1.6mm pcb stackup
MTI specializes in turn-key electronics manufacturing manufacturing service, providing comprehensive solutions from product documentation to high-quality product delivery worldwide.
With a wide range, good quality, reasonable prices and stylish designs, our products are extensively used in security.Our products are widely recognized and trusted by users and can meet continuously changing economic and social needs.We welcome new and old customers from all walks of life to contact us for future business relationships and mutual success!
| Product name | 1.6mm pcb stackup |
| Keyword | pcb manufacturer,prototype printed circuit board assembly,12v pcb,100 pcb keyboard,100 mechanical keyboard pcb |
| Place of Origin | China |
| Board Thickness | 1~3.2mm |
| Applicable Industries | new energy, etc. |
| Service | OEM/ODM manufacturing |
| Certificate | ISO-9001:2015, ISO-14001:2015,ISO-13485:2012.UL/CSA |
| Solder Mask Color | Blue |
| Advantage | We keep good quality and competitive price to ensure our customers benefit |
| Sales country | All over the world for example:British Indian Ocean Territory,Mali,Seychelles,Dominican Republic,Georgia,Palau,Egypt,Comoros,Equatorial Guinea |
Your deliverables are always ahead of schedule and of the highest quality.
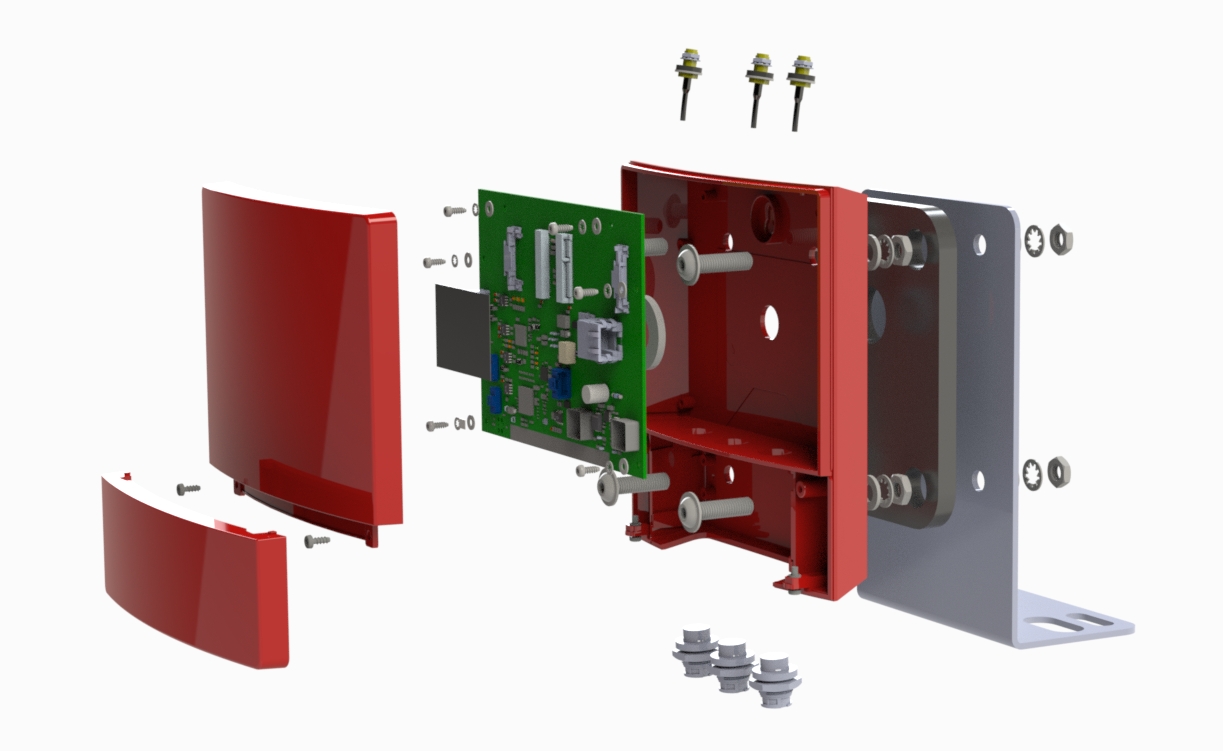
We have rich experience engineer to create a layout using a software platform like Altium Designer. This layout shows you the exact appearance and placement of the components on your board.
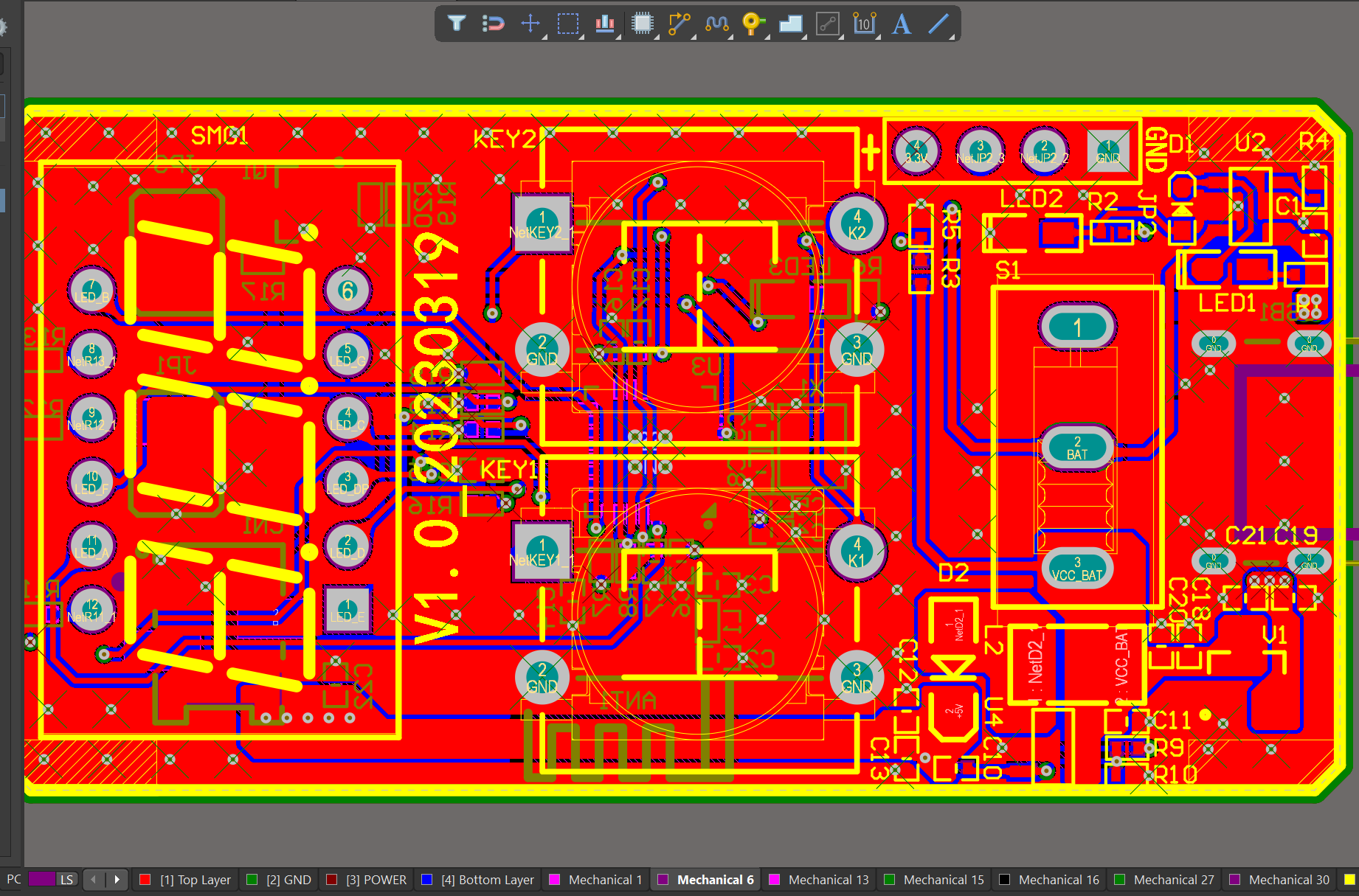
One of our Hardware Design Services is small-batch manufacturing, which allows you to test your idea quickly and verify the functionality of the hardware design and PCB board.
FAQs Guide
2.What are the differences between a prototype and production PCB?
3.How important is the trace width and spacing in a PCB design?
4.What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a rigid or flexible PCB?
5.How does the type of PCB finish affect its durability and lifespan?
6.How do PCBs support the integration of different electronic components?
7.What are the factors to consider when choosing the right PCB material for a specific application?
1.How does the hole size and shape impact the manufacturing process of a PCB?
We continue to invest in research and development and continue to launch innovative products.
The hole size and shape on a PCB can impact the manufacturing process in several ways:
1. Drilling process: The size and shape of the holes determine the type of drill bit and the drilling speed required for creating the holes. Smaller holes require smaller drill bits and slower drilling speeds, while larger holes require larger drill bits and faster drilling speeds. The shape of the hole can also affect the stability of the drill bit and the accuracy of the drilling process.
2. Plating process: After the holes are drilled, they need to be plated with a conductive material to create electrical connections between different layers of the PCB. The size and shape of the holes can affect the plating process, as larger or irregularly shaped holes may require more plating material and longer plating times.
3. Soldering process: The size and shape of the holes can also impact the soldering process. Smaller holes may require more precise placement of components and more careful soldering techniques, while larger holes may allow for easier soldering.
4. Component placement: The size and shape of the holes can also affect the placement of components on the PCB. Smaller holes may limit the size of components that can be used, while larger holes may allow for more flexibility in component placement.
5. PCB design: The size and shape of the holes can also impact the overall design of the PCB. Different hole sizes and shapes may require different routing and layout strategies, which can affect the overall functionality and performance of the PCB.
Overall, the size and shape of the holes on a PCB can significantly impact the manufacturing process and should be carefully considered during the design phase to ensure efficient and accurate production.
2.What are the differences between a prototype and production PCB?
We have a good reputation and image in the industry. The quality and price advantage of 1.6mm pcb stackup products is an important factor in our hard overseas market.
1. Purpose: The main difference between a prototype and production PCB is their purpose. A prototype PCB is used for testing and validation of a design, while a production PCB is used for mass production and commercial use.
2. Design: Prototype PCBs are usually hand-soldered and have a simpler design compared to production PCBs. Production PCBs are designed with more precision and complexity to meet the specific requirements of the final product.
3. Materials: Prototype PCBs are often made with cheaper materials such as FR-4, while production PCBs use higher quality materials such as ceramic or metal core for better performance and durability.
4. Quantity: Prototype PCBs are usually made in small quantities, while production PCBs are manufactured in large quantities to meet the demand of the market.
5. Cost: Due to the use of cheaper materials and smaller quantities, prototype PCBs are less expensive compared to production PCBs. Production PCBs require a larger investment due to the use of higher quality materials and larger quantities.
6. Lead time: Prototype PCBs have a shorter lead time as they are made in smaller quantities and can be hand-soldered. Production PCBs have a longer lead time as they require more complex manufacturing processes and larger quantities.
7. Testing: Prototype PCBs are extensively tested to ensure the design is functional and meets the required specifications. Production PCBs also undergo testing, but the focus is more on quality control and consistency in mass production.
8. Documentation: Prototype PCBs may not have detailed documentation as they are often hand-soldered and used for testing purposes. Production PCBs have detailed documentation to ensure consistency in manufacturing and for future reference.
9. Modifications: Prototype PCBs are easier to modify and make changes to, as they are not mass-produced. Production PCBs are more difficult to modify as any changes can affect the entire production process.
10. Reliability: Production PCBs are designed and manufactured to be more reliable and durable, as they will be used in the final product. Prototype PCBs may not have the same level of reliability as they are used for testing and may not undergo the same level of quality control.
3.How important is the trace width and spacing in a PCB design?
Our 1.6mm pcb stackup products have competitive and differentiated advantages, and actively promote digital transformation and innovation.
The trace width and spacing in a PCB design are crucial factors that can greatly affect the performance and reliability of the circuit. Here are some reasons why:
1. Current carrying capacity: The trace width determines the amount of current that can flow through the trace without causing excessive heating. If the trace width is too narrow, it can lead to overheating and damage to the circuit.
2. Voltage drop: The trace width also affects the voltage drop across the trace. A narrow trace will have a higher resistance, resulting in a higher voltage drop. This can cause a decrease in the voltage level at the end of the trace, affecting the performance of the circuit.
3. Signal integrity: The spacing between traces is critical for maintaining signal integrity. If the spacing is too narrow, it can lead to crosstalk and interference between signals, resulting in errors and malfunctions in the circuit.
4. Thermal management: The spacing between traces also plays a role in thermal management. Adequate spacing between traces allows for better air circulation, which helps dissipate heat from the circuit. This is especially important for high-power circuits.
5. Manufacturing constraints: The trace width and spacing also need to be considered in the manufacturing process. If the traces are too close together, it can be challenging to etch and inspect the PCB, leading to manufacturing defects.
In summary, the trace width and spacing are critical parameters that need to be carefully considered in PCB design to ensure proper functioning and reliability of the circuit.
4.What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a rigid or flexible PCB?
We have the leading technology and innovation capabilities, and attach importance to employee training and development, and provide promotion opportunities.
Advantages of rigid PCB:
1. Durability: Rigid PCBs are more durable and can withstand higher levels of stress and strain compared to flexible PCBs.
2. Better for high-speed applications: Rigid PCBs are better suited for high-speed applications as they have better signal integrity and lower signal loss.
3. Cost-effective: Rigid PCBs are generally less expensive to manufacture compared to flexible PCBs.
4. Easier to assemble: Rigid PCBs are easier to assemble and can be used with automated assembly processes, making them more efficient for mass production.
5. Higher component density: Rigid PCBs can accommodate a higher number of components and have a higher component density compared to flexible PCBs.
Disadvantages of rigid PCB:
1. Limited flexibility: Rigid PCBs are not flexible and cannot be bent or twisted, making them unsuitable for certain applications.
2. Bulkier: Rigid PCBs are bulkier and take up more space compared to flexible PCBs, which can be a disadvantage in compact electronic devices.
3. Prone to damage: Rigid PCBs are more prone to damage from vibrations and shocks, which can affect their performance.
Advantages of flexible PCB:
1. Flexibility: Flexible PCBs can be bent, twisted, and folded, making them suitable for applications where space is limited or where the PCB needs to conform to a specific shape.
2. Lightweight: Flexible PCBs are lightweight and take up less space compared to rigid PCBs, making them ideal for portable electronic devices.
3. Better for high vibration environments: Flexible PCBs are more resistant to vibrations and shocks, making them suitable for use in high vibration environments.
4. Higher reliability: Flexible PCBs have fewer interconnects and solder joints, reducing the chances of failure and increasing reliability.
Disadvantages of flexible PCB:
1. Higher cost: Flexible PCBs are generally more expensive to manufacture compared to rigid PCBs.
2. Limited component density: Flexible PCBs have a lower component density compared to rigid PCBs, which can limit their use in high-density applications.
3. Difficult to repair: Flexible PCBs are more difficult to repair compared to rigid PCBs, as they require specialized equipment and expertise.
4. Less suitable for high-speed applications: Flexible PCBs have higher signal loss and lower signal integrity compared to rigid PCBs, making them less suitable for high-speed applications.
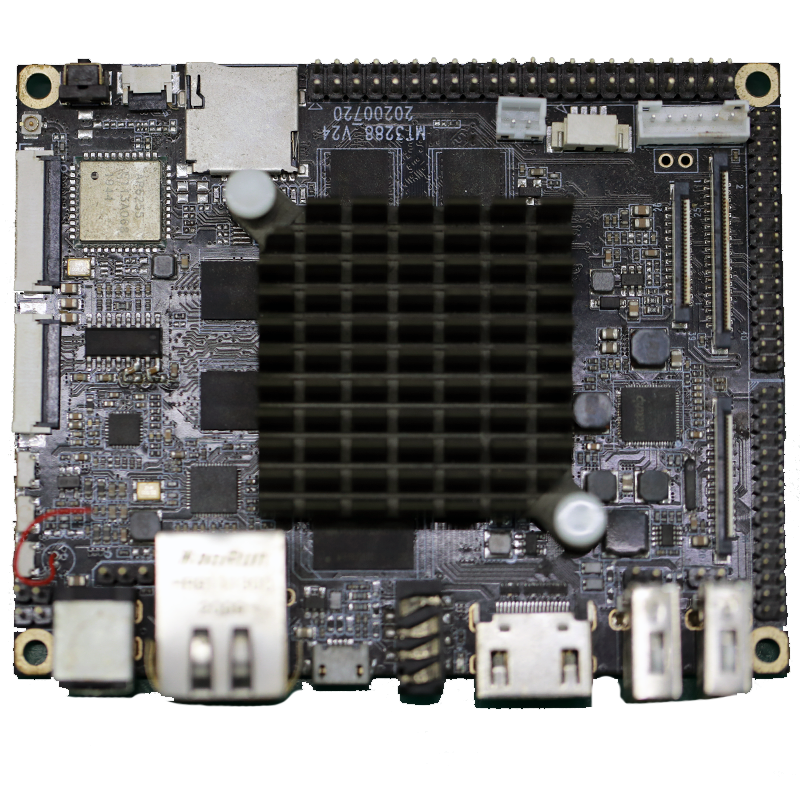
5.How does the type of PCB finish affect its durability and lifespan?
I have a comprehensive after -sales service system, which can pay attention to market trends in time and adjust our strategy in a timely manner.
The type of PCB finish can have a significant impact on the durability and lifespan of a PCB. The finish is the final coating applied to the surface of the PCB to protect it from environmental factors and ensure proper functionality. Some common types of PCB finishes include HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling), ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold), and OSP (Organic Solderability Preservative).
1. HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling):
HASL is a popular and cost-effective finish that involves coating the PCB with a layer of molten solder and then leveling it with hot air. This finish provides good solderability and is suitable for most applications. However, it is not very durable and can be prone to oxidation, which can affect the performance of the PCB over time. HASL finish also has a limited shelf life and may require rework after a certain period.
2. ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold):
ENIG is a more advanced and durable finish compared to HASL. It involves depositing a layer of nickel and then a layer of gold on the surface of the PCB. This finish provides excellent corrosion resistance and is suitable for high-reliability applications. ENIG finish also has a longer shelf life and does not require rework as frequently as HASL.
3. OSP (Organic Solderability Preservative):
OSP is a thin organic coating applied to the surface of the PCB to protect it from oxidation. It is a cost-effective finish and provides good solderability. However, OSP finish is not as durable as ENIG and may require rework after a certain period. It is also not suitable for high-temperature applications.
In summary, the type of PCB finish can affect its durability and lifespan in the following ways:
– Corrosion resistance: Finishes like ENIG and OSP provide better corrosion resistance compared to HASL, which can affect the performance and lifespan of the PCB.
– Shelf life: Finishes like ENIG have a longer shelf life compared to HASL, which may require rework after a certain period.
– Solderability: All finishes provide good solderability, but ENIG and OSP are more suitable for high-reliability applications.
– Environmental factors: The type of finish can also affect the PCB’s resistance to environmental factors like humidity, temperature, and chemicals, which can impact its durability and lifespan.
In conclusion, choosing the right type of PCB finish is crucial for ensuring the durability and longevity of the PCB. Factors such as the application, environmental conditions, and budget should be considered when selecting the appropriate finish for a PCB.
6.How do PCBs support the integration of different electronic components?
We actively participate in the 1.6mm pcb stackup industry associations and organization activities. The corporate social responsibility performed well, and the focus of brand building and promotion.
PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) are essential for the integration of different electronic components in electronic devices. They provide a platform for connecting and supporting the various components, allowing them to work together seamlessly. Here are some ways in which PCBs support the integration of different electronic components:
1. Electrical connections: PCBs have a network of copper traces that connect the different electronic components on the board. These traces act as conductors, allowing electricity to flow between the components and enabling them to communicate and work together.
2. Mounting surface: PCBs provide a stable and secure mounting surface for electronic components. The components are soldered onto the board, ensuring that they are firmly attached and will not move or become loose during operation.
3. Space-saving: PCBs are designed to be compact and space-saving, allowing for the integration of multiple components on a single board. This is especially useful in small electronic devices where space is limited.
4. Customization: PCBs can be customized to accommodate different types and sizes of electronic components. This allows for flexibility in design and the integration of a wide range of components, making it easier to create complex electronic devices.
5. Signal routing: PCBs have multiple layers, with each layer dedicated to a specific function. This allows for efficient routing of signals between components, reducing interference and ensuring that the components can communicate effectively.
6. Power distribution: PCBs have dedicated power planes that distribute power to the different components on the board. This ensures that each component receives the required amount of power, preventing damage and ensuring proper functioning.
7. Thermal management: PCBs also play a crucial role in managing the heat generated by electronic components. They have copper layers that act as heat sinks, dissipating heat and preventing the components from overheating.
In summary, PCBs provide a robust and efficient platform for integrating different electronic components. They enable the components to work together seamlessly, ensuring the proper functioning of electronic devices.
7.What are the factors to consider when choosing the right PCB material for a specific application?
We are centered on customers and always pay attention to customers’ needs for 1.6mm pcb stackup products.
1. Electrical properties: The electrical properties of the PCB material, such as dielectric constant, loss tangent, and insulation resistance, should be carefully considered to ensure optimal performance for the specific application.
2. Thermal properties: The thermal conductivity and coefficient of thermal expansion of the PCB material are important factors to consider, especially for applications that require high power or operate in extreme temperatures.
3. Mechanical properties: The mechanical strength, stiffness, and flexibility of the PCB material should be evaluated to ensure it can withstand the physical stresses and strains of the application.
4. Chemical resistance: The PCB material should be resistant to any chemicals or solvents that it may come into contact with during its use.
5. Cost: The cost of the PCB material should be considered, as it can vary significantly depending on the type and quality of the material.
6. Availability: Some PCB materials may be more readily available than others, which can affect production timelines and costs.
7. Manufacturing process: The chosen PCB material should be compatible with the manufacturing process, such as etching, drilling, and plating, to ensure efficient and reliable production.
8. Environmental factors: The application environment, such as humidity, moisture, and exposure to UV light, should be taken into account when selecting a PCB material to ensure it can withstand these conditions.
9. Signal integrity: For high-frequency applications, the PCB material should have low signal loss and good signal integrity to prevent interference and ensure accurate signal transmission.
10. RoHS compliance: If the application requires compliance with environmental regulations, such as the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive, the PCB material should be chosen accordingly.
Tags:12 volt pcb led,104 keyboard pcb,1 layer vs 2 layer pcb



