10 pin pcb connector
MTI is a professional manufacturer of PCB and PCBA , we supply one-stop service. The company’s main services include PCB production, PCB Assembly and electronic materials purchasing, SMT patch, circuit board welding, circuit board plug-in.
Our clientele spans across major continents (Asia,Europe,America)and encompasses various industries, including healthcare,telecommunications
| Product name | 10 pin pcb connector |
| Keyword | printed circuit board assembly manufacturer,10 pin pcb connector,2.4 ghz pcb antenna design,assembling circuit boards,1 pin pcb connector |
| Place of Origin | China |
| Board Thickness | 1~3.2mm |
| Applicable Industries | telecommunications, etc. |
| Service | OEM/ODM manufacturing |
| Certificate | ISO-9001:2015, ISO-14001:2015,ISO-13485:2012.UL/CSA |
| Solder Mask Color | Black |
| Advantage | We keep good quality and competitive price to ensure our customers benefit |
| Sales country | All over the world for example:Egypt,Navassa Island,Saint Pierre and Miquelon,Timor-Leste,Wake Island,Samoa,Dominican Republic,Mongolia,Anguilla |
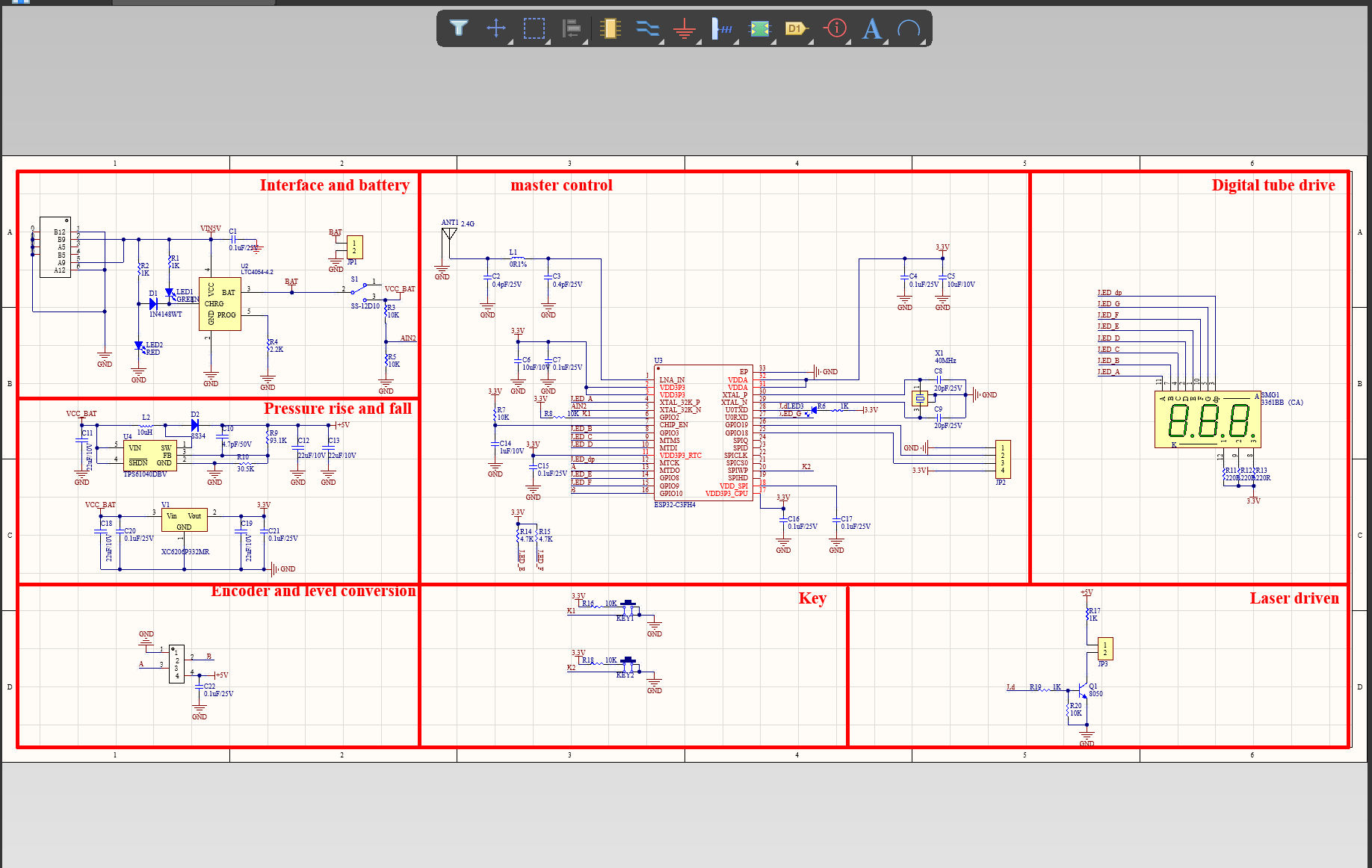
We have rich experience engineer to create a layout using a software platform like Altium Designer. This layout shows you the exact appearance and placement of the components on your board.
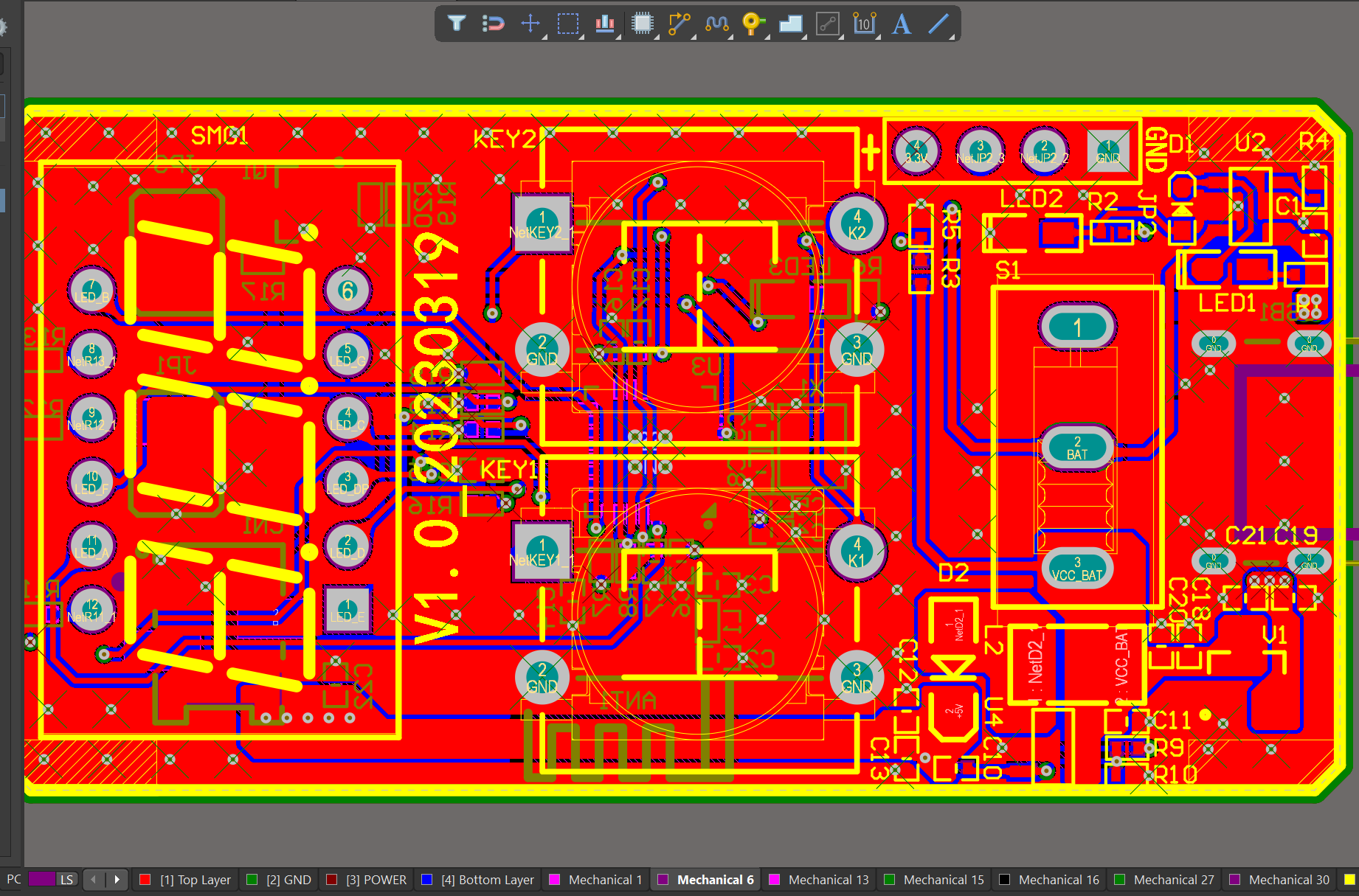
Your deliverables are always ahead of schedule and of the highest quality.
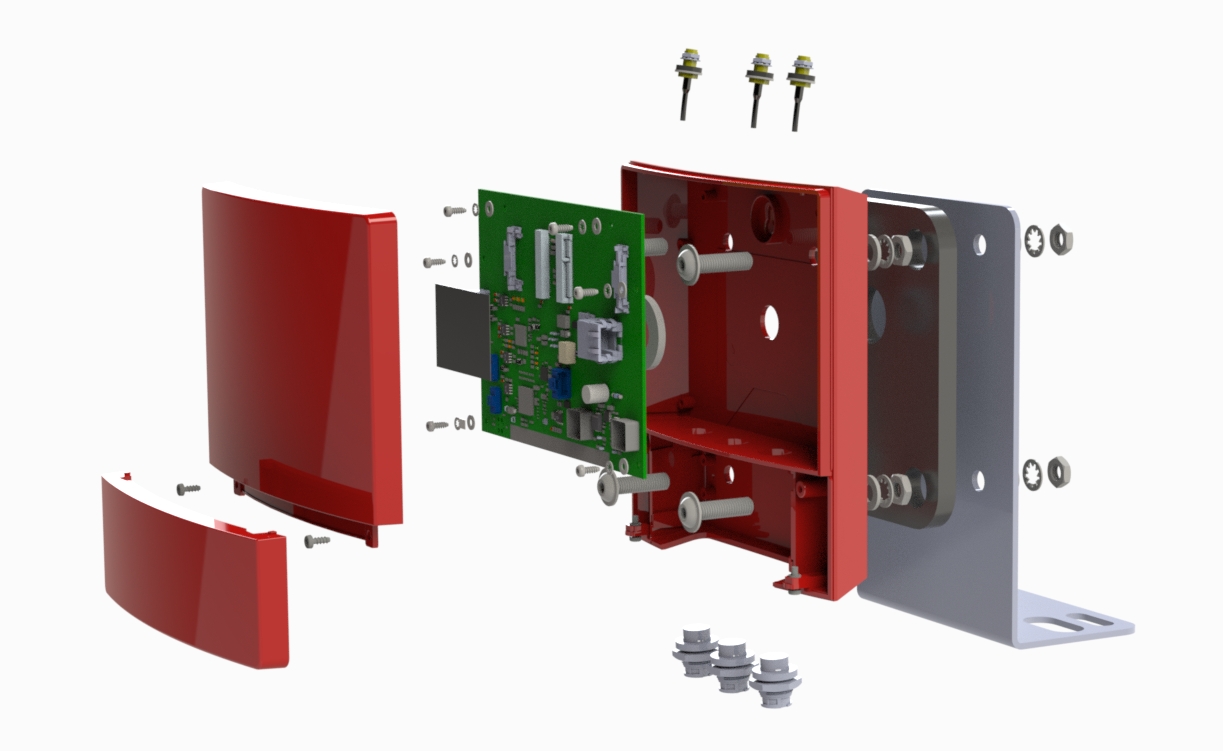
One of our Hardware Design Services is small-batch manufacturing, which allows you to test your idea quickly and verify the functionality of the hardware design and PCB board.
FAQs Guide
2.What is the difference between single-sided and double-sided PCBs?
3.How do PCBs handle overcurrent and short circuits?
4.How does the type of PCB connection (wired or wireless) impact its design and features?
5.How important is the trace width and spacing in a PCB design?
6.Is it possible to have different components on each side of a PCB?
7.Can PCBs be customized based on specific design requirements?
1.What are the differences between a prototype and production PCB?
We have a good reputation and image in the industry. The quality and price advantage of 10 pin pcb connector products is an important factor in our hard overseas market.
1. Purpose: The main difference between a prototype and production PCB is their purpose. A prototype PCB is used for testing and validation of a design, while a production PCB is used for mass production and commercial use.
2. Design: Prototype PCBs are usually hand-soldered and have a simpler design compared to production PCBs. Production PCBs are designed with more precision and complexity to meet the specific requirements of the final product.
3. Materials: Prototype PCBs are often made with cheaper materials such as FR-4, while production PCBs use higher quality materials such as ceramic or metal core for better performance and durability.
4. Quantity: Prototype PCBs are usually made in small quantities, while production PCBs are manufactured in large quantities to meet the demand of the market.
5. Cost: Due to the use of cheaper materials and smaller quantities, prototype PCBs are less expensive compared to production PCBs. Production PCBs require a larger investment due to the use of higher quality materials and larger quantities.
6. Lead time: Prototype PCBs have a shorter lead time as they are made in smaller quantities and can be hand-soldered. Production PCBs have a longer lead time as they require more complex manufacturing processes and larger quantities.
7. Testing: Prototype PCBs are extensively tested to ensure the design is functional and meets the required specifications. Production PCBs also undergo testing, but the focus is more on quality control and consistency in mass production.
8. Documentation: Prototype PCBs may not have detailed documentation as they are often hand-soldered and used for testing purposes. Production PCBs have detailed documentation to ensure consistency in manufacturing and for future reference.
9. Modifications: Prototype PCBs are easier to modify and make changes to, as they are not mass-produced. Production PCBs are more difficult to modify as any changes can affect the entire production process.
10. Reliability: Production PCBs are designed and manufactured to be more reliable and durable, as they will be used in the final product. Prototype PCBs may not have the same level of reliability as they are used for testing and may not undergo the same level of quality control.
2.What is the difference between single-sided and double-sided PCBs?
Our mission is to provide customers with the best solutions for 10 pin pcb connector.
Single-sided PCBs have copper traces and components on only one side of the board, while double-sided PCBs have copper traces and components on both sides of the board. This allows for more complex circuit designs and a higher density of components on a double-sided PCB. Single-sided PCBs are typically used for simpler circuits and are less expensive to manufacture, while double-sided PCBs are used for more complex circuits and are more expensive to manufacture.
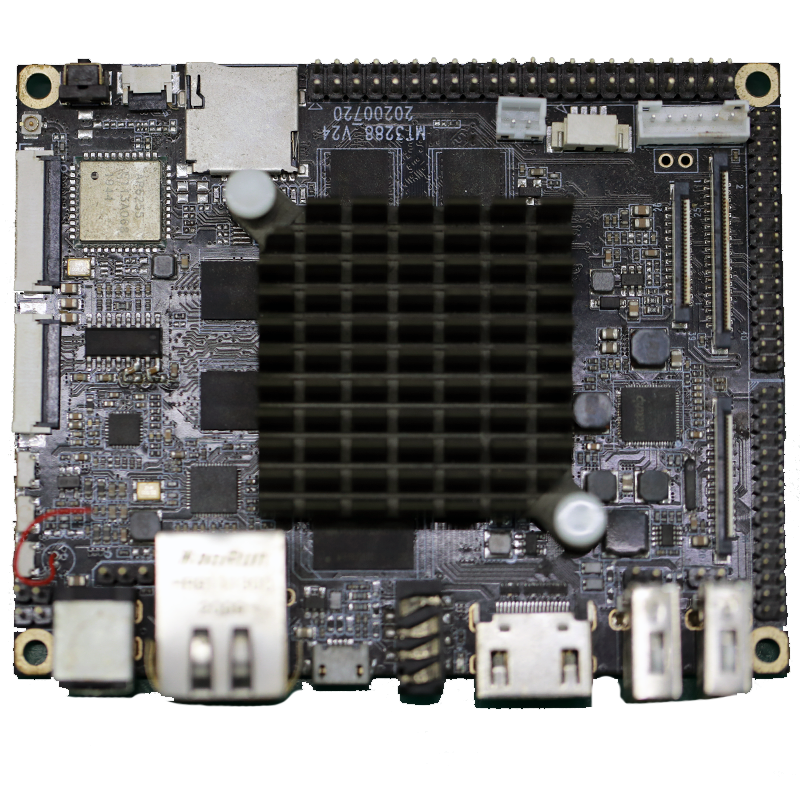
3.How do PCBs handle overcurrent and short circuits?
We have a first -class management team, and we pay attention to teamwork to achieve common goals.
PCBs (printed circuit boards) have several mechanisms in place to handle overcurrent and short circuits:
1. Fuses: Fuses are the most common protection mechanism used on PCBs. They are designed to break the circuit when the current exceeds a certain threshold, preventing damage to the components and the board.
2. Circuit breakers: Similar to fuses, circuit breakers are designed to break the circuit when the current exceeds a certain threshold. However, unlike fuses, circuit breakers can be reset and reused.
3. Overcurrent protection devices: These devices, such as overcurrent protection diodes, are designed to limit the amount of current flowing through the circuit. They act as a safety valve, preventing excessive current from damaging the components.
4. Thermal protection: Some PCBs have thermal protection mechanisms, such as thermal fuses or thermal cutoffs, which are designed to break the circuit when the temperature of the board exceeds a certain threshold. This helps prevent damage to the board and components due to overheating.
5. Short circuit protection: PCBs may also have short circuit protection mechanisms, such as polymeric positive temperature coefficient (PPTC) devices, which are designed to limit the current in the event of a short circuit. These devices have a high resistance at normal operating temperatures, but their resistance increases significantly when the temperature rises due to a short circuit, limiting the current flow.
Overall, PCBs use a combination of these protection mechanisms to handle overcurrent and short circuits, ensuring the safety and reliability of the board and its components.
4.How does the type of PCB connection (wired or wireless) impact its design and features?
Our products & services cover a wide range of areas and meet the needs of different fields.
The type of PCB connection, whether wired or wireless, can have a significant impact on the design and features of the PCB. Some of the key ways in which the type of connection can impact the PCB design and features are:
1. Size and form factor: Wired PCBs typically require physical connectors and cables, which can add to the overall size and form factor of the PCB. On the other hand, wireless PCBs do not require physical connectors and cables, allowing for a smaller and more compact design.
2. Power consumption: Wired PCBs require a constant supply of power to function, whereas wireless PCBs can operate on battery power. This can impact the power consumption and battery life of the device, which in turn can affect the overall design and features of the PCB.
3. Flexibility and mobility: Wireless PCBs offer greater flexibility and mobility as they do not have physical connections that restrict movement. This can be advantageous in applications where the device needs to be moved or used in different locations.
4. Data transfer speed: Wired PCBs typically have faster data transfer speeds compared to wireless PCBs. This can impact the design and features of the PCB, as certain applications may require high-speed data transfer.
5. Cost: The type of connection can also impact the cost of the PCB. Wired PCBs may require additional components such as connectors and cables, which can add to the overall cost. Wireless PCBs, on the other hand, may require more advanced technology and components, making them more expensive.
6. Reliability: Wired PCBs are generally considered more reliable as they have a physical connection, which is less prone to interference or signal loss. Wireless PCBs, on the other hand, may be more susceptible to interference and signal loss, which can impact their reliability.
Overall, the type of PCB connection can significantly impact the design and features of the PCB, and it is important to carefully consider the specific requirements of the application when choosing between wired and wireless connections.

5.How important is the trace width and spacing in a PCB design?
Our 10 pin pcb connector products have competitive and differentiated advantages, and actively promote digital transformation and innovation.
The trace width and spacing in a PCB design are crucial factors that can greatly affect the performance and reliability of the circuit. Here are some reasons why:
1. Current carrying capacity: The trace width determines the amount of current that can flow through the trace without causing excessive heating. If the trace width is too narrow, it can lead to overheating and damage to the circuit.
2. Voltage drop: The trace width also affects the voltage drop across the trace. A narrow trace will have a higher resistance, resulting in a higher voltage drop. This can cause a decrease in the voltage level at the end of the trace, affecting the performance of the circuit.
3. Signal integrity: The spacing between traces is critical for maintaining signal integrity. If the spacing is too narrow, it can lead to crosstalk and interference between signals, resulting in errors and malfunctions in the circuit.
4. Thermal management: The spacing between traces also plays a role in thermal management. Adequate spacing between traces allows for better air circulation, which helps dissipate heat from the circuit. This is especially important for high-power circuits.
5. Manufacturing constraints: The trace width and spacing also need to be considered in the manufacturing process. If the traces are too close together, it can be challenging to etch and inspect the PCB, leading to manufacturing defects.
In summary, the trace width and spacing are critical parameters that need to be carefully considered in PCB design to ensure proper functioning and reliability of the circuit.
6.Is it possible to have different components on each side of a PCB?
We focus on innovation and continuous improvement to maintain a competitive advantage.
Yes, it is possible to have different components on each side of a PCB. This is known as a double-sided PCB or a two-layer PCB. The components on each side can be connected through vias, which are small holes drilled through the PCB that allow for electrical connections between the layers. This allows for more compact and complex circuit designs. However, it also adds complexity to the manufacturing process and may increase the cost of the PCB.

7.Can PCBs be customized based on specific design requirements?
We have rich industry experience and professional knowledge, and have strong competitiveness in the market.
Yes, PCBs (printed circuit boards) can be customized based on specific design requirements. This is typically done through the use of computer-aided design (CAD) software, which allows for the creation of a custom layout and design for the PCB. The design can be tailored to meet specific size, shape, and functionality requirements, as well as incorporate specific components and features. The customization process may also involve selecting the appropriate materials and manufacturing techniques to ensure the PCB meets the desired specifications.
Tags:108 keyboard pcb , circuit boards assembly , 100 watt amplifier pcb , gh60 pcb



