatures.
3. Mechanical properties: The mechanical strength, stiffness, and flexibility of the PCB material should be evaluated to ensure it can withstand the physical stresses and strains of the application.
4. Chemical resistance: The PCB material should be resistant to any chemicals or solvents that it may come into contact with during its use.
5. Cost: The cost of the PCB material should be considered, as it can vary significantly depending on the type and quality of the material.
6. Availability: Some PCB materials may be more readily available than others, which can affect production timelines and costs.
7. Manufacturing process: The chosen PCB material should be compatible with the manufacturing process, such as etching, drilling, and plating, to ensure efficient and reliable production.
8. Environmental factors: The application environment, such as humidity, moisture, and exposure to UV light, should be taken into account when selecting a PCB material to ensure it can withstand these conditions.
9. Signal integrity: For high-frequency applications, the PCB material should have low signal loss and good signal integrity to prevent interference and ensure accurate signal transmission.
10. RoHS compliance: If the application requires compliance with environmental regulations, such as the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive, the PCB material should be chosen accordingly.
4.Can PCBs be made with different thicknesses?
We operate our fast turn printed circuit board assembly business with integrity and honesty.
Yes, PCBs (printed circuit boards) can be made with different thicknesses. The thickness of a PCB is determined by the thickness of the copper layer and the thickness of the substrate material. The copper layer thickness can range from 0.5 oz to 3 oz, while the substrate material thickness can range from 0.2 mm to 3.2 mm. The most common thicknesses for PCBs are 1.6 mm and 0.8 mm, but custom thicknesses can be requested from PCB manufacturers. The thickness of a PCB can affect its mechanical strength, thermal properties, and electrical performance.
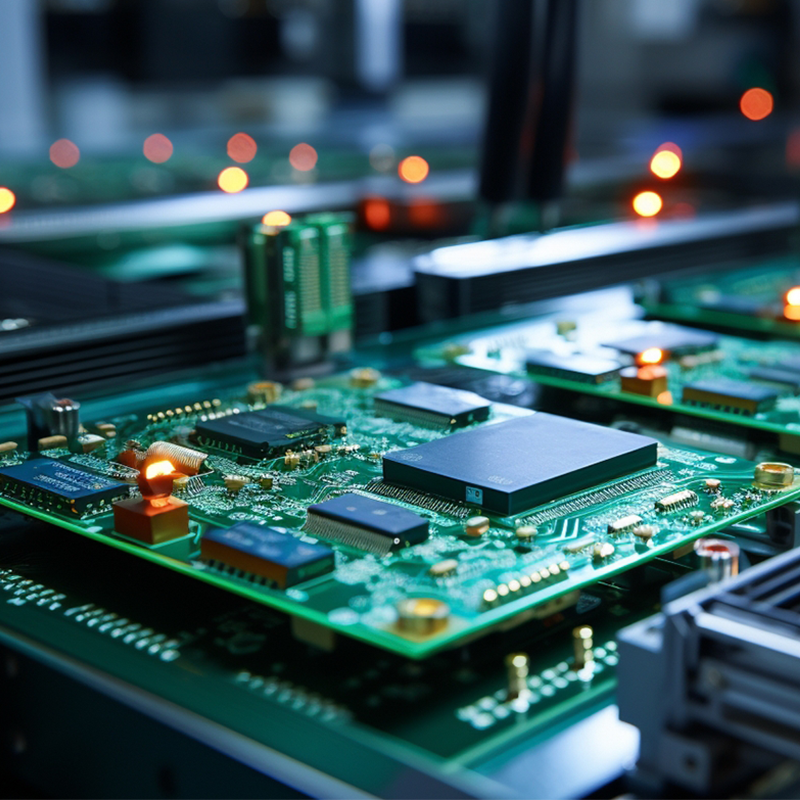
5.What is impedance control and why is it important in PCBs?
We enjoy high authority and influence in the industry and continue to innovate products and service models.
Impedance control is the ability to maintain a consistent electrical impedance throughout a printed circuit board (PCB). It is important in PCBs because it ensures that signals can travel through the board without distortion or loss of quality.
Impedance control is particularly important in high-speed digital and analog circuits, where even small variations in impedance can cause signal reflections and distortions. This can lead to errors in data transmission and affect the overall performance of the circuit.
In addition, impedance control is crucial in ensuring signal integrity and reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI). By maintaining a consistent impedance, the PCB can effectively filter out unwanted signals and prevent them from interfering with the desired signals.
Overall, impedance control is essential for achieving reliable and high-quality performance in PCBs, especially in complex and sensitive electronic systems. It requires careful design and manufacturing techniques, such as controlled trace widths and spacing, to achieve the desired impedance levels.
6.How important is the trace width and spacing in a PCB design?
Our fast turn printed circuit board assembly products have competitive and differentiated advantages, and actively promote digital transformation and innovation.
The trace width and spacing in a PCB design are crucial factors that can greatly affect the performance and reliability of the circuit. Here are some reasons why:
1. Current carrying capacity: The trace width determines the amount of current that can flow through the trace without causing excessive heating. If the trace width is too narrow, it can lead to overheating and damage to the circuit.
2. Voltage drop: The trace width also affects the voltage drop across the trace. A narrow trace will have a higher resistance, resulting in a higher voltage drop. This can cause a decrease in the voltage level at the end of the trace, affecting the performance of the circuit.
3. Signal integrity: The spacing between traces is critical for maintaining signal integrity. If the spacing is too narrow, it can lead to crosstalk and interference between signals, resulting in errors and malfunctions in the circuit.
4. Thermal management: The spacing between traces also plays a role in thermal management. Adequate spacing between traces allows for better air circulation, which helps dissipate heat from the circuit. This is especially important for high-power circuits.
5. Manufacturing constraints: The trace width and spacing also need to be considered in the manufacturing process. If the traces are too close together, it can be challenging to etch and inspect the PCB, leading to manufacturing defects.
In summary, the trace width and spacing are critical parameters that need to be carefully considered in PCB design to ensure proper functioning and reliability of the circuit.
7.How does component placement affect signal integrity in a PCB design?
We pay attention to the transformation of intellectual property protection and innovation achievements. Your OEM or ODM order design we have a complete confidentiality system.
Component placement plays a crucial role in determining the signal integrity of a PCB design. The placement of components affects the routing of traces, which in turn affects the impedance, crosstalk, and signal integrity of the PCB.
1. Impedance: The placement of components affects the impedance of the traces. If components are placed too far apart, the traces will be longer, resulting in higher impedance. This can lead to signal reflections and degradation of the signal.
2. Crosstalk: Crosstalk is the interference between two traces on a PCB. The placement of components can affect the distance between traces, which can increase or decrease crosstalk. If components are placed too close together, the crosstalk between traces can increase, leading to signal distortion.
3. Signal routing: The placement of components also affects the routing of traces. If components are placed in a way that requires traces to make sharp turns or cross over each other, it can result in signal degradation. This can be avoided by carefully placing components in a way that allows for smooth and direct routing of traces.
4. Grounding: Proper grounding is essential for maintaining signal integrity. The placement of components can affect the grounding scheme of the PCB. If components are placed too far from the ground plane, it can result in a longer return path for signals, leading to ground bounce and noise.
5. Thermal considerations: The placement of components can also affect the thermal performance of the PCB. If components that generate a lot of heat are placed too close together, it can result in hot spots and affect the performance of the PCB.
To ensure good signal integrity, it is important to carefully consider the placement of components during the PCB design process. Components should be placed in a way that minimizes trace length, reduces crosstalk, allows for direct routing of traces, and ensures proper grounding and thermal management.
Tags:pcb manufacturing and assembly,printed circuits assembly corporation