Understanding the specific demands concerning varistors in Montagem de PCB (PCBA) design is essential. Here’s a breakdown of what PCBA design demands from varistors:
Operating Temperature/Storage:
Maintain the working temperature of the circuit within the specified range outlined in the product’s specifications. After montagem, store the circuit within the product’s specified temperature range when it’s not operational. Avoid using temperatures higher than the specified maximum operating temperature.
Operating Voltage:
Keep the voltage applied across the varistor terminals below the maximum permissible voltage. Incorrect usage might result in product failure, short circuits, or potential heating issues. Although the usage voltage should be below the rated voltage, in cases of continuous high-frequency or pulse voltage, thoroughly assess the varistor’s reliability.
Component Heating:
Ensure that the surface temperature of the varistor remains below the highest specified operating temperature (considering temperature elevation caused by the component’s self-heating) as dictated in the product specifications. Confirm varistor temperature elevation due to circuit conditions under the actual operational state of the equipment.
Restricted Usage Areas:
- Varistors shouldn’t be used in the following environments:
- Places with water or saltwater.
- Areas prone to condensation.
- Locations with corrosive gases (such as hydrogen sulfide, sulfur dioxide, ammonia, etc.).
- Conditions where the vibration or shock exceeds the specified range in the product specifications.
PCB Selection:
The performance of aluminum oxide circuit boards may deteriorate due to thermal shock (temperature cycling). It’s crucial to confirm if the circuit board affects the product quality during use.
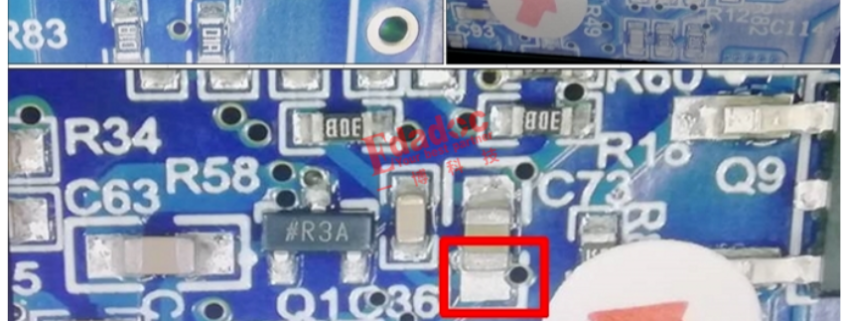
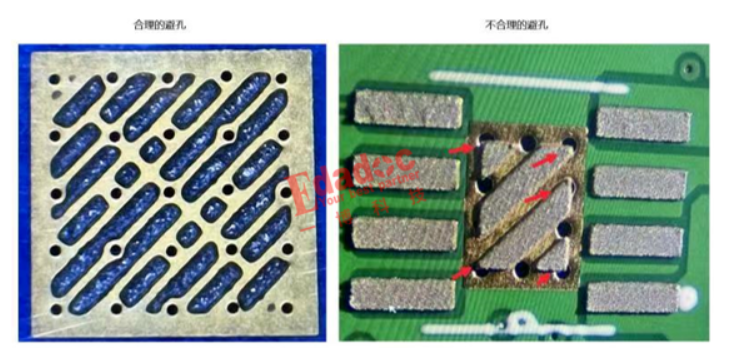
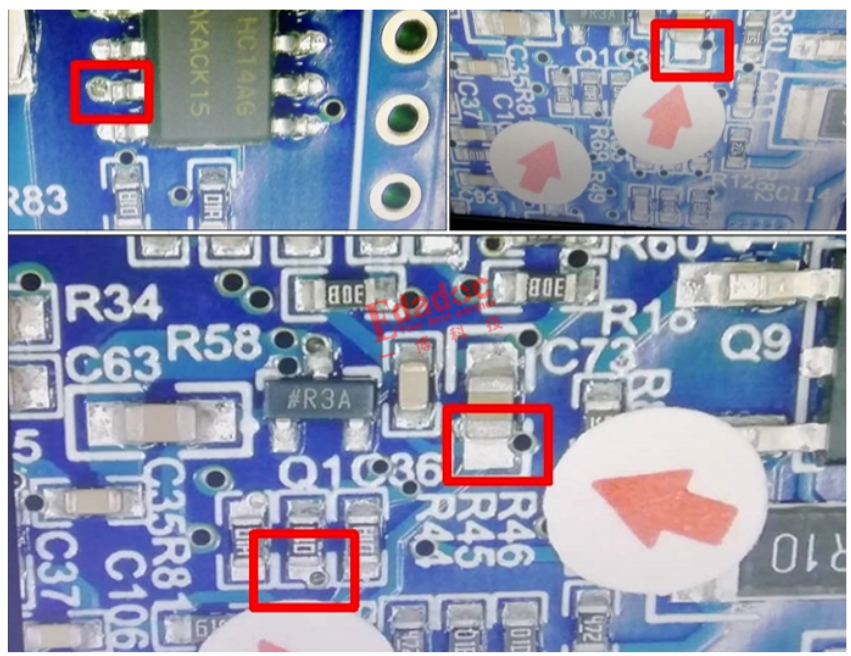
Pad Size Setting:
More soldering leads to increased pressure on the varistor, leading to quality issues like surface cracks. Therefore, when designing the solder pad on the circuit board, suitable shapes and sizes must be set according to the soldering volume. Maintain an equal size for the solder pads. Uneven solder volumes on the left and right pads can cause delayed solidification on the side with more solder, leading to stress-induced cracks on the other side during solder cooling.
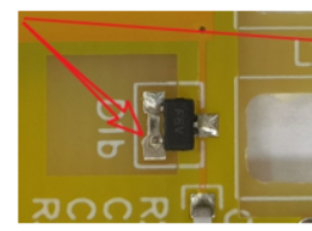
Component Configuration:
Installing varistors in PCBA or subjecting circuit boards to bending during operation may result in varistor fractures. Hence, configuring components must consider the circuit board’s resistance to bending and avoid applying excessive pressure.