10 oz copper pcb
MTI is a professional manufacturer of PCB and PCBA , we supply one-stop service. The company’s main services include PCB production, PCB Assembly and electronic materials purchasing, SMT patch, circuit board welding, circuit board plug-in.
Our clientele spans across major continents (Oceania,Africa,Europe,America)and encompasses various industries, including healthcare,security
| Product name | 10 oz copper pcb |
| Keyword | flex pcba flexible pcb,1073 pcb,06141 pcb 305 |
| Place of Origin | China |
| Board Thickness | 1~3.2mm |
| Applicable Industries | communications, etc. |
| Service | OEM/ODM manufacturing |
| Certificate | ISO-9001:2015, ISO-14001:2015,ISO-13485:2012.UL/CSA |
| Solder Mask Color | Black |
| Advantage | We keep good quality and competitive price to ensure our customers benefit |
| Sales country | All over the world for example:Cook Islands,Norfolk Island,Nigeria,Cameroon,Tanzania,Tromelin Island,Ireland,Czech Republic,Belarus |
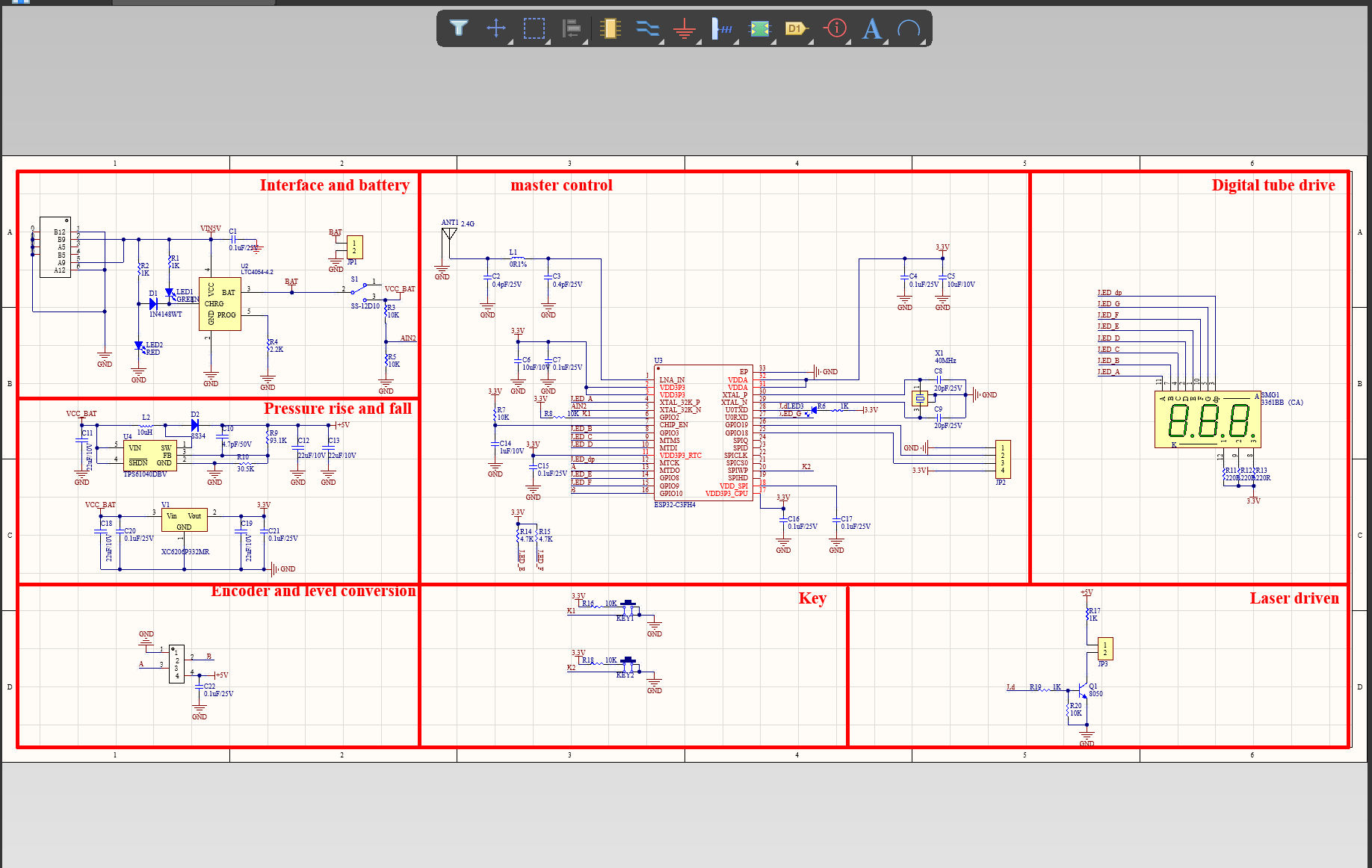
We have rich experience engineer to create a layout using a software platform like Altium Designer. This layout shows you the exact appearance and placement of the components on your board.
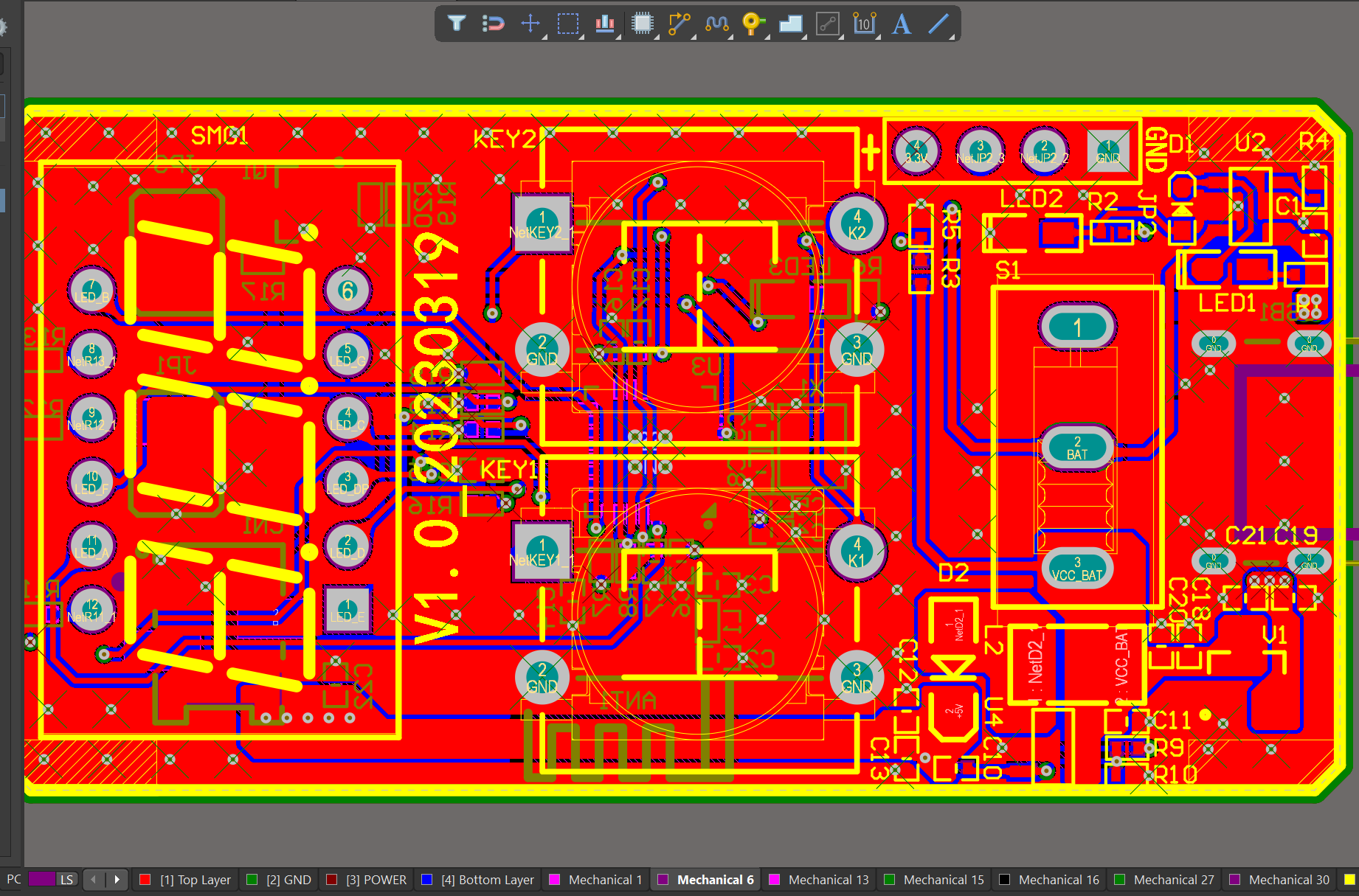
Your deliverables are always ahead of schedule and of the highest quality.
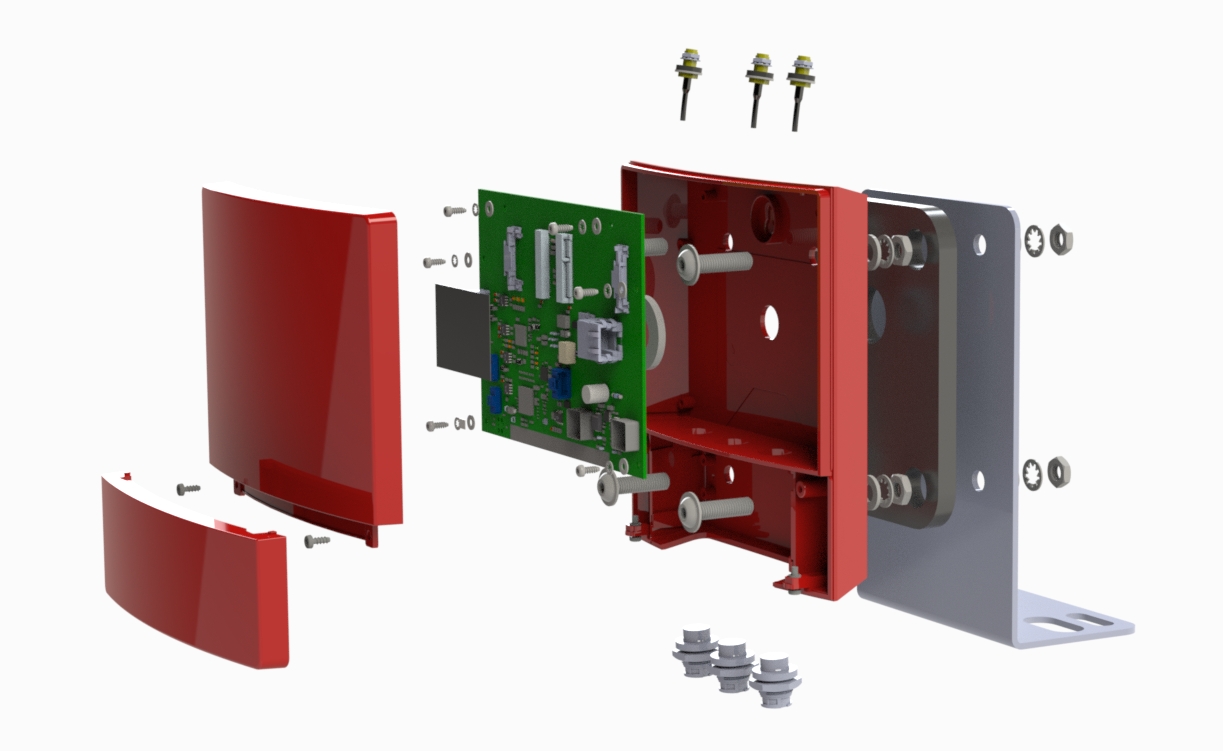
One of our Hardware Design Services is small-batch manufacturing, which allows you to test your idea quickly and verify the functionality of the hardware design and PCB board.
FAQs Guide
2.How does the type of surface finish on a PCB affect its performance?
3.What are the key features of a PCB?
4.What makes a PCB resistant to environmental factors such as moisture and temperature?
5.How does the type of PCB finish affect its durability and lifespan?
1.How do surface mount components differ from through-hole components in a PCB?
We pay attention to user experience and product quality, and provide the best product quality and lowest production cost for cooperative customers.
Surface mount components (SMD) and through-hole components (THD) are two different types of electronic components used in printed circuit boards (PCBs). The main difference between them lies in their method of mounting onto the PCB.
1. Mounting Method:
The main difference between SMD and THD components is their mounting method. SMD components are mounted directly onto the surface of the PCB, while THD components are inserted into holes drilled into the PCB and soldered on the other side.
2. Size:
SMD components are generally smaller in size compared to THD components. This is because SMD components do not require leads or pins for mounting, allowing for a more compact design. THD components, on the other hand, have leads or pins that need to be inserted into the PCB, making them larger in size.
3. Space Efficiency:
Due to their smaller size, SMD components allow for a more space-efficient design on the PCB. This is especially important in modern electronic devices where space is limited. THD components take up more space on the PCB due to their larger size and the need for holes to be drilled.
4. Cost:
SMD components are generally more expensive than THD components. This is because SMD components require more advanced manufacturing techniques and equipment, making them costlier to produce.
5. Assembly Process:
The assembly process for SMD components is automated, using pick-and-place machines to accurately place the components onto the PCB. This makes the process faster and more efficient compared to THD components, which require manual insertion and soldering.
6. Electrical Performance:
SMD components have better electrical performance compared to THD components. This is because SMD components have shorter leads, resulting in less parasitic capacitance and inductance, leading to better signal integrity.
In summary, SMD components offer a more compact design, better electrical performance, and a faster assembly process, but at a higher cost. THD components, on the other hand, are larger in size, less expensive, and can handle higher power and voltage ratings. The choice between SMD and THD components depends on the specific requirements of the PCB design and the intended use of the electronic device.
2.How does the type of surface finish on a PCB affect its performance?
10 oz copper pcb is not a product only, but also can help you comes to money-making.
The type of surface finish on a PCB can affect its performance in several ways:
1. Electrical Performance: The surface finish can impact the electrical properties of the PCB, such as impedance, signal integrity, and resistance. A smooth and uniform surface finish can help maintain consistent electrical properties, while a rough or uneven finish can cause signal loss and interference.
2. Solderability: The surface finish plays a crucial role in the solderability of the PCB. A good surface finish should provide a flat and even surface for the components to be soldered onto. A poor surface finish can result in solder defects, such as bridging, voids, and poor wetting, which can affect the reliability of the PCB.
3. Corrosion Resistance: The surface finish can also affect the corrosion resistance of the PCB. A high-quality surface finish can protect the copper traces from oxidation and other environmental factors, ensuring the long-term reliability of the PCB.
4. Assembly Process: Different surface finishes may require different assembly processes, such as the type of solder used or the temperature and time required for reflow. This can affect the overall efficiency and cost of the PCB assembly process.
5. Cost: The type of surface finish can also impact the cost of the PCB. Some surface finishes, such as gold plating, are more expensive than others, such as HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling). Choosing the right surface finish can help balance the cost and performance requirements of the PCB.
Overall, the surface finish on a PCB can significantly impact its performance, reliability, and cost. It is essential to carefully consider the requirements and choose the most suitable surface finish for the specific application.
3.What are the key features of a PCB?
We are committed to providing personalized solutions and established long -term strategic cooperative relationships with customers.
1. Substrate: The base material on which the circuit is printed, usually made of fiberglass or composite epoxy.
2. Conductive Traces: Thin copper lines that connect the components on the PCB.
3. Pads: Small copper areas on the PCB surface where components are soldered.
4. Vias: Holes drilled through the PCB to connect the different layers of the circuit.
5. Solder Mask: A layer of protective material that covers the copper traces and pads, preventing accidental short circuits.
6. Silkscreen: A layer of ink that is printed on the PCB to label the components and provide other useful information.
7. Components: Electronic devices such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits that are mounted on the PCB.
8. Mounting Holes: Holes drilled on the PCB to allow it to be securely attached to a larger device or enclosure.
9. Copper Pour: Large areas of copper that are used to provide a common ground or power plane for the circuit.
10. Edge Connectors: Metal contacts on the edge of the PCB that allow it to be connected to other circuits or devices.
11. Solder Bridges: Small areas of exposed copper that allow for the connection of two or more traces.
12. Test Points: Small pads or holes on the PCB that allow for testing and troubleshooting of the circuit.
13. Silkscreen Legend: Printed text or symbols on the silkscreen layer that provide additional information about the PCB and its components.
14. Designators: Letters or numbers printed on the silkscreen layer to identify specific components on the PCB.
15. Reference Designators: A combination of letters and numbers that identify the location of a component on the PCB according to the schematic diagram.
4.What makes a PCB resistant to environmental factors such as moisture and temperature?
We should perform well in market competition, and the prices of 10 oz copper pcb products have a great competitive advantage.
1. Material Selection: The choice of materials used in the PCB can greatly affect its resistance to environmental factors. Materials such as FR-4, polyimide, and ceramic are known for their high resistance to moisture and temperature.
2. Conformal Coating: Applying a conformal coating to the PCB can provide an additional layer of protection against moisture and temperature. This coating acts as a barrier between the PCB and the environment, preventing any moisture or contaminants from reaching the components.
3. Solder Mask: The solder mask used on the PCB can also play a role in its resistance to environmental factors. A high-quality solder mask can provide a protective layer against moisture and temperature, preventing any damage to the components.
4. Component Placement: Proper placement of components on the PCB can also contribute to its resistance to environmental factors. Components that are sensitive to moisture or temperature should be placed away from areas that are prone to these factors, such as near heat sources or in areas with high humidity.
5. Thermal Management: Adequate thermal management is crucial for maintaining the temperature of the PCB within safe limits. This can be achieved through the use of heat sinks, thermal vias, and proper ventilation.
6. Design Considerations: The design of the PCB can also impact its resistance to environmental factors. Factors such as trace width, spacing, and routing can affect the PCB’s ability to withstand temperature changes and moisture exposure.
7. Testing and Quality Control: Proper testing and quality control measures can ensure that the PCB is built to withstand environmental factors. This includes testing for moisture resistance, thermal cycling, and other environmental stressors.
8. Compliance with Standards: Following industry standards and regulations for PCB design and manufacturing can also contribute to its resistance to environmental factors. These standards often include guidelines for material selection, component placement, and testing procedures.

5.How does the type of PCB finish affect its durability and lifespan?
I have a comprehensive after -sales service system, which can pay attention to market trends in time and adjust our strategy in a timely manner.
The type of PCB finish can have a significant impact on the durability and lifespan of a PCB. The finish is the final coating applied to the surface of the PCB to protect it from environmental factors and ensure proper functionality. Some common types of PCB finishes include HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling), ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold), and OSP (Organic Solderability Preservative).
1. HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling):
HASL is a popular and cost-effective finish that involves coating the PCB with a layer of molten solder and then leveling it with hot air. This finish provides good solderability and is suitable for most applications. However, it is not very durable and can be prone to oxidation, which can affect the performance of the PCB over time. HASL finish also has a limited shelf life and may require rework after a certain period.
2. ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold):
ENIG is a more advanced and durable finish compared to HASL. It involves depositing a layer of nickel and then a layer of gold on the surface of the PCB. This finish provides excellent corrosion resistance and is suitable for high-reliability applications. ENIG finish also has a longer shelf life and does not require rework as frequently as HASL.
3. OSP (Organic Solderability Preservative):
OSP is a thin organic coating applied to the surface of the PCB to protect it from oxidation. It is a cost-effective finish and provides good solderability. However, OSP finish is not as durable as ENIG and may require rework after a certain period. It is also not suitable for high-temperature applications.
In summary, the type of PCB finish can affect its durability and lifespan in the following ways:
– Corrosion resistance: Finishes like ENIG and OSP provide better corrosion resistance compared to HASL, which can affect the performance and lifespan of the PCB.
– Shelf life: Finishes like ENIG have a longer shelf life compared to HASL, which may require rework after a certain period.
– Solderability: All finishes provide good solderability, but ENIG and OSP are more suitable for high-reliability applications.
– Environmental factors: The type of finish can also affect the PCB’s resistance to environmental factors like humidity, temperature, and chemicals, which can impact its durability and lifespan.
In conclusion, choosing the right type of PCB finish is crucial for ensuring the durability and longevity of the PCB. Factors such as the application, environmental conditions, and budget should be considered when selecting the appropriate finish for a PCB.
Tags:12 layer pcb stackup , 1.6mm pcb



